(Press-News.org) Sustainably reducing inappropriate IV use by more than a third
Reasearch led by Amsterdam UMC, across more than 5 years and 1100 patients has demonstrated a strategy for reducing inappropriate IV use by a third, an effect that was sustained across the five-year period. This should also lead to reduction in the associated infections that effect one in ten patients. These results are published today in The Lancet eClinicalMedicine.
"Infections caused by both IVs and catheters occur in more than 10% of patients and studies indicate that up to a quarter are not necessary. Simply, this means that patients are placed at an unnecessarily high risk of infection. This can delay, or even hamper their recovery,” says Suzanne Geerlings, professor of internal medicine at Amsterdam UMC.
In order to combat this the research team published in 2017 a strategy in the Lancet Infectious Diseases. This strategy resulted in a 37% reduction in the number of unnecessary or, inappropriately used, catheters.
"When we speak of inappropriate use, this usually refers to catheters that are placed for too long or, in the case of urinary catheters, when there is insufficient support for the patient,” adds Geerlings.
Across the 1113 patients included in the study, 962 received an IV catheter, typically used for the administration of fluids, with the remaining 151 receiving a urinary catheter with the remaining 962 receiving an IV catheter.
"What is really interesting is that no study has ever looked at how lasting these recommendations are, and this is true for many new strategies in the healthcare sector. In this case, we see clearly that the effects were sustained over last five years,” says Geerlings.
The what, now the why
To understand why their strategy continued to work, the research team carried out interviews with 18 healthcare professionals across the Netherlands. These interviews revealed that the strategy had permanently altered the workflow in four of the five hospitals included in the study.
"By talking with those 'on the ground’, we learned what worked and, perhaps more crucially, what didn't," says Tessa van Horrik, researcher at Amsterdam UMC and the first author the study.
"The main barriers to maintaining the strategy were a combination of other priorities, a shortage of time, of personnel or of both and, understandably, in some cases, there was simply no one to lead the implementation across the five-year period. This shows us that the strategy can work, as long as the resources are there.” adds van Horrik.
Although, the study also demonstrated that these resources need not be permanent. It was demonstrated that a temporary investment, in either time or leadership, was sufficient to reduce the unnecessary or inappropriate use of IVs and catheters.
END
Sustainably reducing inappropriate IV use by more than a third
Infections caused by both IVs occur in 10% of patients and up to a quarter are not necessary. Research from Amsterdam UMC shows how to reduce this use and, thus, infections
2024-08-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UAF scientists discover phenomenon impacting Earth’s radiation belts
2024-08-16
Two University of Alaska Fairbanks scientists have discovered a new type of “whistler,” an electromagnetic wave that carries a substantial amount of lightning energy to the Earth’s magnetosphere.
The research is published today in Science Advances.
Vikas Sonwalkar, a professor emeritus, and Amani Reddy, an assistant professor, discovered the new type of wave. The wave carries lightning energy, which enters the ionosphere at low latitudes, to the magnetosphere. The energy is reflected upward by the ionosphere’s ...
New AI tool captures how proteins behave in context
2024-08-16
A fish on land still waves its fins, but the results are markedly different when that fish is in water. Attributed to renowned computer scientist Alan Kay, the analogy is used to illustrate the power of context in illuminating questions under investigation.
In a first for the field of artificial intelligence (AI), a tool called PINNACLE embodies Kay’s insight when it comes to understanding the behavior of proteins in their proper context as determined by the tissues and cells in which these proteins act and ...
Researchers investigate parent perceptions of virtual learning
2024-08-16
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, a majority of schools across the U.S. shifted to virtual learning. In a new study, published in Social Education Research, researchers conducted interviews with parents of students who attended middle or high schools to understand how virtual learning impacted their daily routines, stress levels, and the academic performance of the children.
The transition to virtual learning necessitated the creation of online lessons in a very short time period and with limited training of teachers. As a result, parents and students had to deal with unexpected changes in their home lives and learning environments.
“Virtual learning will not be limited ...
Ancient DNA reveals Indigenous dog lineages found at Jamestown, Virginia
2024-08-16
Previous scientific studies have indicated that North American dog lineages were replaced with European ones between 1492 and the present day. To better understand the timing of this replacement, researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and the University of Iowa sequenced mitochondrial DNA from archaeological dogs. Their findings suggest a complex social history of dogs during the early colonial period.
