(Press-News.org) Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the epigenetics company TruDiagnostic have uncovered DNA markers associated with retroelements, remnants of ancient viral genetic material, in our genes that act as highly accurate epigenetic clocks predicting chronological age. The results support the idea that certain retroelements in the human genome may be involved in aging.
Retroelements have been known to impact gene regulation, gene expression, genomic stability and the trajectory of various human diseases, but their potential as biomarkers for aging had been largely unexplored.
The study, published Aug. 2 in Aging Cell, concluded that these retroelement clocks embedded in the human genome capture unique signals of aging not previously recognized by other clocks that measure chronological age. Most aging clocks estimate a person’s biological age based on patterns of epigenetic markers—chemical tags called methyl groups that are attached to DNA and affect how genes are expressed. The pattern of methylation on retroelements seems to change as people age causing some genes to be more active which may lead to genomic instability, inflammation and age-related diseases.
Aging is a complex process influenced by genetic, environmental and epigenetic factors, with researchers pursuing reliable markers that can predict biological age—a snapshot of a person’s age at the biochemical level which impacts health and overall well-being. On the other hand, chronological age represents the number of years a person has lived. Depending on the individual, the two may not correlate.
Building an Aging Clock Based on Retroelements
Researchers used a machine learning model from TruDiagnostic to analyze epigenetic data from 12,670 individuals with ages ranging from 12 to 100. Using the resulting DNA methylation patterns of retroelements, specifically human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) and long interspersed nuclear element (LINEs), they developed a composite retroelement-Age clock called “Retro-Age.”
“Now, with Retro-Age, we have greater insight and a fresh perspective into the aging process and a potentially powerful tool to predict biological age,” said first author Dr. Lishomwa Ndhlovu, the Herbert J. and Ann L. Siegel Distinguished Professor of Medicine and professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The researchers found that the Retro-Age clock remained accurate when testing various human tissues, complemented existing epigenetic clocks and even extended to other mammalian species. Their findings point to the possibility that retroelement activity might be a fundamental aspect of aging across different species.
Turning Back the Clock—Impact of Environmental Factors
The researchers also found that the DNA methylation patterns they observed were not only predictive of age but also responsive to outside factors like antiretroviral therapy taken by people living with HIV. HIV infection accelerates epigenetic aging, while antiretroviral therapy appears to reverse the clock to some degree. This suggests that retroelement activity is influenced by both the infection and its treatment, affecting the biological aging process in people living with HIV.
“The reactivation of specific retroelements increases with age, potentially leading to biological hallmarks of aging such as inflammation, cellular senescence and genomic instability,” said corresponding author Dr. Michael Corley, assistant professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Weill Cornell Medicine. “Our findings indicate that retroelement clocks capture previously undetected facets of biological aging and may open the door to future treatments for these and other age-related conditions.”
Monitoring the activity of retroelements could help track the effectiveness of anti-aging therapies, health outcomes in aging populations and the impact of lifestyle changes on biological aging, said the researchers.
Drs. Ndhlovu and Corley plan to explore new treatments or therapeutic interventions for age-related diseases by targeting the epigenetic states of specific retroelements in the human genome. This approach, they noted, may eventually reverse or mitigate the biological effects of aging, improving an individual’s health span and lifespan.
Many Weill Cornell Medicine physicians and scientists maintain relationships and collaborate with external organizations to foster scientific innovation and provide expert guidance. The institution makes these disclosures public to ensure transparency. For this information, please see the profiles for Dr. Lishomwa Ndhlovu and Dr. Michael Corley.
The research reported in this story was funded by the National Institutes of Health, with grant awards R01AG082056, R01HL160392, R01MH134391, and UM1AI164559(ACEL14288).
END
Study finds potential link between DNA markers and aging process
2024-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improving access to heart-failure screening with saliva
2024-08-19
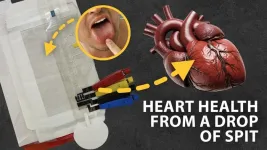
DENVER, Aug. 19, 2024 — Heart failure is a leading cause of death worldwide and is especially fatal for people who don’t have access to medical facilities. So, a team of researchers aims to bring heart failure screening from the lab to the home. Their point-of-care electrochemical biosensor prototype, which resembles a see-through lateral flow test for COVID-19, can measure levels of two biomarkers for heart failure in as little as 15 minutes from just a drop of saliva.
Trey Pittman, a graduate student at Colorado State University, will present his team’s research at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid ...
