(Press-News.org) A technique that uses videos and machine learning to quantify motor symptoms in early-stage Parkinson’s disease could help reveal signs of the disease and other movement disorders earlier, which could lead to better treatment outcomes.
In a study just published in Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, a team of researchers from the University of Florida and the Fixel Institute for Neurological Diseases shows that video assessment can help detect early Parkinsonism in an individual by comparing the movement of the left and right sides of their body. The approach, researchers say, exploits the fact that Parkinson’s disease usually starts asymmetrically, meaning one side is more affected than the other in early stages of the disease.
Researchers applied machine learning to analyze videos of individuals performing simple movements with their hands and legs that are commonly used by neurologists. The team looked for subtle differences between healthy individuals and those with early Parkinson’s disease. Their approach achieved 86% accuracy in distinguishing between the two groups.
“The technique is non-invasive, uses standard video recordings, and could potentially help in detecting signs of Parkinsonism earlier, improving treatment outcomes and patient management,” said lead author Deigo Guarin, an assistant professor of applied physiology and kinesiology at UF.
END
What the trained eye cannot see: Detecting movement defects in early stage Parkinson's disease
2024-08-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
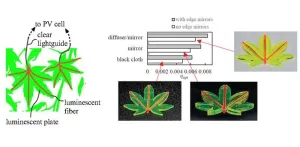
Leaf-like solar concentrators promise major boost in solar efficiency
2024-08-15
Since its invention in the 1970s, the luminescent solar concentrator (LSC) has aimed to enhance solar energy capture by using luminescent materials to convert and concentrate sunlight onto photovoltaic (PV) cells. Unlike traditional concentrators that rely on mirrors and lenses, LSCs can harvest diffuse light and have been used in applications such as building-integrated photovoltaics, where their semitransparent and colorful nature offers aesthetic benefits. However, scaling up LSCs to cover large areas has been challenging due to issues like self-absorption of photoluminescent (PL) photons within the waveguide. Researchers ...
UTEP awarded $2.5 M NIH grant to study nicotine dependence in women
2024-08-15
EL PASO, Texas (Aug. 15, 2024) — Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso will undertake a new study that could lead to improved nicotine cessation treatments for women. The work is supported by a new $2.5 million grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Principal investigator Laura O'Dell, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Psychology at UTEP, will lead the multidisciplinary study into how stress produced by nicotine withdrawal is intensified by variations in ovarian hormones in women.
The study ...
DOE announces $10 million to support climate resilience centers across America
2024-08-15
WASHINGTON, D.C. – To support vulnerable communities responding to continued and extreme climate effects, the Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $10 million in funding for innovative Climate Resilience Centers (CRCs) in 10 different states. University-led research teams will leverage the world class modeling, data and research capabilities from DOE national laboratories customized for their local regions with a focus on climate prediction of weather hazard risks to better prepare communities. The CRCs are part of the Biden-Harris Administration’s Justice40 Initiative and are designed to ensure that all Americans are benefitting from scientific research.
“Every ...
Science in Space to Cure Disease on Earth—the International Space Station National Lab and NASA announce new funding opportunity
2024-08-15
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), August 15, 2024—The International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory is collaborating with NASA on a solicitation for space-based research addressing some of the most significant diseases of our time—such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disease. ISS National Lab Research Announcement (NLRA) 2024-09: Igniting Innovation: Science in Space to Cure Disease on Earth, released in partnership with NASA’s Biological and Physical Sciences division, is aimed at overcoming challenges hindering progress in disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. This NLRA ...
YALE NEWS: Sick days: Assessing the economic costs of long COVID
2024-08-15
A new Yale study finds that the effects of long COVID have caused many Americans to miss extensive work time, and that 14% of study participants reported not returning to work in the months after their infection.
The findings, published recently in PLOS One, suggest that long COVID may have affected millions of Americans and generated steep economic costs, highlighting the need for policies to support those with the condition, researchers said.
The study drew on a long-term survey of individuals who contracted COVID-19 — dubbed Innovative ...
Equity weighting increases the social cost of carbon, warrants careful dialogue
2024-08-15
In a Policy Forum, Brian Prest and colleagues discuss how new regulatory guidelines from the U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB), known as Circular A-4, could impact the social cost of carbon (SCC). The new equity weighting approach recommended by the OMB, they say, leads to a dramatic increase in SCC estimates, and thus requires careful dialogue and discussion. The social cost of carbon is an estimate of the economic damage caused by emitting an additional ton of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It helps guide decisions about balancing the costs of reducing emissions with the benefits of mitigating climate change. Traditionally, ...
Chicxulub impactor was a carbonaceous-type asteroid from beyond Jupiter
2024-08-15
Scientists have pinpointed the origin and composition of the asteroid that caused the mass extinction 66 million years ago, revealing it was a rare carbonaceous asteroid from beyond Jupiter, according to a new study. The findings help resolve long-standing debates about the nature of Chicxulub impactor, reshaping our understanding of Earth's history and the extraterrestrial rocks that have collided with it. Earth has experienced several mass extinction events. The most recent event occurred 66 million years ago at the boundary between the Cretaceous and Paleogene eras (K-Pg boundary) and resulted in the loss of roughly 60% of the planet’s species, including non-avian dinosaurs. ...
A role for a newly identified brain activity during sleep-dependent memory consolidation
2024-08-15
A newly identified activity in the brain that occurs while we sleep – a barrage of action potentials, or a BARR – plays a crucial role in rebalancing the hippocampal neural network during memory consolidation. The findings offer fresh insights into how our brains preserve memories while maintaining stability, as we slumber. Memory consolidation – a process that stabilizes and strengthens our recent experiences into long-term memories – occurs when we sleep. During the non-rapid eye movement (NREM) phase of sleep, ...
Scientists discover superbug's rapid path to antibiotic resistance
2024-08-15
Researchers at the University of Sheffield have discovered how a hospital superbug Clostridioides difficile (C.diff) can rapidly evolve resistance to vancomycin, the frontline drug used in the UK
Scientists found that in less than two months the bacteria could develop resistance to 32 times the initial antibiotic concentration
C.diff, a type of bacteria which often affects people who have been taking antibiotics, has been identified by the World Health Organisation as one of the top global public health threats, and is responsible ...
New technique prints metal oxide thin film circuits at room temperature
2024-08-15
Researchers have demonstrated a technique for printing thin metal oxide films at room temperature, and have used the technique to create transparent, flexible circuits that are both robust and able to function at high temperatures.
“Creating metal oxides that are useful for electronics has traditionally required making use of specialized equipment that is slow, expensive, and operates at high temperatures,” says Michael Dickey, co-corresponding author of a paper on the work and the Camille and Henry Dreyfus Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at North Carolina State University. “We wanted ...