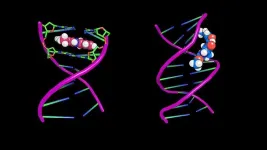
(Press-News.org) Proteins left behind by COVID-19 long after initial infection can cause cortisol levels in the brain to plummet, inflame the nervous system and prime its immune cells to hyper-react when another stressor arises, according to new animal research by University of Colorado Boulder scientists.
The study, published in the journal Brain Behavior and Immunity, sheds new light on what might underly the neurological symptoms of Long COVID, an intractable syndrome which impacts as many as 35% of those infected with the virus.
The findings come as COVID makes a striking summer comeback, with cases rising in 84 countries and numerous high-profile athletes at the Paris Olympics testing positive.
“Our study suggests that low cortisol could be playing a key role in driving many of these physiological changes that people are experiencing with Long COVID,” said lead author Matthew Frank, PhD, a senior research associate with the Department of Psychology and Neuroscience at CU Boulder.
Previous research has shown that SARS-CoV-2 antigens, immune-stimulating proteins shed by the virus that causes COVID-19, linger in the blood stream of Long COVID patients as much as a year after infection. They’ve also been detected in the brains of COVID patients who have died.
To explore just how such antigens impact the brain and nervous system, the research team injected an antigen called S1 (a subunit of the “spike” protein) into the spinal fluid of rats and compared them to a control group.
After 7 days, in rats exposed to S1, levels of the cortisol-like hormone corticosterone plummeted by 31% in the hippocampus, the region of the brain associated with memory, decision making and learning. After 9 days, levels were down 37%.
“Nine days is a long time in the life span of a rat,” said Frank, noting that rats live on average for two to three years.
He notes that cortisol is a critical anti-inflammatory, helps convert fuel into energy and is important for regulating blood pressure and the sleep-wake cycle and keeping the immune response to infection in check. One recent study showed that people with Long COVID tend to have low cortisol levels. So do people with chronic fatigue syndrome, research shows.
“Cortisol has so many beneficial properties that if it is reduced it can have a host of negative consequences,” said Frank.
In another experiment, the researchers exposed different groups of rats to an immune stressor (a weakened bacteria) and observed their heart rate, temperature and behavior as well as the activity of immune cells in the brain called glial cells.
They found that the group of rats that had previously been exposed to the COVID protein S1 responded far more strongly to the stressor, with more pronounced changes in eating, drinking, behavior, core body temperature and heart rate, more neuroinflammation and stronger activation of glial cells.
“We show for the first time that exposure to antigens left behind by this virus can actually change the immune response in the brain so that it overreacts to subsequent stressors or infection,” said Frank.
He stresses that the study was in animals and that more research is necessary to determine whether and how low cortisol might lead to Long COVID symptoms in people.
But he theorizes that the process might go something like this: COVID antigens lower cortisol, which serves to keep inflammatory responses to stressors in check in the brain. Once a stressor arises – whether it be a bad day at work, a mild infection or a hard workout – the brain’s inflammatory response is unleashed without those limits and serious symptoms come screaming back.
Those might include, fatigue, depression, brain fog, insomnia and memory problems.
Frank said he is doubtful that cortisol treatments alone could be an effective treatment for Long COVID, as they would not get at the root cause and come with a host of side effects.
Instead, the findings suggest that identifying and minimizing different stressors might help manage symptoms.
Rooting out the source of antigens –including tissue reservoirs where bits of virus continue to hide out – might also be an approach worth exploring, he suggests.
The study was funded by the nonprofit PolyBio Research Foundation. More research is underway.
“There are many individuals out there suffering from this debilitating syndrome. This research gets us closer to understanding what, neurobiologically, is going on and how cortisol may be playing a role,” said Frank.
END
Low cortisol, hair-trigger stress response in the brain may underlie Long COVID
2024-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
What time the malaria-bearing mosquito bites you might make a difference
2024-08-19
What time the malaria-bearing mosquito bites you might make a difference
Circadian rhythms appear to influence vulnerability to malaria parasites
A discovery by McGill-affiliated researchers could lead to more effective treatment of malaria and other parasitic diseases.
When mice are infected in the middle of the night with the parasites causing cerebral malaria, the symptoms of the disease are less severe than for those inflected during the day, and the spread of the parasites within the hosts is more limited, research teams from McGill University, the Douglas Research Centre ...
SwRI develops novel DNA-targeting therapeutic screening technique
2024-08-19
SAN ANTONIO — August 19, 2024 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has developed a unique technology to screen new DNA-targeting therapeutics designed to treat cancer and other diseases. Combining SwRI’s 3D drug screening software tool and machine learning techniques, SwRI scientists successfully predicted the DNA binding affinity and cancer cell toxicity for a variety of relevant drug compounds under development.