Expanding a child’s heart implant with light
2024-08-19
DENVER, Aug. 19, 2024 — Children born with defects that impair the heart’s lower chambers undergo a series of invasive surgeries early in life. The first surgery includes implantation of a plastic tube called a shunt to improve blood flow. However, as children grow, the shunt is often replaced to accommodate their changing bodies. Now, researchers have designed a shunt that expands when activated by light. If developed successfully, this device could reduce the number of open-chest surgeries these children receive.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 ...
New insights on how bird flu crosses the species barrier
2024-08-19
In recent years, public health measures, surveillance, and vaccination have helped bring about significant progress in reducing the impact of seasonal flu epidemics, caused by human influenza viruses A and B. However, a possible outbreak of avian influenza A (commonly known as ‘bird flu’) in mammals, including humans, poses a significant threat to public health.
The Cusack group at EMBL Grenoble studies the replication process of influenza viruses. A new study from this group sheds light on the different mutations that the avian influenza virus can undergo to be able to replicate in mammalian cells.
Some avian influenza ...
Energy companies pressure landowners into fracking, study shows
2024-08-19
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Energy companies use persistent and personalized pressure to get landowners to give permission for hydraulic fracturing (fracking), and even when landowners decline, companies use legalized compulsion to conduct fracking anyway, according to a new study led by researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York and UNLV.
“Hydraulic fracturing is a controversial issue, but a lot of the controversy has been focused on the big-picture consequences, for the climate and the economy,” said Benjamin Farrer, lead author and former PhD student at Binghamton University. “One of our hopes for this paper is that it will encourage policymakers ...
UC Irvine team says urban street networks, building density shape severity of floods
2024-08-19
Irvine, Calif., Aug. 19, 2024 — Cities around the globe are experiencing increased flooding due to the compounding effects of stronger storms in a warming climate and urban growth. New research from the University of California, Irvine suggests that urban form, specifically the building density and street network of a neighborhood, is also affecting the intensity of flooding.
For a paper published today in Nature Communications, researchers in UC Irvine’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering turned to statistical mechanics ...
Nurses play key role in addressing mental well-being for people after a stroke
2024-08-19
Statement Highlights:
The latest research indicates that 16% to 85% of people recovering from a stroke experience at least one psychosocial symptom, including depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue and/or decreased quality of life.
Critical nursing interventions, such as regular mental health screenings, education, symptom management and follow-up care, are key to reducing the negative effects on a patient’s mental well-being after a stroke, yet only a small proportion of patients receive treatment. ...
Why these educators believe whole-class reading creates a sense of community in the classroom
2024-08-19
With teaching methods for reading and writing under constant scrutiny, and high-stakes testing creating intense pressure to teach strictly to state standards, is there still value in whole-class reading?
Two educators believe that whole-class reading should go hand-in-hand with individual instructional reading, and they say it is vital for cultivating a sense of classroom community while developing critical thinking in young minds.
Educators Lynsey Burkins and Franki Sibberson, both teachers and educators from Ohio, have published a book called In Community ...
Researchers develop an instant version of trendy, golden turmeric milk
2024-08-18
DENVER, Aug. 18, 2024 — If you’ve visited a trendy café in the past few years, you might have noticed “golden” turmeric milk on the menu. Though recently advertised as a caffeine-free, healthy coffee alternative, the drink is a fancified version of haldi doodh — a traditional Indian beverage often used as an at-home cold remedy. And now, researchers have developed an efficient method to make a plant-based, instant version that maintains the beneficial properties of the ingredients while also extending its shelf life.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ...
Peering into the mind of artificial intelligence to make better antibiotics
2024-08-18
DENVER, Aug. 18, 2024 — Artificial intelligence (AI) has exploded in popularity. It powers models that help us drive vehicles, proofread emails and even design new molecules for medications. But just like a human, it’s hard to read AI’s mind. Explainable AI (XAI), a subset of the technology, could help us do just that by justifying a model’s decisions. And now, researchers are using XAI to not only scrutinize predictive AI models more closely, but also to peer deeper into the field of chemistry.
The researchers will present ...
Evidence stacks up for poisonous books containing toxic dyes
2024-08-18
DENVER, Aug. 18, 2024 — If you come across brightly colored, cloth-bound books from the Victorian era, you might want to handle them gently, or even steer clear altogether. Some of their attractive hues come from dyes that could pose a health risk to readers, collectors or librarians. The latest research on these poisonous books used three techniques — including one that hasn’t previously been applied to books — to assess dangerous dyes in a university collection and found some volumes may be unsafe to handle.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid meeting being ...