(Press-News.org) People who are homeless often endure constant and intrusive police interactions, leaving them feeling intimidated, harassed and stigmatised, a new study finds.
More people of all ages and backgrounds are finding themselves homeless, often due to job loss or illness, as well as a lack of affordable housing. Between 2016 and 2021 homelessness increased by 5.2% in Australia.
Professor of Law Thalia Anthony from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS) said the research aimed to give a voice to people experiencing homelessness and reveal how policing affects their lives.
“We often get the perspective of support agencies, courts and lawyers, but the system very rarely hears the voices of those experiencing homelessness,” said Professor Anthony, who was lead author of these published findings.
“We expected people to say they wanted better policing, more support. Instead, we found that what they really want is freedom from police intrusion in their lives. They want to be left alone. Of course, they also want access to housing.”
The study involving homeless people, Hyper‑policing the Homeless: Lived Experience and the Perils of Benevolent and Malevolent Policing, was recently published in the journal Critical Criminology.
Professor Anthony and legal services across the country interviewed more than 160 homeless individuals from all Australian capital cities and two regional centres about their interactions with police and the criminal justice system.
Descriptions of interactions included constant surveillance, identification checks, questioning, fines, move-on orders, charges, and arrests. A constant police presence left many feeling continuously targeted and punished for being homeless and needing to live on the street.
“Just leave us alone. We’re just trying to find somewhere warm to sleep,” said one participant. Police welfare checks, even questions such as “how are you going?” were seen as unnecessarily encroaching.
First Nations people were particularly affected. They experience homelessness at rates six times higher than the general Australian population, and report greater levels of police violence.
Accounts of physical abuse, such as a First Nations woman having her fingers broken in a police cell, as well as fears around dying in custody, illustrate the impact of policing on this community.
Pervasive policing was also a significant source of anxiety and stress for those experiencing homelessness, and added to feelings of social exclusion and marginalisation.
One homeless individual experiencing a mental health episode described how police intervention exacerbated their distress: “I just feel like it would’ve been a lot better if they just left me alone.”
Interviewees felt they were “low hanging fruit” for police, frequently targeted for minor offenses. Constant police scrutiny can lead to fines and criminal records, which in turn makes it harder to secure housing, creating a vicious cycle of homelessness and criminalisation.
The study draws attention to the stark disparity between government spending on prisons and social housing. In 2021-22, Australia spent $6 billion on prisons, far surpassing expenditures on social housing.
By reallocating resources, the study suggests, Australia can address the root causes of homelessness rather than criminalising those who are already vulnerable.
As one participant said, “The answer is not some normal level of policing or better policing – but freedom from policing.”
The research underscores the pressing need for improved social security nets, community support services and public housing infrastructure.
END
How policing impacts the homeless
People who are homeless often endure constant and intrusive police interactions, leaving them feeling intimidated, harassed and stigmatised, a new study from Australia finds.
2024-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scottish and Irish rocks confirmed as rare record of ‘snowball Earth’
2024-08-16
A rock formation spanning Ireland and Scotland may be the world’s most complete record of “snowball Earth”, a crucial moment in planetary history when the globe was covered in ice, finds a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The study, published in the Journal of the Geological Society of London, found that the Port Askaig Formation, composed of layers of rock up to 1.1km thick, was likely laid down between 662 to 720 million years ago during the Sturtian glaciation – the first of two global freezes thought to have ...
Research provides a roadmap for improving electrochemical performance
2024-08-16
Thomas Edison went through thousands of materials before he finally found the right tungsten filament to create a working lightbulb. This type of trial-and-error research continues today and is responsible for countless inventions that improve our world. Battery systems that help power our lives in many seen (and unseen) ways are one example.
However, improving these materials and devices requires more than experimentation. Modern engineers must also form a deeper understanding of the general principles that govern material performance, from which they can design better materials to achieve challenging product requirements.
In a paper ...
Females’ and males’ muscles differ in sugar and fatty acid handling
2024-08-16
Females’ and males’ muscles differ in glucose and fatty acid handling – but regular physical activity quickly triggers similar beneficial metabolic changes in the muscles of both sexes, new research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September) has found.
