(Press-News.org) U.S. pediatric inpatient psychiatric bed capacity did not change 2017 – 2020, despite increases in pediatric mental health emergency visits, according to a study published in JAMA Pediatrics. Researchers also found substantial geographic variation in inpatient psychiatric bed capacity per 100,000 children, ranging from zero in Alaska to 75 in Arkansas. Over 90 percent of pediatric inpatient beds are in urban centers, raising concerns for youth living in rural areas.
“Access to psychiatric inpatient care for youth is insufficient to meet the growing demand, forcing patients to wait for hours or even days in emergency departments or on medical units until a psychiatric bed becomes available,” said senior author Jennifer Hoffmann, MD, MS, emergency medicine physician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “It is also critical to ensure that access is equitably distributed across the country, as well as available in rural areas where we found a serious shortage of psychiatric beds for youth. Every child deserves access to psychiatric care. The lack of psychiatric beds for children in some areas places a significant burden on families, emotionally and financially.”
Mark S. Johnson, a parent from Juneau, Alaska, described the challenges his family faced: “My 14-year-old stepson needed inpatient mental health treatment but there were no options available in Alaska. Our local hospital kept him under observation while we sought psychiatric placement for him in Washington, over 900 miles from our home. It was very stressful and visiting him every two weeks was expensive.”
Dr. Hoffmann emphasized that early detection of mental health concerns and prevention of mental health emergencies in youth can be part of the solution to the psychiatric bed shortage. This can be accomplished in primary care and school-based health centers. She also stressed the need to support the 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline, which helps to address mental health crises via telephone and text messages.
“Other ways to improve access to youth mental health services could involve mobile mental health units and increased use of telehealth for rural areas,” added Dr. Hoffmann.
Kenneth Michelson, MD, MPH, from Lurie Children’s was a co-author on the study.
Research at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago is conducted through Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute, which is focused on improving child health, transforming pediatric medicine and ensuring healthier futures through the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Lurie Children’s is a nonprofit organization committed to providing access to exceptional care for every child. It is ranked as one of the nation’s top children’s hospitals by U.S. News & World Report. Lurie Children’s is the pediatric training ground for Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. Emergency medicine-focused research at Lurie Children’s is conducted through the Grainger Research Program in Pediatric Emergency Medicine.
END
Number of pediatric inpatient psychiatric beds in the U.S. did not increase 2017-2020 despite youth mental health crisis
Study found substantial variation by state in children’s access to inpatient psychiatric care
2024-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using temporary nurses doesn’t mitigate deaths linked with staff shortages
2024-08-19
A new study led by the University of Southampton has found that using temporary nursing staff to fill rotas only partially combats an increased risk of patient death associated with staff shortages.
Researchers found that avoiding low nurse staffing levels lowers the risk of death among patients – particularly even when drafting in temporary registered nurses to maintain staffing levels. However, despite this, the risk of death remains elevated compared to when the ward is fully staffed by permanent nurses.
Findings from the ...
Telehealth mindfulness-based interventions for chronic pain
2024-08-19
About The Study: Scalable telehealth mindfulness-based interventions improved pain-related function and biopsychosocial outcomes compared to usual care among veterans with chronic pain in this randomized clinical trial. Relatively low-resource telehealth-based mindfulness-based interventions could help accelerate and improve the implementation of nonpharmacological pain treatment in health care systems.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Diana J. Burgess, PhD, email diana.burgess@va.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Expanded child tax credit and food insecurity
2024-08-19
About The Study: Expanded Child Tax Credit (ECTC) enactment was associated with substantially lower food insecurity, and ECTC expiration was associated with substantially greater food insecurity in this cohort study. Key features of the ECTC—monthly payments and no earnings requirements—may be important for food insecurity prevention. Future studies should examine this, along with income as a potential effect modifier.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, ...
Machine learning prediction of autism spectrum disorder from a minimal set of medical and background information
2024-08-19
About The Study: The machine learning model developed in this study shows promise in the early identification of individuals with an elevated likelihood of autism spectrum disorder, using minimal information, which could affect early diagnosis and intervention strategies.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kristiina Tammimies, PhD, email kristiina.tammimies@ki.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.29229)
Editor’s ...
AI model aids early detection of autism
2024-08-19
A new machine learning model can predict autism in young children from relatively limited information. This is shown in a new study from Karolinska Institutet published in JAMA Network Open. The model can facilitate early detection of autism, which is important to provide the right support.
“With an accuracy of almost 80 percent for children under the age of two, we hope that this will be a valuable tool for healthcare,” says Kristiina Tammimies, Associate Professor at KIND, the Department of Women's and Children's Health, Karolinska Institutet and last author of the study.
The research team used a large US database (SPARK) ...
A common fatty acid may help restore healthy vaginal bacteria after infection
2024-08-19
More than half of women globally experience bacterial vaginosis (BV) — an imbalance of naturally occurring microbes in the female genital tract — at least once in their life. The condition can cause painful symptoms and vaginal discharge, and although treatable with antibiotics, it frequently comes back within a short time. If left untreated, BV can lead to problems with pregnancy and an increased risk of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV.
A team of researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; the Ragon Institute of Mass General ...
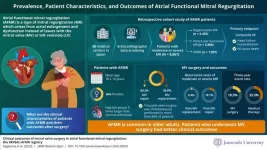
Outcomes of mitral valve surgery in atrial functional mitral regurgitation
2024-08-19
Mitral regurgitation (MR) is a serious heart condition that often requires corrective surgery. It is characterized by the backflow or "regurgitation" of blood from the heart's left ventricle into the left atrium. Atrial Functional Mitral Regurgitation (AFMR), characterized by normal mitral valve (MV) function and left ventricular function but with atrial dilation and defects in the ring-like structure that supports the MV leaflets (mitral annulus), poses diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to its distinct pathophysiological mechanisms. Historically, studies on AFMR have been limited by small ...
Searching old stem cells that stay young forever
2024-08-19
The sea anemone Nematostella vectensis is potentially immortal. Using molecular genetic methods, developmental biologists led by Ulrich Technau from the University of Vienna have now identified possible candidates for multipotent stem cells in the sea anemone for the first time. These stem cells are regulated by evolutionary highly conserved genes, which in humans are usually only active in the formation of egg and sperm cells, but give ancient animal phyla such as cnidarians a high degree of regenerative capacity to even escape ageing. The results are currently being published in Science Advances and could also provide insights into the human ...
Low cortisol, hair-trigger stress response in the brain may underlie Long COVID
2024-08-19
Proteins left behind by COVID-19 long after initial infection can cause cortisol levels in the brain to plummet, inflame the nervous system and prime its immune cells to hyper-react when another stressor arises, according to new animal research by University of Colorado Boulder scientists.
The study, published in the journal Brain Behavior and Immunity, sheds new light on what might underly the neurological symptoms of Long COVID, an intractable syndrome which impacts as many as 35% of those infected with the ...
What time the malaria-bearing mosquito bites you might make a difference
2024-08-19
What time the malaria-bearing mosquito bites you might make a difference
Circadian rhythms appear to influence vulnerability to malaria parasites
A discovery by McGill-affiliated researchers could lead to more effective treatment of malaria and other parasitic diseases.
When mice are infected in the middle of the night with the parasites causing cerebral malaria, the symptoms of the disease are less severe than for those inflected during the day, and the spread of the parasites within the hosts is more limited, research teams from McGill University, the Douglas Research Centre ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Number of pediatric inpatient psychiatric beds in the U.S. did not increase 2017-2020 despite youth mental health crisisStudy found substantial variation by state in children’s access to inpatient psychiatric care