(Press-News.org)
The Earth’s nitrogen cycle is among the most heavily exceeded planetary boundaries. Agricultural production and fossil fuel burning release nitrogen pollutants like ammonia (NH3), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which contribute to air pollution and damage ecosystems. These pollutants harm human health, crops, and ecosystems. Given the growing global energy and food demand, this damage is expected to increase even further.
The potential of nitrogen pollution mitigation technologies and policies – so-called “nitrogen interventions” – for improving air quality and reducing impacts on ecosystems, has been underexplored. A gap exists between traditional nitrogen budget research, which tracks nitrogen flows across air, water, and soil, but lacks detail on biogeochemical transformations, and Earth science research, which models these transformations but usually focuses on a single environmental medium.
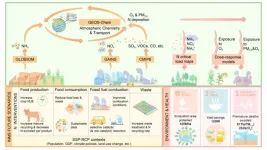
To address this knowledge gap, an international research team combined multidisciplinary methods to evaluate how nitrogen interventions could improve air quality and reduce nitrogen deposition. Their study, published in Science Advances, found that interventions, such as improving fuel combustion conditions, increasing agricultural nitrogen use efficiency, and reducing food loss and waste, could significantly lower premature deaths attributed to air pollution, crop losses, and ecosystems risks. While typically considered for individual goals like air or water quality, recognizing the broad co-benefits of nitrogen management is critical for future policy design and effective pollution control.
“We established an integrated assessment framework combining future nitrogen policy scenarios with integrated assessment models, air quality models and dose-response relationships to assess how ambitious measures can reduce air pollution and ecosystems damage at detailed geographic levels,” explains lead author Yixin Guo, a postdoctoral researcher jointly appointed by Peking University and IIASA.
The study shows that by 2050, high-ambition nitrogen interventions could cut global ammonia and nitrogen oxides emissions by 40% and 52%, respectively, compared to 2015 levels. This would reduce air pollution, preventing 817,000 premature deaths, lower ground-level ozone concentrations, and cut crop yield losses. Without these interventions, environmental damage will worsen by 2050, with Africa and Asia being affected the most. On the other hand, should those measures be implemented, Africa and Asia would benefit from them the most.
“We found that nitrogen interventions offer increasing benefits over time, with greater effects by 2050 than by 2030. The biggest reductions in ammonia and nitrogen oxides are expected in East and South Asia, mainly through improved crop practices and technology adoption in industrial sectors. These reductions will help lower air pollutions levels, making it easier for many regions to achieve the World Health Organization interim targets. Additionally, as populations grow, the health benefits of these interventions will increase, especially in developing areas,” adds Yixin.
“Our results highlight that nitrogen interventions can significantly help achieve multiple SDGs, including Good Health and Well-being (SDG3), Zero Hunger (SDG2), Responsible Consumption and Production (SDG12), and Life on Land (SDG15),” says Lin Zhang, a study coauthor and tenured associated professor at Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Peking University.
“This collaborative research shows how IIASA research can be rolled out globally. Solutions for environmental impacts will vary by region, enabling customized policy recommendations, even for complex issues like nitrogen pollution,” concludes Wilfried Winiwarter, a study coauthor and senior researcher in the Pollution Management Research Group of the IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program.
Reference:
Guo Y., Zhao H., Winiwarter W., Chang J., Wang X., Zhou M., Havlik P., Leclere D., Pan D., Kanter D., Zhang L. (2024) Aspirational Nitrogen Interventions Accelerate Air Pollution Abatement and Ecosystem Protection, Science Advances, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ado0112.
Researcher contacts:
Yixin Guo
Postdoctoral researcher jointed between Peking University and IIASA
Now tenure-track assistant professor at Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences Thrust of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
yixinguo@hkust-gz.edu.cn
Jinfeng Chang
Guest Research Scholar
Integrated Biosphere Futures Research Group
Biodiversity and Natural Resources Program
changj@iiasa.ac.at
Wilfried Winiwarter
Senior Research Scholar
Pollution Management Research Group
Energy, Climate, and Environment Program
winiwart@iiasa.ac.at
Press Officer
Bettina Greenwell
IIASA Press Office
Tel: +43 2236 807 282
greenwell@iiasa.ac.at
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe.
END
More than 70 genes have been linked to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a developmental condition in which differences in the brain lead to a host of altered behaviors, including issues with language, social communication, hyperactivity, and repetitive movements. Scientists are attempting to tease out those specific associations gene by gene, neuron by neuron.
One such gene is Astrotactin 2 (ASTN2). In 2018, researchers from the Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology at Rockefeller University discovered how defects in the protein produced by the gene disrupted ...
