(Press-News.org) AURORA, Colo. (August 16, 2024) – A new study, out now in Drug and Alcohol Dependence, that details trends among psychiatric hospitalizations between 2015-2019 finds that while most hospitalizations did not involve any substances, methamphetamine-related hospitalizations have increased while overall number of psychiatric hospitalizations remained stable.
Additionally, researchers detail that psychiatric hospitalizations caused by methamphetamine use were highest in the Mountain West region but were also shifting geographically. “Rates of methamphetamine-involved psychiatric hospitalizations with were by far the highest in the Mountain West. As expected, this mirrors rates of self-reported methamphetamine use and methamphetamine-related overdose deaths in the Mountain West.” says Susan Calcaterra, MD, MPH, professor at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus and study lead author. “Psychiatric hospitalizations involving methamphetamine use is really taking off in the Midwest and Northeast, in particular.”
While rates of methamphetamine-related psychiatric hospitalizations increased 68% over the study period, opioid-related hospitalizations decreased by 22%. Methamphetamine rate increases may be attributed to methamphetamines ubiquitousness and affordability, as well as the lack of resources available to manage methamphetamine use. Why opioid-involved psychiatric hospitalizations declined is less clear but may be related to the lethality of fentanyl.
“An important takeaway from this study is the need for resources to address the mental and physical treatment of methamphetamine use,” says Calcaterra.
“While the vast majority of psychiatric hospitalizations in this timeframe did not involve substance use, the significant increase in methamphetamine use means we have to better consider harm reduction in clinical settings. Evidence-based interventions such as contingency management which involves offering incentives for abstinence, harm reduction education, provision of naloxone for overdose reversal and access to expanded mental health treatments are proven to help mitigate dangerous effects from methamphetamine use, especially when contaminated with fentanyl much like the campaigns aimed at public awareness around opioid use.”
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes, and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado – which see more than 2 million adult and pediatric patient visits yearly. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by $705 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
END
Methamphetamine-involved psychiatric hospitalizations have increased, study says
While most psychiatric hospitalizations did not involve substances, methamphetamine-related encounters increased while opioid-involved encounters decreased
2024-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Green warriors: plants on the frontline against microplastics
2024-08-16
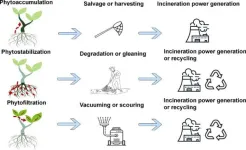
In an innovative ecological article, researchers have unveiled the potential of phytoremediation to curb microplastic pollution. This approach leverages natural plant processes to absorb and diminish micro and nanoplastics, offering a viable solution for managing environmental plastic pollution. This viewpoint advocates utilizing plant life as an effective tool against the widespread issue of plastic contamination in ecosystems.
With escalating concerns about the enduring impact of plastic waste, phytoremediation emerges as a promising solution. This method utilizes plants ...
Decoding mysterious seismic signals
2024-08-16
For the decades since their discovery, seismic signals known as PKP precursors have challenged scientists. Regions of Earth’s lower mantle scatter incoming seismic waves, which return to the surface as PKP waves at differing speeds.
The origin the precursor signals, which arrive ahead of the main seismic waves that travel through Earth’s core, has remained unclear, but research led by University of Utah geophysicists sheds new light on this mysterious seismic energy.
PKP precursors appear to propagate from places deep below North America and the western Pacific and possibly bear an association with “ultra-low velocity zones,” thin layers ...
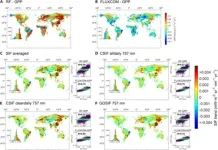
Green light for accurate vegetation research: new evaluation of global SIF datasets
2024-08-16
A recent study has pinpointed the top-performing solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) products for precise global monitoring of photosynthesis and vegetation dynamics. By thoroughly evaluating eight widely-used SIF datasets, the research team identified Global OCO-2 SIF (GOSIF) and Contiguous Solar-Induced Fluorescence (CSIF) as leading tools for estimating gross primary productivity (GPP) and forecasting key phenological stages. These findings provide crucial direction for scientists aiming to enhance global vegetation ...
