(Press-News.org) When states require insurers to cover mental and behavioral health, children get better access to care, according to a UC San Francisco-led study of nearly 30,000 U.S. caregivers.
They found that 1 in 8 caregivers had difficulty accessing mental health services for their children between 2016 and 2019. But those who lived in states with the most comprehensive mental and behavioral health coverage laws were about 20% less likely to report trouble accessing care than those who lived in states with the least comprehensive laws.
Caregivers of Black and Asian children were more likely to report poor access to mental and behavioral health care, as were caregivers of children who experienced more adverse childhood events (ACEs).
“Unfortunately, in my own practice, I regularly see children who are unable to access needed mental health care, and their symptoms continue to worsen until they reach a crisis point,” said first author Ashley Foster, MD, a pediatric emergency care physician at UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospital San Francisco. “That inspired me to study whether more comprehensive laws about mental health insurance coverage can influence whether kids can get the care they need, and that is exactly what we found.”
The study appears Aug. 12 in JAMA Network Open.
While legislation appears to influence access, it also matters how well states enforce their laws.
“Even when families have insurance, mental and behavioral health providers may refuse to accept certain insurance types – or insurance altogether,” Foster said. “For those who do access care, there may be high co-pays or deductibles, which can affect perceptions of access.”
To counter this, the authors wrote, states should invest in community-based mental health services, develop a workforce that better reflects the state's cultural diversity and support reimbursement for tele-mental health care. States also should define the disorders that must be covered by insurance, such as autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Authors: Additional co-authors include Jennifer A. Hoffmann, MD, MS, of Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago; Megan Douglas, JD, of Morehouse School of Medicine; Michael C. Monuteaux, ScD, Kathrine E. Douglas, MD, and Joel D. Hudgins, MD, MPH, of Boston Children’s Hospital; Teal W. Benevides, PhD, MS, OTR/L, of Augusta University; and Amanda M. Stewart, MD, MPH, of Children’s National Hospital.
Funding: None.
Disclosures: None.
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
END
Strong insurance laws help kids get access to mental health care
2024-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
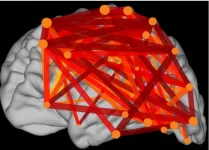
State-of-the-art brain recordings reveal how neurons resonate
2024-08-12
For decades, scientists have focused on how the brain processes information in a hierarchical manner, with different brain areas specialized for different tasks. However, how these areas communicate and integrate information to form a coherent whole has remained a mystery. Now, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have brought us closer to solving it by observing how neurons synchronize across the human brain while reading. The findings are published in Nature Human Behavior and are also the basis of a thesis by UC San Diego School of Medicine doctoral candidate Jacob Garrett.
“How the activity of the brain relates to the subjective ...
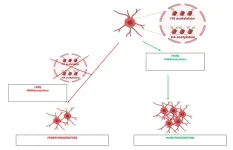
New study reveals unique histone tag in adult oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, opening doors for advanced myelin repair therapies
2024-08-12
NEW YORK, August 12, 2024 — In a groundbreaking study, researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have identified a distinct histone tag in adult oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) that may pave the way for innovative therapies targeting myelin repair, a critical target for several neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders, including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and schizophrenia. The histone tag, characterized by lysine 8 acetylation on histone H4, identifies a significant departure from the histone modifications found in neonatal OPCs.
Detailed in a ...
SwRI launches Electrified Vehicle and Energy Storage Evaluation-II battery consortium
2024-08-12
SAN ANTONIO — August 12, 2024 – Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) is launching the next phase of an electric vehicle (EV) battery consortium dedicated to understanding performance of energy storage systems. The Electrified Vehicle and Energy Storage Evaluation-II (EVESE-II) consortium builds on more than a decade of SwRI-led, precompetitive research with companies across the mobility sector.
“We are proud to serve the EV industry by bringing together manufacturers, suppliers and battery designers and developers with materials scientists to address a variety of challenges,” said Dr. Andre Swarts, an SwRI staff engineer ...
Possible explanation for link between diabetes and Alzheimer's
2024-08-12
People with type 2 diabetes are at increased risk of Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive problems. A new study led by Umeå University, Sweden, shows that the reason may be that people with type 2 diabetes have more difficulty getting rid of a protein that may cause the disease.
"The results may be important for further research into possible treatments to counteract the risk of people with type 2 diabetes being affected by Alzheimer's," says Olov Rolandsson, senior professor at the Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine at Umeå University, research leader and first author of the study.
The substances ...
Surf spots are global ally in climate fight, study finds
2024-08-12
Surf Spots are Global Ally in Climate Fight, Study Finds
Nearly 90 million metric tonnes of planet-warming carbon found surrounding surf breaks across the world; U.S., Australia, Indonesia, Brazil identified as conservation priorities
ARLINGTON, Va. (Aug. 12, 2024) – A first-of-its-kind study, published today in Conservation Science and Practice, has found that the forests, mangroves and marshes surrounding surf breaks store almost 90 Mt (million metric tonnes) of climate-stabilizing “irrecoverable carbon,” making these coastal locations ...
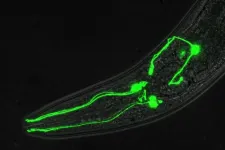
Taking a ‘one in a million’ shot to tackle dopamine-linked brain disorders
2024-08-12
Dopamine, a powerful brain chemical and neurotransmitter, is a key regulator of many important functions such as attention, experiencing pleasure and reward, and coordinating movement. The brain tightly regulates the production, release, inactivation and signaling of dopamine via a host of genes whose identity and link to human disease continue to expand.
Brain disorders associated with altered dopamine signaling include substance use disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease. The complexity of the human brain and its ...
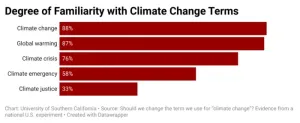
Just say “climate change” – not “climate emergency”
2024-08-12
The terms “climate change” and “global warming” are not only more familiar to people than some of their most common synonyms, but they also generate more concern about the warming of the Earth, according to a USC study published today in the journal Climatic Change.
The study began by looking at how familiar people are with the terms “global warming,” “climate change,” “climate crisis,” “climate emergency,” and “climate justice.” ...
Mature forests vital in frontline fight against climate change
2024-08-12
Mature forests have a key role to play in the fight against climate change – extracting carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and locking it into new wood, a new study reveals.
Researchers discovered that older trees responded to increased atmospheric levels of CO2 by increasing production of woody biomass – countering existing theories that mature woodland has no capacity to respond to elevated CO2 levels.
The experts found exposure to elevated levels of the greenhouse gas (ambient ...
Balancing technology and governance are key to achieving climate goals
2024-08-12
Despite advancements in clean energy, global CO2 emissions continue to rise. IIASA researchers contributed to a new international study that underscores the importance of integrating technological advancements with robust institutional capacities to formulate effective climate policies.
The Paris Agreement's goal to limit global warming to 1.5°C demands rapid reductions in CO2 emissions and heightened attention to non-CO2 greenhouse gases. Despite advancements in clean energy, global CO2 ...
Align or die
2024-08-12
A previously unknown mechanism of active matter self-organization essential for bacterial cell division follows the motto ‘dying to align’: Misaligned filaments ‘die’ spontaneously to form a ring structure at the center of the dividing cell. The study, led by the Šarić group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), was published in Nature Physics. The work could find applications in developing synthetic self-healing materials.
How does matter, lifeless by definition, self-organize and make us alive? One of the hallmarks of life, self-organization, is the spontaneous formation ...