(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, August 14, 2024 – Researchers from the Center for Injury Research and Prevention (CIRP) at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found discrepancies between crash reports and hospital data that might paint an incomplete or inaccurate picture of how crashes impact the safety of child passengers. Enhancing the quality of injury data reported in crash reports can aid researchers in assessing the effectiveness of various transportation safety strategies for children. The findings were recently published by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Traffic crashes remain the leading cause of unintentional injury and death for young children, and approximately 80% involve children riding as passengers in motor vehicles. Child Restraint Systems (CRS) are important in reducing risk of severe injuries. However, to date, no study has specifically compared crash- and hospital-reported injuries among child passengers involved in crashes. Incorrect information in a crash report, the most used source of motor vehicle crash injury data, can hinder the evaluation of how effectively CRS or vehicle technology reduces injuries.
“Our study demonstrated crash-involved child passengers’ injury information, specifically injury frequency, location, and severity, are reported differently across crash reports and hospital records,” said first study author Emma Sartin, PhD, MPH, CPST, research scientist with the NJ-SHO Center for Integrated Data at CHOP. “This could misrepresent our understanding of how many children are injured in crashes, as well as the types of injuries they may experience. Since this information is often used to allocate funding for traffic safety efforts and programs, its inaccuracy can also lead to funding being misdirected away from the communities that may need it most.”
Using data from the New Jersey Safety and Health Outcomes (NJ-SHO) Data Warehouse, researchers identified child passengers under the age of 13 involved in a crash from 2017 through 2019 and compared their injuries documented in both crash and hospital reports. They characterized injury frequency, severity and location, as well as the frequency of injuries by age and restraint type.
Of 84,060 crash-involved child passengers, the researchers found that crash reports documented 7,858 (9%) children with at least “possible” injuries. However, only 2,577 (3%) of all the crash-involved child passengers had at least one documented injury in hospital reports. Crash and hospital data were incongruent for both body region of injury and injury severity.
Importantly, among the few children who had any documented injuries, most of those injuries were classified as “minor.” However, the proportion of injured children increased as CRS type progressed, with children in rear-facing car seats having the fewest injuries compared with children restrained in seat belts who had more serious injuries in this study group. These findings underscore previous research highlighting the importance of delaying transitions between various types of CRS as long as possible.
“Our study found that crash and hospital reports provide different pictures regarding the injuries sustained by child passengers, which has important considerations for injury research, CRS and vehicle manufacturing, and policymaking. We are especially concerned about the increase in injuries observed among older children and those who were not using CRS,” said Rachel K. Myers, PhD, senior study author and associate director of the Center for Injury Research and Prevention (CIRP) at CHOP. “We believe efforts to understand barriers to keeping children restrained in age-appropriate CRS are important in our continued efforts to protect children, and findings like these have only been made possible by large data linkages connected with public health efforts.”
This study was supported by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development grant K99HD10592 and the Center for Child Injury Prevention Studies (CChIPS).
Sartin et al, “Congruency of crash- and hospital- reported injuries among child passengers.” Am J Prev Med. Online July 16, 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2024.07.008 epre.2024.07.008
About Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia:
A non-profit, charitable organization, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia was founded in 1855 as the nation’s first pediatric hospital. Through its long-standing commitment to providing exceptional patient care, training new generations of pediatric healthcare professionals, and pioneering major research initiatives, the hospital has fostered many discoveries that have benefited children worldwide. Its pediatric research program is among the largest in the country. The institution has a well-established history of providing advanced pediatric care close to home through its CHOP Care Network, which includes more than 50 primary care practices, specialty care and surgical centers, urgent care centers, and community hospital alliances throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey, as well as the Middleman Family Pavilion and its dedicated pediatric emergency department in King of Prussia. In addition, its unique family-centered care and public service programs have brought Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia recognition as a leading advocate for children and adolescents. For more information, visit https://www.chop.edu.
END
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers find possible inaccuracies in crash-reported child passenger injuries
Improvements needed to better guide policy and best practice recommendations
2024-08-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ontario Institute for Cancer Research announces awards for eight research teams developing innovative ways to diagnose and treat cancer
2024-08-14
August 14, 2024, TORONTO — A new round of awards from the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research (OICR) will jumpstart eight promising studies that could change how cancers are diagnosed and treated.
OICR announced the results of its Pre-Clinical Acceleration Team Awards — part of the Institute’s Clinical Translational Pathway, which helps advance new discoveries so they can benefit people affected by cancer.
The winning research teams are based across Ontario and are tackling some of the most common and hardest to treat cancers. They are developing solutions to find cancer earlier, diagnose it more ...
