(Press-News.org) The Institute of Physics and IOP Publishing (IOPP) are launching Progress In Physics 2024, a two-day hybrid workshop hosted at the Institute of Physics’ office in London from 9-10 October 2024. The event will cover topics on condensed matter and will bring together leading physics researchers to exchange knowledge in both an in-person and online format.
Progress in Physics 2024 aligns with the mission of IOPP’s new Progress In seriesTM of journals. The series builds on the success of IOPP’s flagship journal Reports on Progress in PhysicsTM which celebrates its 90th anniversary this year.
With plenary talks from Reports on Progress in Physics’ editorial board, invited talks from world-leading speakers, a poster competition and networking opportunities, Progress In Physics 2024 will provide a global platform for physicists and policy makers. Confirmed speakers include:
Subir Sachdev, Editor-in-Chief of Reports on Progress in Physics and Herchel Smith Professor of Physics at Harvard University, US
Piers Coleman, Professor of Physics at Rutgers University, US
Hae-Young Kee, Professor of Physics & Canada Research Chair in Theory of Quantum Materials at the University of Toronto, Canada
Zi Yang Meng, Professor of Physics at the University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Nandini Trivedi, Professor of Physics at Ohio State University, US
Fu-Chun Zhang, Professor of Physics at the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Professor Sachdev said: “Progress In Physics 2024 will bring cutting-edge physics research together in one place. I’m proud to be part of this hybrid event which is designed to maximise accessibility for all attendees whilst allowing opportunity for in-person connection and conversation.”
Dr. David Gevaux, Chief Editor of the Progress In series said: “Condensed matter is a broad and flourishing research topic that spans many aspects of modern science including physics, chemistry and engineering. Progress In Physics 2024 is an opportunity to celebrate this vast, interdisciplinary field and its place within IOPP’s Progress In series.”
For full details about the scientific programme and how to register please visit the conference website at https://iop.eventsair.com/pip2024/.
END
IOP Publishing hosts Progress In Physics 2024 – a two-day hybrid conference focused on condensed matter physics
2024-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
2024-08-16
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
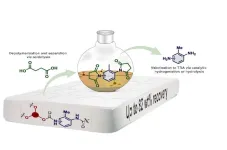
Researchers at Aarhus University have found a better method to recycle polyurethane foam from items like mattresses. This is great news for the budding industry that aims to chemically recover the original components of the material – making their products cheaper and better.
Polyurethane (PUR) is an indispensable plastic material used in mattresses, insulation in refrigerators and buildings, shoes, cars, airplanes, wind turbine blades, cables, and much more. It could be called a wonder material if it weren’t also an environmental ...
Right on schedule: Physicists use modeling to forecast a black hole's feeding patterns with precision
2024-08-16
Powerful telescopes like NASA’s Hubble, James Webb, and Chandra X-ray Observatory provide scientists a window into deep space to probe the physics of black holes. While one might wonder how you can “see” a black hole, which famously absorbs all light, this is made possible by tidal disruption events (TDEs) - where a star is destroyed by a supermassive black hole and can fuel a “luminous accretion flare.” With luminosities thousands of billions of times brighter than the Sun, accretion events enable astrophysicists to study supermassive black holes (SMBHs) at cosmological distances.
TDEs occur when a star is violently ripped ...
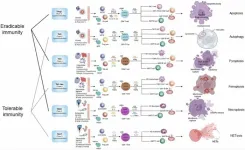
Cell death types and their relations to host immune pathways
2024-08-16
“We have proposed a framework encompassing all discovered host immunological pathways, such as TH1, TH2a, TH2b, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ immune reactions”
BUFFALO, NY- August 16, 2024 – A new review was published as the cover paper of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15, entitled, “Types of cell death and their relations to host immunological pathways”.
Various ...
Perceived parental distraction by technology and mental health among emerging adolescents
2024-08-16
About The Study: In a cohort study of 1,300 emerging adolescents ages 9 to 11 across three assessments, higher levels of anxiety symptoms were associated with higher levels of perceived parental technoference later in development. Higher levels of perceived parental technoference were associated with higher levels of inattention and hyperactivity symptoms later in development. The findings of this study speak to the need to discuss digital technology use and mental health with parents and emerging adolescents as a part of routine care.
