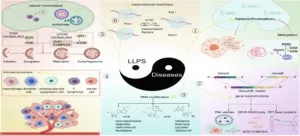
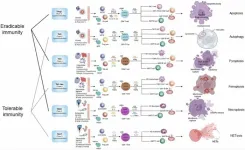
Cell death types and their relations to host immune pathways
“We have proposed a framework encompassing all discovered host immunological pathways, such as TH1, TH2a, TH2b, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ immune reactions”
2024-08-16
(Press-News.org)
“We have proposed a framework encompassing all discovered host immunological pathways, such as TH1, TH2a, TH2b, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ immune reactions”
BUFFALO, NY- August 16, 2024 – A new review was published as the cover paper of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15, entitled, “Types of cell death and their relations to host immunological pathways”.
Various immune pathways in the host, such as TH1, TH2, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ, have been identified. While TH2 and TH9 responses primarily target multicellular parasites, host immune pathways against viruses, intracellular microorganisms (like bacteria, protozoa, and fungi), and extracellular microorganisms utilize programmed cell death mechanisms to initiate immune responses and effectively eliminate pathogens.
In their review, researchers Kuo-Cheng Lu, Kuo-Wang Tsai, Yu-Kuen Wang, and Wan-Chung Hu from Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Fu Jen Catholic University, Taoyuan Armed Forces General Hospital, Tri-Service General Hospital and Ming Chuan University, reviewed these cell death pathways associated with the host immunological pathways.
"These relationships can help us understand the host defense mechanisms against invading pathogens and provide new insights for developing better therapeutic strategies against infections or autoimmune disorders.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206035
Correspondence Author: Wan-Chung Hu - Wanchung.Hu09@tzuchi.com.tw
Keywords: apoptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, necroptosis, NETosis, pyroptosis
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-16
About The Study: In a cohort study of 1,300 emerging adolescents ages 9 to 11 across three assessments, higher levels of anxiety symptoms were associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference later in development. Higher levels of perceived parental technoference were associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms later in development. The findings of this study speak to the need to discuss digital technology use and mental health with parents and emerging adolescents as a part of routine care.
Corresponding Author: To contact ...
2024-08-16
This paper, led by Professor Wu (Wenzhou Institute University, Wenzhou Medical University) and Professor Huang (Northeastern University), explores LLPS, a phenomenon closely associated with various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. As a frontier research area, LLPS plays a significant role in cancer through its regulation of multiple facets, including signaling pathways, gene expression, and tumor microenvironment. Dysregulation of LLPS leads to the formation of various aggregates, such as amyloid proteins, suggesting that modulating LLPS in ...
2024-08-16
The brain is responsible for the "general command" of human thinking and coordination of the body. Thus, various brain diseases can cause great damage to the human body and nervous system. Brain tumors are caused by abnormal cells that grow and multiply irregularly within the brain. Glioma is one of the most common malignant tumors in adults. It originates from glial cells and the surrounding infiltrating tissue, compresses other normal tissues in the brain during the growth process, and blurs the boundary of the tumor. ...
2024-08-16
Society relies heavily on diverse fluidic technologies. The ability toprecisely capture and release various chemical and biological fluids plays a fundamental role in many fields.A long-standing challenge is to design a platform that enables the switchable capture and release of liquids with precise spatial and temporal control and accurate volumes of the fluid. Recently, researchers at The Polytechnic University of Hong Kong (PolyU) have invented a new method to effectively overcome this challenge.
Led by Prof. WANG Liqiu, Otto Poon Charitable Foundation Professor in Smart and Sustainable Energy, Chair ...
2024-08-16
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots for drug delivery within in the human body, as well as other applications such as locating leaks in gas pipelines.
The new battery, which is 0.1 millimeters long and 0.002 millimeters thick — roughly the thickness of a human hair — can capture oxygen from air and use it to oxidize zinc, creating a current of up to 1 volt. That is enough to power a small circuit, sensor, or actuator, the researchers showed.
“We think this is going to be very enabling ...
2024-08-16
Studying cell migration is vital because it plays a crucial role in many biological processes, including immune response, wound healing, and cancer metastasis. Understanding how cells move and behave can lead to breakthroughs in treating diseases, developing new drugs, and creating innovative therapies. For example, in cancer research, tracking how cancer cells migrate can reveal how tumors grow and spread through the human body. This insight can led to the discovery of more efficient and targeted treatments to stop or even prevent metastasis.
Scientists have introduced CellTracksColab, a tool that simplifies cell tracking data analysis. This free platform leverages advanced ...
2024-08-16
Researchers at Utrecht University in the Netherlands have identified a new way in which the toxic protein aggregates associated with Huntington’s disease may damage nerve cells and cause them to die. The study, to be published August 16 in the Journal of Cell Biology (JCB), suggests that the aggregates can poke holes in the membrane that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell, damaging the DNA inside the nucleus and changing the activity of neuronal genes.
Huntington’s disease is a devastating neurogenerative disorder caused by a mutation in the HTT gene that results in cells producing abnormally large versions of the huntingtin protein. These ...
2024-08-16
The Colorado River and its tributaries provide water for hydropower, irrigation and drinking water in seven U.S. states and Mexico. Much of this water comes from the snowpack that builds up over the winter and then melts each spring. Every year in early April, water managers use the snowpack to predict how much water will be available for the upcoming year.
But since 2000, these predictions have been incorrect, with the actual streamflow being consistently lower than the predicted streamflow. That’s left water managers ...
2024-08-16
On May 11, a gorgeous aurora surprised stargazers across the southern United States. That same weekend, a tractor guided by GPS missed its mark.
What do the visibility of the northern lights have in common with compromised farming equipment in the Midwest?
A uniquely powerful geomagnetic storm, according to two newly published papers co-authored by Virginia Tech's Scott England.
“The northern lights are caused by energetic, charged particles hitting our upper atmosphere, which are impacted by numerous factors in space, including the sun,” said England, associate professor in the Kevin T. Crofton Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering. “During ...
2024-08-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new national study provides the best evidence to date that generous unemployment insurance benefits during the COVID-19 pandemic helped reduce reliance on high-cost credit use.
Researchers found that lower-income residents of states with more generous benefits were significantly less likely than those living in less-generous states to take out new credit cards, personal finance loans and payday loans or other alternative financial service offerings.
The study, published recently in the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cell death types and their relations to host immune pathways
“We have proposed a framework encompassing all discovered host immunological pathways, such as TH1, TH2a, TH2b, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ immune reactions”