(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. – Four of the nation’s top scientists have each been awarded $1 million in direct funding via the Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellows program.
The program was established to develop, sustain, and promote scientific and academic excellence in Office of Science (SC) research through collaborations between universities and national laboratories.
The awards, authorized by the America COMPETES act, are bestowed on senior national laboratory scientists. The United States has 17 stellar national laboratories which are powerhouses of science and technology, tackling the world’s greatest scientific challenges.
“It is an honor to recognize the outstanding research of these awardees,” said Harriet Kung, Acting Director of the DOE Office of Science. “They are advancing science solutions for the nation and taking on some of our biggest challenges in bioenergy, materials science, physics, and computing. I look forward to their continued success and impactful results especially as they continue to move forward in their careers, inspiring a new generation of scientists ready to tackle the big questions and challenges of the future.”
The 2024 DOE Office of Science Distinguished Fellows are:
Mary Raafat Mikhail Bishai, Brookhaven National Laboratory, honored for enduring contributions at the intensity frontier of high energy physics in unraveling fundamental properties of neutrinos; extraordinary leadership and service to the particle physics community; and deep commitment to broadening participation through mentoring next generation scientists.
Lois Curfman McInnes, Argonne National Laboratory, honored for exceptional accomplishments in innovative algorithms and software; leadership in major projects, including Scientific Discovery through Advanced Computing (SciDAC) and the Exascale Computing Project; promotion of scientific productivity and software sustainability; and for outstanding efforts to broaden participation in high-performance computing and related science and engineering.
Kristin Persson, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, honored for pioneering advancements in data-driven materials design and discovery through first-principles based computations and analysis algorithms that yield materials with optimal properties for engineers and scientists worldwide to accelerate innovation, and for her management and outreach skills that promote the DOE missions.
Gerald A. Tuskan, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, honored for foundational scientific advances in the development of resilient bioenergy feedstock crops; for excellence in leading large, multi-institutional science teams toward a robust, sustainable bioeconomy; and for supporting the next generation of diverse scientists.
The Fellows were selected based on their outstanding scientific leadership and engagement with research communities. They were also recognized because of sustained scientific excellence and achievement; relevance to programmatic goals of the DOE Office of Science; service to the research community; mentoring of early career scientists and/or engineers; and commitments to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
Each of the scientists will give an online public lecture in the coming months. Here are dates and information for the public online lectures from each Distinguished Scientist Fellow:
DOE SC Distinguished Scientist Fellow Lecture: Mary Raafat Mikhail Bishai, Ph.D.
Jan 14, 2025, 1:30-3:00 pm ET
Register to attend virtually.
DOE SC Distinguished Scientist Fellow Lecture: Lois Curfman McInnes, Ph.D.
Feb 10, 2025, 1:30 – 3:00 pm ET
Register to attend virtually.
DOE SC Distinguished Scientist Fellow Lecture: Kristin Persson, Ph.D.
Oct 17, 2024, 1:30 – 3:00 pm ET
Register to attend virtually.
DOE SC Distinguished Scientist Fellow Lecture: Gerald A. Tuskan, Ph.D.
Nov 19, 2024, 1:30 – 3:00 pm ET
Register to attend virtually.
For more information about the Distinguished Scientist Fellows Program, please visit the Distinguished Scientist Fellows website. The Department of Energy is committed to supporting a diverse cadre of investigators and fostering safe, diverse, equitable, and inclusive work, research, and funding environments; read the Office of Science’s Statement of Commitment for more information.
END
Department of Energy announces 2024 Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellows and lecture series
The awards, authorized by the America COMPETES act, are bestowed on senior national laboratory scientists.
2024-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mary Bishai named Distinguished Scientist Fellow
2024-08-12
UPTON, N.Y. — Physicist Mary Bishai of the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has been named a 2024 DOE Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellow. The honor recognizes her “enduring contributions at the intensity frontier of high energy physics in unraveling fundamental properties of neutrinos, extraordinary leadership and service to the particle physics community, and deep commitment to broadening participation through mentoring next generation scientists.”
As described in a DOE Office of Science press release issued today, the ...
Can meditation and stretching relieve cramping caused by cirrhosis?
2024-08-12
People suffering from cirrhosis may find some symptom relief from two accessible activities: stretching and meditation.
A study from the University of Michigan compared the two therapies as a means to relieve nocturnal muscle cramps and found both effective.
The resulting paper, “The RELAX randomized controlled trial: Stretching versus meditation for nocturnal muscle cramps,” appeared in Liver International.
The study
Two out of every three people with cirrhosis experience muscle cramps at night that wake them from sleep.
Since ...