Corresponding Author: To contact ...
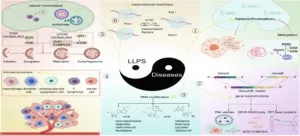
Liquid-liquid phase separation in diseases
2024-08-16
This paper, led by Professor Wu (Wenzhou Institute University, Wenzhou Medical University) and Professor Huang (Northeastern University), explores LLPS, a phenomenon closely associated with various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. As a frontier research area, LLPS plays a significant role in cancer through its regulation of multiple facets, including signaling pathways, gene expression, and tumor microenvironment. Dysregulation of LLPS leads to the formation of various aggregates, such as amyloid proteins, suggesting that modulating LLPS in ...
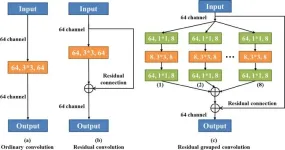
Advanced U-net segmentation model using residual grouped convolution and attention mechanism for brain tumor MRI image segmentation
2024-08-16
The brain is responsible for the "general command" of human thinking and coordination of the body. Thus, various brain diseases can cause great damage to the human body and nervous system. Brain tumors are caused by abnormal cells that grow and multiply irregularly within the brain. Glioma is one of the most common malignant tumors in adults. It originates from glial cells and the surrounding infiltrating tissue, compresses other normal tissues in the brain during the growth process, and blurs the boundary of the tumor. ...
PolyU develops versatile fluidic platform for programmable liquid processing
2024-08-16
Society relies heavily on diverse fluidic technologies. The ability toprecisely capture and release various chemical and biological fluids plays a fundamental role in many fields.A long-standing challenge is to design a platform that enables the switchable capture and release of liquids with precise spatial and temporal control and accurate volumes of the fluid. Recently, researchers at The Polytechnic University of Hong Kong (PolyU) have invented a new method to effectively overcome this challenge.
Led by Prof. WANG Liqiu, Otto Poon Charitable Foundation Professor in Smart and Sustainable Energy, Chair ...
MIT engineers design tiny batteries for powering cell-sized robots
2024-08-16
A tiny battery designed by MIT engineers could enable the deployment of cell-sized, autonomous robots for drug delivery within in the human body, as well as other applications such as locating leaks in gas pipelines.
The new battery, which is 0.1 millimeters long and 0.002 millimeters thick — roughly the thickness of a human hair — can capture oxygen from air and use it to oxidize zinc, creating a current of up to 1 volt. That is enough to power a small circuit, sensor, or actuator, the researchers showed.
“We think this is going to be very enabling ...
New tool simplifies cell tracking data analysis
2024-08-16
Studying cell migration is vital because it plays a crucial role in many biological processes, including immune response, wound healing, and cancer metastasis. Understanding how cells move and behave can lead to breakthroughs in treating diseases, developing new drugs, and creating innovative therapies. For example, in cancer research, tracking how cancer cells migrate can reveal how tumors grow and spread through the human body. This insight can led to the discovery of more efficient and targeted treatments to stop or even prevent metastasis.
Scientists have introduced CellTracksColab, a tool that simplifies cell tracking data analysis. This free platform leverages advanced ...
Exploring Huntington’s disease, researchers discover that protein aggregates poke holes in nuclear membrane
2024-08-16
Researchers at Utrecht University in the Netherlands have identified a new way in which the toxic protein aggregates associated with Huntington’s disease may damage nerve cells and cause them to die. The study, to be published August 16 in the Journal of Cell Biology (JCB), suggests that the aggregates can poke holes in the membrane that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell, damaging the DNA inside the nucleus and changing the activity of neuronal genes.
Huntington’s disease is a devastating neurogenerative disorder caused by a mutation in the HTT gene that results in cells producing abnormally large versions of the huntingtin protein. These ...