SwRI expanded the capabilities of its Rhodium™ drug development tool to visualize and rapidly predict how ...
Swiping through online videos increases boredom, study finds
2024-08-19
Swiping through online videos to relieve boredom may actually make people more bored and less satisfied or engaged with the content, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
The study included seven experiments with a total of more than 1,200 participants from the United States or college students at the University of Toronto. In two baseline experiments, participants switched from one online video to the next when they were bored, and they predicted they would feel less bored by switching videos instead ...
Kelvin K. Droegemeier on ‘Working Toward a Computational Framework to Support Earth System Science and Climate Projection’
2024-08-19
Editor’s note: NCSA is cohosting an International Summit on a Computational System for Frontier Earth System Science and Climate Simulation & Projection September 29 through October 2, 2024 at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
Toward a Computational Framework for Earth System Models at Kilometer Resolution to Support Earth System Science and Climate Projection
By Kelvin K. Droegemeier, Professor of Atmospheric Science and Special Advisor to the Chancellor for Science and Policy at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
Almost daily, and often without realizing it, we rely upon computers to guide our decisions. Whether finding the fastest ...
National Academy of Medicine selects FAU for substance use, opioid crises collaborative
2024-08-19
As of 2024, approximately 2.7 million Americans aged 12 and older were estimated to have misused prescription opioids in the past year. Moreover, alcohol, cannabis, cocaine, methamphetamines, among other substances, reflect a complex landscape that requires ongoing efforts aimed at prevention, treatment and policy changes to address the various issues associated with each substance.
Florida Atlantic University was recently selected to participate in the National Academy of Medicine’s (NAM) Action Collaborative on Combatting Substance Use Opioid Crises Core Competency Implementation Pilot Project. To improve coordination ...
Study finds potential link between DNA markers and aging process
2024-08-19
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the epigenetics company TruDiagnostic have uncovered DNA markers associated with retroelements, remnants of ancient viral genetic material, in our genes that act as highly accurate epigenetic clocks predicting chronological age. The results support the idea that certain retroelements in the human genome may be involved in aging.
Retroelements have been known to impact gene regulation, gene expression, genomic stability and the trajectory of various human diseases, but their potential as biomarkers for aging had been largely unexplored.
The ...
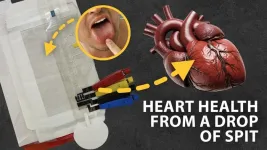
Improving access to heart-failure screening with saliva
2024-08-19
DENVER, Aug. 19, 2024 — Heart failure is a leading cause of death worldwide and is especially fatal for people who don’t have access to medical facilities. So, a team of researchers aims to bring heart failure screening from the lab to the home. Their point-of-care electrochemical biosensor prototype, which resembles a see-through lateral flow test for COVID-19, can measure levels of two biomarkers for heart failure in as little as 15 minutes from just a drop of saliva.
Trey Pittman, a graduate student at Colorado State University, will present his team’s research at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid ...
Expanding a child’s heart implant with light
2024-08-19
DENVER, Aug. 19, 2024 — Children born with defects that impair the heart’s lower chambers undergo a series of invasive surgeries early in life. The first surgery includes implantation of a plastic tube called a shunt to improve blood flow. However, as children grow, the shunt is often replaced to accommodate their changing bodies. Now, researchers have designed a shunt that expands when activated by light. If developed successfully, this device could reduce the number of open-chest surgeries these children receive.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 ...
New insights on how bird flu crosses the species barrier
2024-08-19
In recent years, public health measures, surveillance, and vaccination have helped bring about significant progress in reducing the impact of seasonal flu epidemics, caused by human influenza viruses A and B. However, a possible outbreak of avian influenza A (commonly known as ‘bird flu’) in mammals, including humans, poses a significant threat to public health.
The Cusack group at EMBL Grenoble studies the replication process of influenza viruses. A new study from this group sheds light on the different mutations that the avian influenza virus can undergo to be able to replicate in mammalian cells.
Some avian influenza ...
Energy companies pressure landowners into fracking, study shows
2024-08-19
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Energy companies use persistent and personalized pressure to get landowners to give permission for hydraulic fracturing (fracking), and even when landowners decline, companies use legalized compulsion to conduct fracking anyway, according to a new study led by researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York and UNLV.
“Hydraulic fracturing is a controversial issue, but a lot of the controversy has been focused on the big-picture consequences, for the climate and the economy,” said Benjamin Farrer, lead author and former PhD student at Binghamton University. “One of our hopes for this paper is that it will encourage policymakers ...