Exercise has a potent effect on skeletal muscle and is the most effective strategy to prevent weight loss-related muscle loss and type 2 diabetes. ...
USDA-NIFA awards $300K to study food safety, plant pathogens and pests in hydroponics
2024-08-15
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — As controlled environment agriculture and vertical farming gain a greater foothold in modern agriculture, a new $300,000 grant aims to enhance hydroponic lettuce production.
Kristen Gibson, director of the Arkansas Center for Food Safety and Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station faculty member, is the lead researcher on the grant from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture. Gibson says the grant provides an opportunity to meet the needs of the hydroponics industry.
“The industry is always looking for what’s going to help them grow the best product, increase profit and ...
YALE NEWS: Brain wiring is guided by activity even in very early development
2024-08-15
New Haven, Conn. — In humans, the process of learning is driven by different groups of cells in the brain firing together. For instance, when the neurons associated with the process of recognizing a dog begin to fire in a coordinated manner in response to the cells that encode the features of a dog — four legs, fur, a tail, etc. — a young child will eventually be able to identify dogs going forward. But brain wiring begins before humans are born, before they have experiences or senses like sight to guide this cellular circuitry. How does that happen?
In a new ...
Eyes on the field: How Texas A&M researchers are working to revolutionize NFL officiating
2024-08-15
Hamza Memon and Nicholas Panzo, students at Texas A&M University School of Engineering Medicine (ENMED), are leading an innovative project at the intersection of sports and ophthalmology to improve National Football League (NFL) officiating . Rooted deeply in Houston’s vibrant sports culture, these Class of 2026 students combine their interest in ophthalmology and their love for sports to contribute significantly to a groundbreaking project with the NFL.
The two students met during a summer engineering program and quickly bonded over their shared aspirations in sports and ophthalmology. This friendship led ...
Blind cavefish have extraordinary taste buds
2024-08-15
Over thousands of years, cavefish evolved and lost their vision, earning the moniker “the blind cavefish,” but some cavefish also developed an inordinate number of taste buds on the head and chin.
In a new study, now published in the Nature journal Communications Biology, scientists at the University of Cincinnati have determined when the taste buds start to appear in areas beyond the oral cavity. The study was supported by the National Science Foundation.
To begin, blind cavefish evolved in cave ponds in northeastern Mexico. They are pale pink and nearly translucent compared to their silvery counterparts ...
What the trained eye cannot see: Detecting movement defects in early stage Parkinson's disease
2024-08-15
A technique that uses videos and machine learning to quantify motor symptoms in early-stage Parkinson’s disease could help reveal signs of the disease and other movement disorders earlier, which could lead to better treatment outcomes.
In a study just published in Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, a team of researchers from the University of Florida and the Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases shows that video assessment can help detect early Parkinsonism in an individual by comparing the movement of the left and right sides of their body. The approach, researchers say, exploits the fact ...
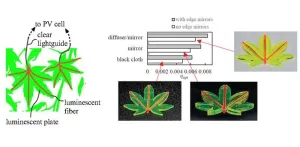
Leaf-like solar concentrators promise major boost in solar efficiency
2024-08-15
Since its invention in the 1970s, the luminescent solar concentrator (LSC) has aimed to enhance solar energy capture by using luminescent materials to convert and concentrate sunlight onto photovoltaic (PV) cells. Unlike traditional concentrators that rely on mirrors and lenses, LSCs can harvest diffuse light and have been used in applications such as building-integrated photovoltaics, where their semitransparent and colorful nature offers aesthetic benefits. However, scaling up LSCs to cover large areas has been challenging due to issues like self-absorption of photoluminescent (PL) photons within the waveguide. Researchers ...
UTEP awarded $2.5 M NIH grant to study nicotine dependence in women
2024-08-15
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 15, 2024) — Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso will undertake a new study that could lead to improved nicotine cessation treatments for women. The work is supported by a new $2.5 million grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Principal investigator Laura O'Dell, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Psychology at UTEP, will lead the multidisciplinary study into how stress produced by nicotine withdrawal is intensified by variations in ovarian hormones in women.
The study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] How policing impacts the homelessPeople who are homeless often endure constant and intrusive police interactions, leaving them feeling intimidated, harassed and stigmatised, a new study from Australia finds.