(Press-News.org) Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago, in partnership with University of Utah Health, has been approved for $12 million in research funding by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) for a study that will compare two ways to use antibiotics in young children with mild pneumonia, one of the leading reasons children seek acute care, who are well enough to be cared for at home.
The first approach is to prescribe and give antibiotics immediately, which is the current standard of care. The second way is to prescribe an antibiotic but not give it unless the child’s symptoms worsen or do not improve within three days, an approach that is known as a Safety-Net Antibiotic Prescription (SNAP). The study aims to determine whether SNAP, compared to immediate prescribing, results in decreased antibiotic use and similar clinical improvement in children with mild pneumonia.
“Most pneumonias in young children are caused by a virus, which the body fights off without antibiotics. Despite this, most children with pneumonia are currently treated with antibiotics,” said Co-Principal Investigator Todd Florin, MD, MSCE, Associate Division Head for Academic Affairs and Research in the Division of Emergency Medicine at Lurie Children’s and Associate Professor of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “It is important to avoid exposing children to unnecessary antibiotics for many reasons, including their side effects, such as rashes that can mimic allergies or an upset stomach. We also want to avoid the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, a global health threat. A SNAP treatment strategy is currently recommended for ear infections in children and has safely decreased antibiotic use for this condition. This strategy has not been evaluated in pneumonia. We hope our study shows a similar impact and identifies factors that influence implementation of a SNAP strategy.”
The research team is working with 12 pediatric primary care offices and three urgent care centers that are part of the Pediatric Research Consortium at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, and four pediatric emergency departments across the country, including Lurie Children’s and Utah’s Intermountain Primary Children’s Hospital, to enroll 1,823 children between 1 and 6 years of age who have been diagnosed with mild pneumonia. The team will assign children randomly to a group that receives immediate antibiotic prescribing or to a group that uses the SNAP approach.
The research team will follow up with the parent/guardian three times over the 14 days after the child's appointment to collect information about symptom improvement, antibiotic use, return to healthcare, child quality of life, parent satisfaction, and antibiotic side effects. The research team will also study how SNAP is implemented by talking to parents/guardians and pediatricians about factors that might make it easier or harder to use this approach.
“The decision to compare immediate antibiotic prescribing and the SNAP approach was informed by our research on how parents and pediatricians feel about navigating the care of children with pneumonia in real-world settings,” said Co-Principal Investigator Julia E. Szymczak, PhD, Associate Professor of Epidemiology and Co-Director of the Utah Quality Advancement Laboratory in the Department of Internal Medicine at the Spencer Fox Eccles School of Medicine at U of U Health. “It is important for researchers to generate evidence that patients and clinicians need to guide difficult healthcare decisions, such as when to use an antibiotic. Nobody wants to give unnecessary medicine, but it is scary to care for a child with pneumonia and it’s often unclear whether an antibiotic will help. SNAP empowers parents to give their child a chance to fight off the infection on their own while also having fast access to antibiotics if it becomes clear they are needed.”
The study was selected through PCORI’s highly competitive review process in which patients, caregivers and other stakeholders join scientists to evaluate proposals. The award has been approved pending completion of PCORI’s business and programmatic review and issuance of a formal award contract.
PCORI is an independent, nonprofit organization authorized by Congress with a mission to fund patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research that provides patients, their caregivers and clinicians with the evidence-based information they need to make better-informed health and health care decisions.
About Lurie Children’s
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute, which is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Emergency medicine-focused research at Lurie Children’s is conducted through the Grainger Research Program in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
About University of Utah Health
University of Utah Health provides leading-edge and compassionate care for a referral area that encompasses Idaho, Wyoming, Montana, and much of Nevada. A hub for health sciences research and education in the region, U of U Health has a $522 million research enterprise and trains the majority of Utah’s physicians, and more than 1,670 scientists and 1,460 health care providers at its Colleges of Health, Nursing, and Pharmacy and Schools of Dentistry and Medicine. With more than 20,000 employees, the system includes 12 community clinics and five hospitals. U of U Health is recognized nationally as a transformative health care system and provider of world-class care.
END
Lurie Children’s Hospital awarded $12 million by PCORI to study best approach to treat mild pneumonia in young children
2024-08-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
PCORI announces $165 million in funding for new health research
2024-08-13
PCORI announces $165 million in funding for new health research
Approved awards support patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER) on telehealth interventions, heart care and various health concerns
Aug. 13, 2024
WASHINGTON, D.C. – The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) today announced the approval of funding awards totaling more than $165 million for new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER), as well as research to improve methods and strengthen the science of engagement in patient-centered CER. Among the 10 CER studies awarded, three will evaluate the effectiveness of telehealth interventions ...