The European Union's law on artificial intelligence came into force on 1 August. The new AI Act essentially regulates what artificial intelligence can and cannot do in the EU. A team led by computer science professor Holger Hermanns from Saarland University and law professor Anne Lauber-Rönsberg from Dresden University of Technology has examined how the new legislation impacts the practical work of programmers. The results of their analysis will be published in the autumn.
'The AI Act shows ...
Imagine having to do your job, but not being able to visually process the data right in front of you. Nearly eight percent of genetic males and half a percent of genetic females have some form of Color Vision Deficiency (CVD), or the decreased ability to discern between particular colors. CVD is commonly referred to as color blindness.
Scientists use colors to convey information. Many scientists in the weather radar community have CVD and the use and interpretation of color is an important aspect of their work. Most colormaps ...
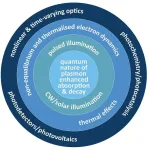
A new scientific review explores the exciting potential of hot carriers, energetic electrons generated by light in plasmonic nanostructures. These tiny structures hold immense promise for future technologies due to their unique way of interacting with light and creating hot carriers.
Hot carriers are electrons with a surplus of energy. When light strikes a plasmonic nanostructure, it can excite these electrons, pushing them out of equilibrium. This non-equilibrium state unlocks a range of fascinating phenomena. Hot carriers can be used to control light itself, potentially leading to ...
New research from Smithsonian’s Bird Friendly Coffee program highlights a type of biodiversity that often gets overlooked: soil bacteria and fungal communities. For over twenty years, Smithsonian research has shown that coffee farms with shade trees protect more biodiversity than intensified, monoculture coffee farms. The new research, published today in Applied Soil Ecology, shows that soil bacteria and fungi on coffee farms also respond to the intensity of coffee farm management. To conduct this research, the team collected soils samples on coffee farms in Colombia, El Salvador, and Peru and used DNA analysis to profile bacterial and fungal soil on ...
Geoscientists from the University of Cologne have led an international study to determine the origin of the huge piece of rock that hit the Earth around 66 million years ago and permanently changed the climate. The scientists analysed samples of the rock layer that marks the boundary between the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods. This period also saw the last major mass extinction event on Earth, in which around 70 percent of all animal species became extinct. The results of the study published in Science indicate that the asteroid formed outside Jupiter’s orbit during the ...
The Institute of Physics and IOP Publishing (IOPP) are launching Progress In Physics 2024, a two-day hybrid workshop hosted at the Institute of Physics’ office in London from 9-10 October 2024. The event will cover topics on condensed matter and will bring together leading physics researchers to exchange knowledge in both an in-person and online format.
Progress in Physics 2024 aligns with the mission of IOPP’s new Progress In seriesTM of journals. The series builds on the success of IOPP’s flagship journal Reports on Progress in PhysicsTM which celebrates its 90th anniversary this year.
With ...
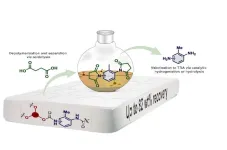
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
Researchers at Aarhus University have found a better method to recycle polyurethane foam from items like mattresses. This is great news for the budding industry that aims to chemically recover the original components of the material – making their products cheaper and better.
Polyurethane (PUR) is an indispensable plastic material used in mattresses, insulation in refrigerators and buildings, shoes, cars, airplanes, wind turbine blades, cables, and much more. It could be called a wonder material if it weren’t also an environmental ...
Powerful telescopes like NASA’s Hubble, James Webb, and Chandra X-ray Observatory provide scientists a window into deep space to probe the physics of black holes. While one might wonder how you can “see” a black hole, which famously absorbs all light, this is made possible by tidal disruption events (TDEs) - where a star is destroyed by a supermassive black hole and can fuel a “luminous accretion flare.” With luminosities thousands of billions of times brighter than the Sun, accretion events enable astrophysicists to study supermassive black holes (SMBHs) at cosmological distances.
TDEs occur when a star is violently ripped ...
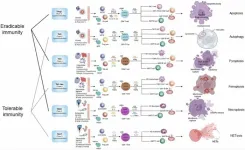
“We have proposed a framework encompassing all discovered host immunological pathways, such as TH1, TH2a, TH2b, TH3, TH9, TH17, TH22, TH1-like, and THαβ immune reactions”
BUFFALO, NY- August 16, 2024 – A new review was published as the cover paper of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), Volume 16, Issue 15, entitled, “Types of cell death and their relations to host immunological pathways”.
Various ...