(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., Aug. 19, 2024 — Cities around the globe are experiencing increased flooding due to the compounding effects of stronger storms in a warming climate and urban growth. New research from the University of California, Irvine suggests that urban form, specifically the building density and street network of a neighborhood, is also affecting the intensity of flooding.
For a paper published today in Nature Communications, researchers in UC Irvine’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering turned to statistical mechanics to generate a new formula allowing urban planners to more easily assess flood risks presented by land development changes.
Co-author Mohammad Javad Abdolhosseini Qomi, UC Irvine associate professor of civil and environmental engineering who holds a joint appointment in UC Irvine’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, said that he and his colleagues were inspired by how physicists study intricate systems such as disordered porous solids, glasses and complex fluids to develop universal theories that can explain city-to-city variations in flood hazards.
“Application of statistical mechanics has yielded an analytical model that can project neighborhood-scale flood hazards anywhere in the world,” Qomi said. “We can probe differences between cities experiencing flood hazards. The platform has been demonstrated to show links between flood losses, urban form and observed rainfall extremes.”
Lead author Sarah Balaian, a UC Irvine Ph.D. candidate in civil and environmental engineering, said that we can expect the future to be marked by more severe weather events and that concentrated masses of people, many of whom lack the means of protection or escape, will be heavily affected by urban flooding.
“Furthermore, detailed modeling worldwide is presently impossible for many cities because of inadequate data, so our team was motivated to develop a new way of looking at flood risk based on the form of the built urban environment,” she said.
Co-author Brett Sanders, UC Irvine Chancellor’s Professor of civil and environmental engineering and professor of urban planning and public policy, said that the new formula was made possible by thousands of flood simulations across many different urban forms – simulations grounded in physical laws of motion.
“We created a physics-based dataset of flood depth and velocity for types of city layouts seen globally and then used data analysis techniques to derive a relatively simple formula that can be used for planning and vulnerability assessments globally,” Sanders said. “The equation can also be taught in our classes so that the next generation of civil engineers is able to anticipate the potential impacts of land development on flood hazards.”
This project received financial support from UC Irvine’s Henry Samueli School of Engineering, the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Education.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UC Irvine is a member of the prestigious Association of American Universities and is ranked among the nation’s top 10 public universities by U.S. News & World Report. The campus has produced five Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UC Irvine has more than 36,000 students and offers 224 degree programs. It’s located in one of the world’s safest and most economically vibrant communities and is Orange County’s second-largest employer, contributing $7 billion annually to the local economy and $8 billion statewide. For more on UC Irvine, visit www.uci.edu.
END
UC Irvine team says urban street networks, building density shape severity of floods
Researchers’ new analytical model can assess neighborhood-level hazards globally
2024-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nurses play key role in addressing mental well-being for people after a stroke
2024-08-19
Statement Highlights:
The latest research indicates that 16% to 85% of people recovering from a stroke experience at least one psychosocial symptom, including depression, anxiety, stress, fatigue and/or decreased quality of life.
Critical nursing interventions, such as regular mental health screenings, education, symptom management and follow-up care, are key to reducing the negative effects on a patient’s mental well-being after a stroke, yet only a small proportion of patients receive treatment. ...
Why these educators believe whole-class reading creates a sense of community in the classroom
2024-08-19
With teaching methods for reading and writing under constant scrutiny, and high-stakes testing creating intense pressure to teach strictly to state standards, is there still value in whole-class reading?
Two educators believe that whole-class reading should go hand-in-hand with individual instructional reading, and they say it is vital for cultivating a sense of classroom community while developing critical thinking in young minds.
Educators Lynsey Burkins and Franki Sibberson, both teachers and educators from Ohio, have published a book called In Community ...
Researchers develop an instant version of trendy, golden turmeric milk
2024-08-18
DENVER, Aug. 18, 2024 — If you’ve visited a trendy café in the past few years, you might have noticed “golden” turmeric milk on the menu. Though recently advertised as a caffeine-free, healthy coffee alternative, the drink is a fancified version of haldi doodh — a traditional Indian beverage often used as an at-home cold remedy. And now, researchers have developed an efficient method to make a plant-based, instant version that maintains the beneficial properties of the ingredients while also extending its shelf life.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ...