People with COPD, asthma have higher risk of health problems from increased wildfire activity, smoke
2024-08-14
MIAMI (August 14, 2024) – Communities impacted by increased wildfire activity and smoke can use a population health-based action plan to help alleviate health risks, particularly for those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma, according to a new perspective article. The article is published in the July 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, ...
Early life exposure to common chemical permanently disrupts gut microbiome
2024-08-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Early life exposure to ‘forever chemicals’ in the environment permanently disrupts the gut microbiome in mice, contributing to the development of metabolic disease in later life, according to new research led by Penn State. The results, published today (Aug. 14) in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, suggest that human exposure to these chemicals during early childhood may be contributing to the recent epidemic of metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes among adults.
The researchers focused specifically on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran ...
Rocks collected on Mars hold key to water and perhaps life on the planet. Bring them back to Earth.
2024-08-14
Over the course of nearly five months in 2022, NASA's Perseverance rover collected rock samples from Mars that could rewrite the history of water on the Red Planet and even contain evidence for past life on Mars.
But the information they contain can't be extracted without more detailed analysis on Earth, which requires a new mission to the planet to retrieve the samples and bring them back. Scientists hope to have the samples on Earth by 2033, though NASA's sample return mission may be delayed.
"These samples are the reason why our mission was flown," said paper ...
Nighttime light data shows inequities in restoring power after Hurricane Michael
2024-08-14
Among the many devasting impacts in the aftermath of a hurricane are power outages, which can take days or even weeks to restore. Communities grappling with the loss of electricity may encounter obstacles in accessing vital services, including food, fuel and health care.
In 2018, Hurricane Michael, a Category 5 storm, wreaked havoc in Florida as it made landfall in the United States. It was strongest recorded to hit the Florida Panhandle with winds of nearly 161 miles per hour and storm surge reaching heights ...
Rising mercury pollution in soil could be related to climate change, study says
2024-08-14
In 2017, the Minamata Convention on Mercury went into effect, designed to help curb mercury emissions and limit exposure across the globe. However, a new study of mercury levels in soil suggests that the treaty’s provisions might not be enough. The study published in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology estimates that soil stores substantially more mercury than previously thought, and it predicts that increases in plant growth due to climate change may add even more.
Mercury is a persistent environmental pollutant, moving through air, water and soil, and accumulating within plants ...
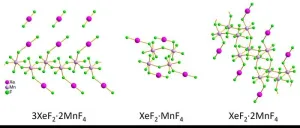
Exploring the structures of xenon-containing crystallites
2024-08-14
Noble gases have a reputation for being unreactive, inert elements, but more than 60 years ago Neil Bartlett demonstrated the first way to bond xenon. He created XePtF6, an orange-yellow solid. Because it’s difficult to grow sufficiently large crystals that contain noble gases, some of their structures — and therefore functions — remain elusive. Now, researchers have successfully examined tiny crystallites of noble gas compounds. They report structures of multiple xenon compounds in ACS Central ...
Oral cancer screening: Insights into epidemiology, risk factors, and screening programs for improved early detection
2024-08-14
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, significantly impacting global health. Head and neck cancers rank as the sixth most prevalent cancers worldwide, with a higher incidence in South-central Asia. Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is the predominant malignancy in this category, posing a significant health concern due to its high mortality and often late-stage diagnosis. The significance of early detection and appropriate screening measures cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in improving survival rates and reducing the disease burden.
Overview ...
AAAS and Chen Institute inaugurate new prize recognizing innovative applications of AI techniques
2024-08-14
In collaboration with the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is announcing the establishment of the Chen Institute and Science Prize for Al Accelerated Research. Submissions are now open for the first year of the prize, which will be awarded in 2025.
The prize will recognize young researchers who apply techniques in artificial intelligence (AI) – such as machine learning, natural language processing, or computer vision – to help the life sciences research community solve important problems and accelerate their work. Successful applicants will have made a fundamental advance that would not have been ...
A method that paves the way for improved fuel cell vehicles
2024-08-14
More efficient and longer-lasting fuel cells are essential for fuel cell-powered heavy-duty hydrogen vehicles to be an alternative to combustion fuelled counterparts. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed an innovative method to study and understand how parts of fuel cells degrade over time. This is an important step towards the improved performance of fuel cells and them becoming commercially successful.
Hydrogen is a fuel alternative that is becoming increasingly interesting for heavy-duty vehicles. Hydrogen-powered vehicles only emit water vapour as exhaust, and if the hydrogen is produced using renewable energy, it is completely free ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers find possible inaccuracies in crash-reported child passenger injuriesImprovements needed to better guide policy and best practice recommendations