Europeans and Native Americans valued their dogs as companion animals, using them for similar work and as symbols of identity. Consequently, ...
Researchers make breakthrough in fight against COVID-19
2024-08-16
A team led by Jose Onuchic at Rice University and Paul Whitford at Northeastern University, both researchers at the National Science Foundation Physics Frontiers Center at the Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP) at Rice, has made a discovery in the fight against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for COVID-19.
The team, in partnership with an experimental effort led by Yale University researchers Walter Mothes and Wenwei Li, has uncovered new insights into how the virus infects human cells and how it can be neutralized. Their findings were published in the ...
Methamphetamine-involved psychiatric hospitalizations have increased, study says
2024-08-16
AURORA, Colo. (August 16, 2024) – A new study, out now in Drug and Alcohol Dependence, that details trends among psychiatric hospitalizations between 2015-2019 finds that while most hospitalizations did not involve any substances, methamphetamine-related hospitalizations have increased while overall number of psychiatric hospitalizations remained stable.
Additionally, researchers detail that psychiatric hospitalizations caused by methamphetamine use were highest in the Mountain West region but were also shifting geographically. “Rates of ...
Green warriors: plants on the frontline against microplastics
2024-08-16
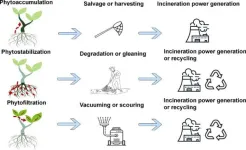
In an innovative ecological article, researchers have unveiled the potential of phytoremediation to curb microplastic pollution. This approach leverages natural plant processes to absorb and diminish micro and nanoplastics, offering a viable solution for managing environmental plastic pollution. This viewpoint advocates utilizing plant life as an effective tool against the widespread issue of plastic contamination in ecosystems.
With escalating concerns about the enduring impact of plastic waste, phytoremediation emerges as a promising solution. This method utilizes plants ...
Decoding mysterious seismic signals
2024-08-16
For the decades since their discovery, seismic signals known as PKP precursors have challenged scientists. Regions of Earth’s lower mantle scatter incoming seismic waves, which return to the surface as PKP waves at differing speeds.
The origin the precursor signals, which arrive ahead of the main seismic waves that travel through Earth’s core, has remained unclear, but research led by University of Utah geophysicists sheds new light on this mysterious seismic energy.
PKP precursors appear to propagate from places deep below North America and the western Pacific and possibly bear an association with “ultra-low velocity zones,” thin layers ...
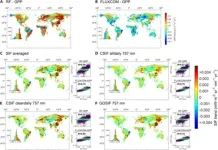
Green light for accurate vegetation research: new evaluation of global SIF datasets
2024-08-16
A recent study has pinpointed the top-performing solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) products for precise global monitoring of photosynthesis and vegetation dynamics. By thoroughly evaluating eight widely-used SIF datasets, the research team identified Global OCO-2 SIF (GOSIF) and Contiguous Solar-Induced Fluorescence (CSIF) as leading tools for estimating gross primary productivity (GPP) and forecasting key phenological stages. These findings provide crucial direction for scientists aiming to enhance global vegetation ...
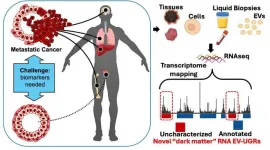
Mount Sinai researchers discover novel nanoparticles in blood with potential to transform cancer diagnosis
2024-08-16
New York, NY [August 16, 2024]—Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified a new class of RNAs packed into tiny particles known as extracellular vesicles (EVs) that could revolutionize how cancer and other diseases are diagnosed. The team found that these molecules undergo changes when cancer is present, suggesting their potential as biomarkers for detecting prostate cancer or as targets for therapy. The work, led by Navneet Dogra, PhD, Edgar Gonzalez-Kozlova, PhD, Tzu-Yi Chen, PhD, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
[Press-News.org] Sustainably reducing inappropriate IV use by more than a thirdInfections caused by both IVs occur in 10% of patients and up to a quarter are not necessary. Research from Amsterdam UMC shows how to reduce this use and, thus, infections