Peering into the mind of artificial intelligence to make better antibiotics
2024-08-18
DENVER, Aug. 18, 2024 — Artificial intelligence (AI) has exploded in popularity. It powers models that help us drive vehicles, proofread emails and even design new molecules for medications. But just like a human, it’s hard to read AI’s mind. Explainable AI (XAI), a subset of the technology, could help us do just that by justifying a model’s decisions. And now, researchers are using XAI to not only scrutinize predictive AI models more closely, but also to peer deeper into the field of chemistry.
The researchers will present ...
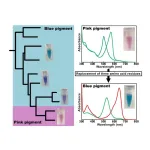
Evidence stacks up for poisonous books containing toxic dyes
2024-08-18
DENVER, Aug. 18, 2024 — If you come across brightly colored, cloth-bound books from the Victorian era, you might want to handle them gently, or even steer clear altogether. Some of their attractive hues come from dyes that could pose a health risk to readers, collectors or librarians. The latest research on these poisonous books used three techniques — including one that hasn’t previously been applied to books — to assess dangerous dyes in a university collection and found some volumes may be unsafe to handle.
The researchers will present their results at the fall meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Fall 2024 is a hybrid meeting being ...
Novel photoreceptor sheds light on how cyanobacteria see color
2024-08-17
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have identified a new photoreceptor in cyanobacteria with a modification in part of its structure which makes it sensitive to green/teal light. The photoreceptor belongs in a family usually sensitive to red/green light in the environment. They identified the parts of its amino acid structure responsible for this behavior; editing them helped restore sensitivity to red and green light, a remarkable example of molecular “plasticity” in action.
Cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae, are phenomenally important players ...
The bee’s knees: New tests created to find fake honey
2024-08-17
Researchers led by Cranfield University have developed new ways to detect sugar syrup adulteration in honey, paving the way for fast and accurate tests to discover fake products.
There is growing consumer demand for honey, with £89.8 million worth of honey imported to the UK in 2023. But as a high-value product it is vulnerable to fraud, with syrups added to dilute the pure honey – a report from the European Commission in 2023 found 46% of 147 honey samples tested were likely to have been adulterated with cheap plant syrups.
Because honey’s characteristics vary due to sources of nectar, season of harvest and ...
Sustainably reducing inappropriate IV use by more than a third
2024-08-17
Sustainably reducing inappropriate IV use by more than a third
Reasearch led by Amsterdam UMC, across more than 5 years and 1100 patients has demonstrated a strategy for reducing inappropriate IV use by a third, an effect that was sustained across the five-year period. This should also lead to reduction in the associated infections that effect one in ten patients. These results are published today in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine.
"Infections caused by both IVs and catheters occur in more than 10% of patients and studies indicate that up to a quarter are not necessary. Simply, this means that patients are placed at ...
UAF scientists discover phenomenon impacting Earth’s radiation belts
2024-08-16
Two University of Alaska Fairbanks scientists have discovered a new type of “whistler,” an electromagnetic wave that carries a substantial amount of lightning energy to the Earth’s magnetosphere.
The research is published today in Science Advances.
Vikas Sonwalkar, a professor emeritus, and Amani Reddy, an assistant professor, discovered the new type of wave. The wave carries lightning energy, which enters the ionosphere at low latitudes, to the magnetosphere. The energy is reflected upward by the ionosphere’s ...
New AI tool captures how proteins behave in context
2024-08-16
A fish on land still waves its fins, but the results are markedly different when that fish is in water. Attributed to renowned computer scientist Alan Kay, the analogy is used to illustrate the power of context in illuminating questions under investigation.
In a first for the field of artificial intelligence (AI), a tool called PINNACLE embodies Kay’s insight when it comes to understanding the behavior of proteins in their proper context as determined by the tissues and cells in which these proteins act and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] UC Irvine team says urban street networks, building density shape severity of floodsResearchers’ new analytical model can assess neighborhood-level hazards globally