(Press-News.org) Rutgers researchers have found a new way to manage the receptors that control the sense of touch, which could lead to treating chronic pain more effectively.
“Identifying a natural molecule that specifically reduces pain sensitivity offers hope for new therapeutic strategies in the management of pain,” said Tibor Rohacs, a professor in the Department of Pharmacology, Physiology and Neuroscience at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and a member of the Rutgers Brain Health Institute. “Our goal is to translate these findings into effective treatments that improve the quality of life for people suffering from chronic pain.”
The study was written by Matthew Gabrielle, a doctoral student in the laboratory of Tibor Rohacs at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School.
A natural molecule called phosphatidic acid can reduce the activity of certain touch-sensing ion channels in the body, according to a study published in Nature Communications.
Researchers found that increasing the levels of phosphatidic acid in cells makes them less sensitive to touch. This finding was confirmed through experiments on sensory neurons and tests in mice, where the animals became more sensitive to touch when the formation of phosphatidic acid was inhibited.
“This finding adds to a growing body of evidence suggesting that lipids are key regulators of somatosensation,” said Gabrielle, referring to the body’s ability to perceive sensations such as touch, temperature and pain. “By targeting the natural pathways that regulate these channels, we can develop more targeted and effective pain treatments that could be especially useful for conditions involving inflammatory pain, where current pain relief options are often inadequate.”
END
Rutgers researchers discover new way to control the sense of touch
Using phosphatidic acid as a regulator of the sense of touch may lead to new treatments for better pain relief, according to a Rutgers Health study
2024-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New UH study targets early signs of vision loss in diabetic patients
2024-08-19
A $3.3 million study at the University of Houston College of Optometry will track the health of patients with prediabetes and diabetes to find out who might develop eye problems and be at risk for future vision loss. The study is being led by Wendy Harrison, associate professor, and is underwritten by the National Eye Institute.
Vision loss in type 2 diabetes results from diabetic retinopathy, caused by damage to blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye. The disease can appear without warning.
“The ...
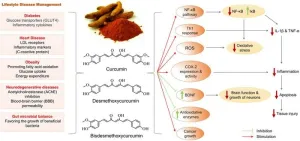
Herbal-based nutraceuticals in management of lifestyle diseases: Experience from Indian population
2024-08-19
Lifestyle diseases, also known as non-communicable diseases (NCDs), have emerged as a major health burden globally, including in India. These diseases, such as obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders, are primarily caused by unhealthy lifestyle choices like sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, and stress. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NCDs are responsible for 41 million deaths annually, accounting for 74% of all global deaths. Notably, 86% of these premature deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
The increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases ...
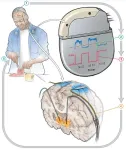
Taming Parkinson’s disease with intelligent brain pacemakers
2024-08-19
Media Contact: Robin.Marks@ucsf.edu, (415) 502-6397
Subscribe to UCSF News
Taming Parkinson’s Disease with Intelligent Brain Pacemakers
UCSF studies show personalized, self-adjusting, neuromodulation has the potential to enhance movement and sleep.
Two new studies from UC San Francisco are pointing the way toward round-the-clock personalized care for people with Parkinson’s disease through an implanted device that can treat movement problems during the day and insomnia at night.
The approach, called adaptive deep brain stimulation, or aDBS, uses methods derived from AI to ...
Self-adjusting brain pacemaker may help reduce Parkinson’s disease symptoms
2024-08-19
A small feasibility study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that an implanted device regulated by the body’s brain activity could provide continual and improved treatment for the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD) in certain people with the disorder. This type of treatment, called adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS), is an improvement on a technique that has been used for PD and other brain disorders for many years. The study found aDBS was markedly more effective at controlling PD symptoms compared to conventional DBS treatments.
“This study marks a big step forward towards ...
Florida’s red flag gun law and firearm and nonfirearm homicide and suicide rates
2024-08-19
About The Study: Although firearm homicide mortality increased after Florida’s red flag law enactment (permitting the temporary removal of firearms by law enforcement officers from individuals posing a danger to themselves or others), this increase was lower than expected compared with its synthetic control, resulting in an 11% rate reduction (0.73 fewer deaths per 100,000). There were no differences from expected mortality rates for nonfirearm homicide, firearm suicide, or nonfirearm suicide.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Catherine Gimbrone, MPH, email c.gimbrone@columbia.edu.
To ...
Number of pediatric inpatient psychiatric beds in the U.S. did not increase 2017-2020 despite youth mental health crisis
2024-08-19
U.S. pediatric inpatient psychiatric bed capacity did not change 2017 – 2020, despite increases in pediatric mental health emergency visits, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also found substantial geographic variation in inpatient psychiatric bed capacity per 100,000 children, ranging from zero in Alaska to 75 in Arkansas. Over 90 percent of pediatric inpatient beds are in urban centers, raising concerns for youth living in rural areas.
“Access to psychiatric inpatient care for youth is insufficient to meet the growing demand, forcing patients to wait for hours or even days in emergency departments or on medical units until a psychiatric bed becomes ...
Using temporary nurses doesn’t mitigate deaths linked with staff shortages
2024-08-19
A new study led by the University of Southampton has found that using temporary nursing staff to fill rotas only partially combats an increased risk of patient death associated with staff shortages.
Researchers found that avoiding low nurse staffing levels lowers the risk of death among patients – particularly even when drafting in temporary registered nurses to maintain staffing levels. However, despite this, the risk of death remains elevated compared to when the ward is fully staffed by permanent nurses.
Findings from the ...
Telehealth mindfulness-based interventions for chronic pain
2024-08-19
About The Study: Scalable telehealth mindfulness-based interventions improved pain-related function and biopsychosocial outcomes compared to usual care among veterans with chronic pain in this randomized clinical trial. Relatively low-resource telehealth-based mindfulness-based interventions could help accelerate and improve the implementation of nonpharmacological pain treatment in health care systems.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Diana J. Burgess, PhD, email diana.burgess@va.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Expanded child tax credit and food insecurity
2024-08-19
About The Study: Expanded Child Tax Credit (ECTC) enactment was associated with substantially lower food insecurity, and ECTC expiration was associated with substantially greater food insecurity in this cohort study. Key features of the ECTC—monthly payments and no earnings requirements—may be important for food insecurity prevention. Future studies should examine this, along with income as a potential effect modifier.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Machine learning prediction of autism spectrum disorder from a minimal set of medical and background information
2024-08-19
About The Study: The machine learning model developed in this study shows promise in the early identification of individuals with an elevated likelihood of autism spectrum disorder, using minimal information, which could affect early diagnosis and intervention strategies.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kristiina Tammimies, PhD, email kristiina.tammimies@ki.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.29229)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Rutgers researchers discover new way to control the sense of touchUsing phosphatidic acid as a regulator of the sense of touch may lead to new treatments for better pain relief, according to a Rutgers Health study