Study finds emergency department visits by children associated with water beads more than doubled from 2021 to 2022
2024-08-13
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – Researchers from the Center for Injury Research and Policy and Central Ohio Poison Center at Nationwide Children’s Hospital have found more than an estimated 8,000 visits to U.S. emergency departments (EDs) associated with water beads from 2007 through 2022, and the number of these visits increased rapidly by more than 130% from 2021 to 2022.
In a study published in American Journal of Emergency Medicine, researchers analyzed 16 years of data and call for a more comprehensive regulatory approach to prevent water bead-associated injuries. The increase in ...
Reduce, reuse, reflycle
2024-08-13
A Macquarie University team proposes using genetically engineered black soldier flies (Hermetia illucens) to address worldwide pollution challenges and produce valuable raw materials for industry, including the USD $500 billion global animal feed market.
In a new paper published on 24 July in the journal Communications Biology, scientists at Macquarie University outline a future where engineered flies could transform waste management and sustainable biomanufacturing, addressing multiple United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Synthetic biologist Dr Kate Tepper is lead author of the paper and a Postdoctoral Research Fellow at Applied BioSciences, Macquarie University.
“One ...
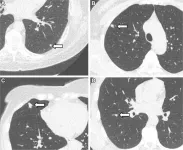
Lung nodules seen in a high percentage of non-smokers
2024-08-13
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A new study of more than 10,000 non-smoking adults found that solid lung nodules were present in a considerable portion of study participants. Non-smokers are traditionally thought to be at low risk for lung nodules and lung cancer. The results of the study were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Incidental lung nodules are common findings on chest CT and in high-risk groups are more likely to be a sign of early-stage lung cancer. Because most previous research on the prevalence and size of lung nodules has typically been ...
Study shows text messages help youth at risk for suicide feel supported after discharge
2024-08-13
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – As the nation’s youth mental health crisis continues, providers continue to find ways to help address gaps in care. Patients who receive care for suicidal thoughts and behaviors need extra support as they transition after they are discharged from inpatient care or the emergency department.
Caring Contacts are validating messages sent to patients via text messages, postcards or letters to offer patients ongoing care and support without placing any demands (such as reminders to attend their next appointment). At Nationwide ...
About 10,000 chemistry presentations will happen in Denver soon
2024-08-13
WASHINGTON, Aug. 13, 2024 — The American Chemical Society (ACS) is hosting ACS Fall 2024, its virtual and in-person meeting, with the theme “Elevating Chemistry.” It will take place in Denver on Aug. 18-22.
About 10,000 presentations will feature cutting-edge developments on a range of scientific topics at ACS Fall 2024. Embargoed press releases and videos are available to members of the media on the EurekAlert! website. Reporters can also email newsroom@acs.org to request access to the embargoed content. View the ACS Fall 2024 schedule for a full list of in-person, hybrid ...
Protecting surf breaks mitigates climate change, helps coastal communities, analysis finds
2024-08-13
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Safeguarding places to hang ten and shoot the curl is an opportunity to simultaneously mitigate climate change, fuel tourism and help surrounding ecosystems, new research has shown.
“There is a growing conservation movement regarding coastal areas that host surf breaks,” said Jacob Bukoski of Oregon State University, one of the study’s co-authors. “Earlier research showed that surf breaks tend to be biodiversity hotspots, but no one had looked at the stocks of carbon held within these ecosystems – carbon that could drive climate change if ...
New species of extinct walrus-like mammal discovered in the North Atlantic
2024-08-13
A new discovery by a team of paleontologists, led by Dr. Mathieu Boisville (University of Tsukuba, Japan), has uncovered a new species of the extinct genus Ontocetus from the Lower Pleistocene deposits in the North Atlantic. This species, named Ontocetus posti, displays surprising similarities in feeding adaptations to the modern walrus (Odobenus rosmarus), highlighting an intriguing case of convergent evolution. The research is published in the open access journal PeerJ Life & Environment.
The fossils ...
Empowering women – a key to both sustainable energy and gender justice
2024-08-13
Involving women in implementing solar energy technologies in developing countries not only has great climate impact. A new study published in Nature Energy and carried out by researchers from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, shows that empowering women through energy care work can change unjust, gendered norms and long-lived injustices.
Unlike going from fossil to renewable fuels within the transport sector, transitioning to renewable energy for electricity production is often done at the local level due to decentralised energy providers. Around the world, there are community-led programmes that provide solar, wind and hydro power, as alternative, greener energy sources. ...
Delivery robots’ green credentials make them more attractive to consumers
2024-08-13
PULLMAN, Wash. – The smaller carbon footprint, or wheel print, of automatic delivery robots can encourage consumers to use them when ordering food, according to a Washington State University study.
The suitcase-sized, self-driving electric vehicles are much greener than many traditional food delivery methods because they have low, or even zero, carbon emissions. In this study, participants who had more environmental awareness and knowledge about carbon emissions were more likely to choose the robots as ...