Study reveals oleoyl-ACP-hydrolase underpins lethal respiratory viral disease
2024-08-12
Respiratory infections can be severe, even deadly, in some individuals, but not in others. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity and other collaborators have gained new understanding of why this is the case by uncovering an early molecular driver that underpins fatal disease. Oleoyl-ACP-hydrolase (OLAH) is an enzyme involved in fatty acid metabolism. A study, published today in Cell, shows that OLAH drives severe disease outcomes.
The important role of OLAH in immune response has gone unrecognized for several reasons, including a lack of noticeable expression in healthy ...
Advances in drug delivery carrier microwave-assisted reactions for enhanced therapeutics and diagnostic purposes
2024-08-12
Microwave irradiation technology is emerging as a powerful tool in the fields of organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and nanocarrier development. Recently, microwave-assisted reactions have gained significant attention for their effectiveness in synthesizing drug delivery carriers. This technology offers notable advantages, including high yield, shorter reaction times, and improved compound purity, making it a promising approach for developing nanoparticles with enhanced physicochemical properties and bioavailability.
For more information, please visit: bit.ly/3SFk4cf
For contributing article in this research topic, visit: bit.ly/3WXyoza
Use ...
Presence of liquid water most probable explanation for data collected by mars lander
2024-08-12
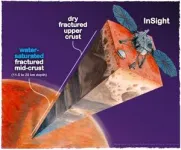
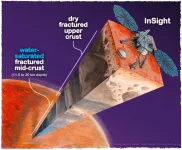
Data about Mars’ planetary crust gathered from the Mars InSight lander are best explained by the conclusion that the crust has stores of liquid water.
Analysis led by Vashan Wright, a geophysicist at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, provides the best evidence to date that the planet still has liquid water in addition to that frozen at its poles. If that conclusion is true, it sets the stage for new research considering the planet’s habitability and continuing a search for life that exists on a place other than Earth. The potential presence of liquid water on Mars has tantalized scientists for decades. Water is essential for a habitable planet.
“Understanding ...
Scientists find oceans of water on Mars. It's just too deep to tap.
2024-08-12
Using seismic activity to probe the interior of Mars, geophysicists have found evidence for a large underground reservoir of liquid water — enough to fill oceans on the planet's surface.
The data from NASA's Insight lander allowed the scientists to estimate that the amount of groundwater could cover the entire planet to a depth of between 1 and 2 kilometers, or about a mile.
While that’s good news for those tracking the fate of water on the planet after its oceans disappeared more than 3 billion years ago, the reservoir won't be of much use to anyone trying to tap into it to supply a future Mars colony. It's ...
UMass Amherst researchers ID body’s ‘quality control’ regulator for protein folding
2024-08-12
AMHERST, Mass. – Anyone who’s tried to neatly gather a fitted sheet can tell you: folding is hard. Get it wrong with your laundry and the result can be a crumpled, wrinkled mess of fabric, but when folding fails among the approximately 7,000 proteins with an origami-like complexity that regulate essential cellular functions, the result can lead to one of a multitude of serious diseases ranging from emphysema and cystic fibrosis to Alzheimer’s disease. Fortunately, our bodies have a quality-control system ...
Forest restoration can boost people, nature and climate simultaneously
2024-08-12
Forest restoration can benefit humans, boost biodiversity and help tackle climate change simultaneously, new research suggests.
Restoring forests is often seen in terms of “trade-offs” – meaning it often focuses on a specific goal such as capturing carbon, nurturing nature or supporting human livelihoods.
The new study, by the universities of Exeter and Oxford, found that restoration plans aimed at a single goal tend not to deliver the others.
However, “integrated” plans would deliver over 80% of the benefits in all three areas at once.
It also found that ...
Pre-surgical antibody treatment might prevent heart transplant rejection
2024-08-12
A new study from scientists at Cincinnati Children’s suggests there may be a way to further protect transplanted hearts from rejection by preparing the donor organ and the recipient with an anti-inflammatory antibody treatment before surgery occurs.
The findings, published online in PNAS, focus on blocking an innate immune response that normally occurs in response to microbial infections. The same response has been shown to drive dangerous inflammation in transplanted hearts.
In the new study – in mice -- transplanted hearts functioned for longer periods when the organ recipients ...
Scientists identify genes linked to relapse in the most common form of childhood leukemia
2024-08-12
Scientists from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Seattle Children’s and the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) have identified novel genetic variations that influence relapse risk in children with standard risk B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (SR B-ALL), the most common childhood cancer. The identification of genomic predictors of relapse in SR B-ALL provides a basis for improved diagnosis, precise tailoring of treatment intensity and potentially the development of novel treatment approaches. The study was published today in the Journal of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
[Press-News.org] Department of Energy announces 2024 Office of Science Distinguished Scientist Fellows and lecture seriesThe awards, authorized by the America COMPETES act, are bestowed on senior national laboratory scientists.