Power up your health with self-sustaining electronics
Breakthrough in smart fabric for sensing and energy harvesting
2024-08-14
(Press-News.org)
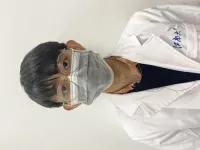
Imagine a coat that captures solar energy to keep you cozy on a chilly winter walk, or a shirt that can monitor your heart rate and temperature. Picture clothing athletes can wear to track their performance without the need for bulky battery packs.
University of Waterloo researchers have developed a smart fabric with these remarkable capabilities. The fabric has the potential for energy harvesting, health monitoring, and movement tracking applications.
The new fabric developed by a Waterloo research team can convert body heat and solar energy into electricity, potentially enabling continuous operation with no need for an external power source. Different sensors monitoring temperature, stress, and more can be integrated into the material.
It can detect temperature changes and a range of other sensors to monitor pressure, chemical composition, and more. One promising application is smart face masks that can track breath temperature and rate and detect chemicals in breath to help identify viruses, lung cancer, and other conditions.
“We have developed a fabric material with multifunctional sensing capabilities and self-powering potential,” said Yuning Li, a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering. “This innovation brings us closer to practical applications for smart fabrics.”
Unlike current wearable devices that often depend on external power sources or frequent recharging, this breakthrough research has created a novel fabric which is more stable, durable, and cost-effective than other fabrics on the market.
This research, conducted in collaboration with Professor Chaoxia Wang and PhD student Jun Peng from the College of Textile Science and Engineering at Jiangnan University, showcases the potential of integrating advanced materials such as MXene and conductive polymers with cutting-edge textile technologies to advance smart fabrics for wearable technology.
Li, director of Waterloo’s Printable Electronic Materials Lab, highlighted the significance of this advancement, which is the latest in the university’s suite of technologies disrupting health boundaries.
“AI technology is evolving rapidly, offering sophisticated signal analysis for health monitoring, food and pharmaceutical storage, environmental monitoring, and more. However, this progress relies on extensive data collection, which conventional sensors, often bulky, heavy, and costly, cannot meet,” Li said. “Printed sensors, including those embedded in smart fabrics, are ideal for continuous data collection and monitoring. This new smart fabric is a step forward in making these applications practical.”
The next phase of research will focus on further enhancing the fabric’s performance and integrating it with electronic components in collaboration with electrical and computer engineers. Future developments may include a smartphone app to track and transmit data from the fabric to healthcare professionals, enabling real-time, non-invasive health monitoring and everyday use.
The study is published in the Journal of Materials Science & Technology.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-14
This review offers an in-depth exploration of Nodular Lymphocyte Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma (NLPHL), highlighting its distinct characteristics across various domains such as epidemiology, clinical presentation, histopathology, immunophenotype, genetic findings, and challenges in differential diagnosis.
Epidemiology and Clinical Presentation
NLPHL is a relatively rare subtype of Hodgkin lymphoma, comprising approximately 10% of all Hodgkin lymphoma cases. It predominantly affects males, with a higher incidence observed ...
2024-08-14
More than a quarter of Australians over the age of 50 take cholesterol-lowering drugs to prevent heart disease and strokes, but our bodies also need cholesterol to survive. Now, scientists from The Australian National University (ANU) say its role as a basic building block of life holds the key to treating deadly diseases caused by parasites, including malaria.
The researchers have developed a trojan horse method that tricks malaria parasites into ingesting a fatal dose of drugs by exploiting the parasite’s need for cholesterol to survive. By attaching ...
2024-08-14
Scientists from Duke-NUS Medical School and the Mechanobiology Institute (MBI) at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have discovered a novel pathway to wake up dormant neural stem cells, offering potential new therapies for neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism, learning disabilities, and cerebral palsy.
In the mammalian adult brain, most neural stem cells, which originate from the nervous system and can grow into various types of brain cells, stay dormant until they receive specific signals that activate them. Once woken up, they produce new neurons, aiding in brain repair and growth.
Defects in neural stem cell activation ...
2024-08-14
An unchartered area in the foothills of the Southern Pyrenees in Spain is providing insights into a poorly known period of Neanderthal history, offering clues that could help archaeologists uncover the mystery of their downfall, according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU).
Abric Pizarro is one of only a few sites worldwide dating from 100,000 to 65,000 years ago during a period called MIS 4. The researchers have gathered hundreds of thousands of artefacts, including stone tools, animal bones and other evidence, providing significant data about the Neanderthal way of life during that time -- largely unknown in human history until now.
The findings ...
2024-08-14
Quick decisions are more likely influenced by initial biases, resulting in faulty conclusions, while decisions that take time are more likely the result in better information, according to new research led by applied mathematicians at the University of Utah.
A team that included Sean Lawley, an associate professor of mathematics, and three former or current Utah graduate students used the power of numbers to test a decision-making model long used in psychology.
They developed a framework to study the decision-making processes in groups of people holding various levels of bias.
“In large populations, what we see is that slow deciders are making more accurate ...
2024-08-14
A new study led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, found that an episode of shingles is associated with about a 20 percent higher long-term risk of subjective cognitive decline. The study’s findings provide additional support for getting the shingles vaccine to decrease risk of developing shingles, according to the researchers. Their results are published in Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.
"Our findings show long-term implications of shingles and highlight the importance of public health efforts to prevent and promote uptake of the shingles vaccine," said ...
2024-08-14
Australians outlive their peers in 5 high income English speaking countries, including the UK and the US, by between 1 to 4 years, finds an analysis of international longevity data, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Most of this advantage accrues between the ages of 45 and 84, with death rates from drug and alcohol misuse, screenable/treatable cancers, and cardiovascular and respiratory diseases all lower, the analysis shows.
While high income countries achieved good life expectancy gains during the 20th century, the trends have been much less favourable in the 21st century, even before the COVID-19 pandemic, note ...
2024-08-14
Feeling that your life lacks purpose and that there are few opportunities for personal growth in older age may precede the development of mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a frequent precursor of dementia, suggests research published online in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
These aspects of psychological wellbeing noticeably decline 2 to 6 years before MCI is diagnosed, even in the absence of evident signs, and irrespective of whether those affected go on to develop dementia, the findings ...
2024-08-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Despite being home to some of the world’s most dangerous animals, Australia has led the English-speaking world in life expectancy for the last three decades. As for other high-income Anglophone countries, the Irish saw the largest gains in life expectancy, while Americans have finished dead last since the early 1990s, according to a team of social scientists led by a Penn State researcher.
The team published their findings today (August 13) in the journal BMJ Open.
“One lesson ...
2024-08-14
SMC Labels – Peer reviewed observational study on humans
Childhood maltreatment is associated with greater cognitive difficulties than previously thought
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London and City University of New York suggests that the cognitive difficulties associated with childhood maltreatment, and particularly neglect, have been grossly underestimated in previous studies.
The research, published in Lancet ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Power up your health with self-sustaining electronics
Breakthrough in smart fabric for sensing and energy harvesting