(Press-News.org) MIAMI (August 14, 2024) – Communities impacted by increased wildfire activity and smoke can use a population health-based action plan to help alleviate health risks, particularly for those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, according to a new perspective article. The article is published in the July 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke and pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the third leading cause of death worldwide, yet awareness of the disease’s symptoms, methods to reduce risk, and disease management remains poor. Symptoms include breathlessness, fatigue and chronic cough.
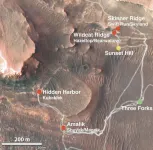
This new perspective article examined the five-part Population Health Approach enacted by the University of California, Davis Health (UCDH). UCDH is located at the epicenter of one of California’s largest wildfires, and the state’s fire season currently lasts up to 6 months of the year.
“Air pollutants from wildfires negatively affect everyone and are particularly dangerous for those with respiratory diseases like COPD and asthma as the pollutants increase lung inflammation,” said Reshma Gupta, M.D., MSHPM, Chief of Population Health and Accountable Care at UCDH and co-author of the study. “As the regional academic center for Northern California, our team routinely sees the negative health outcomes of wildfire smoke. This approach uses new technologies and population health methods to identify those at risk of wildfire smoke-induced health complications and to put interventions in place to mitigate the negative impact of poor air quality on the community.”
The five-part approach includes:
Identify clinically at-risk and underserved patient populations using well-validated, condition-targeted registries;
Assemble multidisciplinary care teams to understand the needs of these communities and patients;
Create custom analytics leveraging public health data to stratify wildfire risk;
Develop care pathways by disease, risk of exposure, and health care access; and
Identify outcome measures tailored to interventions with a commitment to continuous, iterative improvement efforts.
“Over many years, we watched the increasingly frequent and significant impact of wildfires on the patients in our COPD clinic including exacerbations and impaired access to medications. We wanted to do more than provide treatment after the fact,” said Brooks Kuhn, M.D., Co-director of UCDH’s Comprehensive COPD Clinic, Medical Director of UCDH’s Department of Respiratory Care, and co-author of the study. “Through collaboration with our Population Health team, we built resources – and systems to deliver them at the right time – to support and educate high-risk patients, such as those with COPD and asthma, before and during wildfires, not after.”
“This population health-based approach not only helps us lessen the negative impact of wildfire smoke on those with COPD or asthma, but also increases our ability to identify those at high risk of developing these respiratory diseases,” Dr. Gupta added. “Much of the data we use in our approach comes from detailed air quality and wildfire maps throughout the United States, so other health care teams across the county could adopt a similar strategy. Leveraging this data will allow us to help reduce the impact of poor air quality and improve the health of those in our community.”
To access current and past issues of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, visit journal.copdfoundation.org.
###
About the COPD Foundation
The COPD Foundation is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to help millions of people live longer and healthier lives by advancing research, advocacy, and awareness to stop COPD, bronchiectasis, and NTM lung disease. The Foundation does this through scientific research, education, advocacy, and awareness to prevent disease, slow progression, and find a cure. For more information, visit copdfoundation.org, or follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn.
END
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Early life exposure to ‘forever chemicals’ in the environment permanently disrupts the gut microbiome in mice, contributing to the development of metabolic disease in later life, according to new research led by Penn State. The results, published today (Aug. 14) in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, suggest that human exposure to these chemicals during early childhood may be contributing to the recent epidemic of metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes among adults.
The researchers focused specifically on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran ...
Over the course of nearly five months in 2022, NASA's Perseverance rover collected rock samples from Mars that could rewrite the history of water on the Red Planet and even contain evidence for past life on Mars.
But the information they contain can't be extracted without more detailed analysis on Earth, which requires a new mission to the planet to retrieve the samples and bring them back. Scientists hope to have the samples on Earth by 2033, though NASA's sample return mission may be delayed.
"These samples are the reason why our mission was flown," said paper ...
Among the many devasting impacts in the aftermath of a hurricane are power outages, which can take days or even weeks to restore. Communities grappling with the loss of electricity may encounter obstacles in accessing vital services, including food, fuel and health care.
In 2018, Hurricane Michael, a Category 5 storm, wreaked havoc in Florida as it made landfall in the United States. It was strongest recorded to hit the Florida Panhandle with winds of nearly 161 miles per hour and storm surge reaching heights ...
In 2017, the Minamata Convention on Mercury went into effect, designed to help curb mercury emissions and limit exposure across the globe. However, a new study of mercury levels in soil suggests that the treaty’s provisions might not be enough. The study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology estimates that soil stores substantially more mercury than previously thought, and it predicts that increases in plant growth due to climate change may add even more.
Mercury is a persistent environmental pollutant, moving through air, water and soil, and accumulating within plants ...
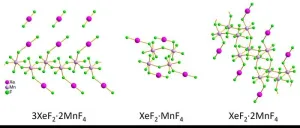
Noble gases have a reputation for being unreactive, inert elements, but more than 60 years ago Neil Bartlett demonstrated the first way to bond xenon. He created XePtF6, an orange-yellow solid. Because it’s difficult to grow sufficiently large crystals that contain noble gases, some of their structures — and therefore functions — remain elusive. Now, researchers have successfully examined tiny crystallites of noble gas compounds. They report structures of multiple xenon compounds in ACS Central ...
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, significantly impacting global health. Head and neck cancers rank as the sixth most prevalent cancers worldwide, with a higher incidence in South-central Asia. Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the predominant malignancy in this category, posing a significant health concern due to its high mortality and often late-stage diagnosis. The significance of early detection and appropriate screening measures cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in improving survival rates and reducing the disease burden.
Overview ...
In collaboration with the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is announcing the establishment of the Chen Institute and Science Prize for Al Accelerated Research. Submissions are now open for the first year of the prize, which will be awarded in 2025.
The prize will recognize young researchers who apply techniques in artificial intelligence (AI) – such as machine learning, natural language processing, or computer vision – to help the life sciences research community solve important problems and accelerate their work. Successful applicants will have made a fundamental advance that would not have been ...
More efficient and longer-lasting fuel cells are essential for fuel cell-powered heavy-duty hydrogen vehicles to be an alternative to combustion fuelled counterparts. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed an innovative method to study and understand how parts of fuel cells degrade over time. This is an important step towards the improved performance of fuel cells and them becoming commercially successful.
Hydrogen is a fuel alternative that is becoming increasingly interesting for heavy-duty vehicles. Hydrogen-powered vehicles only emit water vapour as exhaust, and if the hydrogen is produced using renewable energy, it is completely free ...
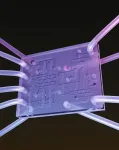
A new, air-powered computer sets off alarms when certain medical devices fail. The invention is a more reliable and lower-cost way to help prevent blood clots and strokes — all without electronic sensors.
Described in a paper in the journal Device, the computer not only runs on air, but also uses air to issue warnings. It immediately blows a whistle when it detects a problem with the lifesaving compression machine it is designed to monitor.
Intermittent pneumatic compression or IPC devices are leg sleeves that fill with air periodically and ...
PULLMAN, Wash. – Evaluators who want to avoid appearing prejudiced may overcorrect and give women inflated performance feedback, new research indicates, which is a practice that could ultimately hinder their ability to improve and advance.
A Washington State University-led research team investigated the connection between overly positive performance reviews and “protective paternalism,” the belief that women need to be handled carefully and shielded from harm.
While it may be well-intentioned, ...