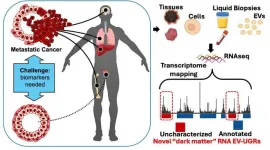
Mount Sinai researchers discover novel nanoparticles in blood with potential to transform cancer diagnosis
2024-08-16
New York, NY [August 16, 2024]—Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified a new class of RNAs packed into tiny particles known as extracellular vesicles (EVs) that could revolutionize how cancer and other diseases are diagnosed. The team found that these molecules undergo changes when cancer is present, suggesting their potential as biomarkers for detecting prostate cancer or as targets for therapy. The work, led by Navneet Dogra, PhD, Edgar Gonzalez-Kozlova, PhD, Tzu-Yi Chen, PhD, ...
Underground event marks excavation completion on colossal caverns for underground neutrino laboratory, DUNE
2024-08-16
Lead, SD (Aug. 15, 2024) — A ribbon-cutting event was held today at the Sanford Underground Research Facility (SURF) in Lead, S.D. to mark the completion of excavation work for the Long-Baseline Neutrino Facility/Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment (LBNF/DUNE), an international project led by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. The “Into the Depths of Discovery” event, hosted by Fermilab and the South Dakota Science and Technology Authority (SDSTA), was attended by supporters of the three-year excavation of the caverns, including state and federal leaders as well as officials from the Department of Energy.
“Today ...
Exposing myths about ballot collection on Native American reservations
2024-08-16
Third-party collection of mail-in ballots has helped rural residents and those with disabilities to vote, yet the practice has become contentious and the target of laws aimed at restricting it.
Critics claim the process is vulnerable to fraud and manipulation.
But new research from the University of Utah’s College of Social & Behavioral Science tells a different story. Ballot collection is more accurately characterized as a pathway for legitimate voter participation, according to a study published last month. Authors Daniel McCool, a professor emeritus in the Department of Political Science, and Weston McCool, a ...
New twist on synthesis technique developed at Rice promises sustainable manufacturing
2024-08-16
James Tour’s lab at Rice University has developed a new method known as flash-within-flash Joule heating (FWF) that could transform the synthesis of high-quality solid-state materials, offering a cleaner, faster and more sustainable manufacturing process. The findings were published in Nature Chemistry on Aug. 8.
Traditionally, synthesizing solid-state materials has been a time-consuming and energy-intensive process, often accompanied by the production of harmful byproducts. But FWF enables gram-scale production of diverse compounds in seconds while reducing energy, water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions by ...
Rare diseases point to connections between metabolism and immunity
2024-08-16
Inherited diseases of metabolism and immunity have more in common than previously recognized, according to a new study published in the journal Science Immunology. The findings point to a new set of metabolic genes that are important for the function of immune system T cells, and they offer insights that could improve care for patients with these disorders.
The study examined genes that cause inborn errors of metabolism (disorders of the processes that cells use to convert food to energy) and inborn errors of immunity (disorders that affect immune system function). These rare and complex diseases are not fully understood.
“There had previously ...
Nitrogen interventions as a key to better health and robust ecosystems
2024-08-16
The Earth’s nitrogen cycle is among the most heavily exceeded planetary boundaries. Agricultural production and fossil fuel burning release nitrogen pollutants like ammonia (NH3), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which contribute to air pollution and damage ecosystems. These pollutants harm human health, crops, and ecosystems. Given the growing global energy and food demand, this damage is expected to increase even further.
The potential of nitrogen pollution mitigation technologies ...
Knocking out one key gene leads to autistic traits
2024-08-16
More than 70 genes have been linked to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a developmental condition in which differences in the brain lead to a host of altered behaviors, including issues with language, social communication, hyperactivity, and repetitive movements. Scientists are attempting to tease out those specific associations gene by gene, neuron by neuron.
One such gene is Astrotactin 2 (ASTN2). In 2018, researchers from the Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology at Rockefeller University discovered how defects in the protein produced by the gene disrupted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
[Press-News.org] Methamphetamine-involved psychiatric hospitalizations have increased, study saysWhile most psychiatric hospitalizations did not involve substances, methamphetamine-related encounters increased while opioid-involved encounters decreased