New York, NY [August 16, 2024]—Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified a new class of RNAs packed into tiny particles known as extracellular vesicles (EVs) that could revolutionize how cancer and other diseases are diagnosed. The team found that these molecules undergo changes when cancer is present, suggesting their potential as biomarkers for detecting prostate cancer or as targets for therapy. The work, led by Navneet Dogra, PhD, Edgar Gonzalez-Kozlova, PhD, Tzu-Yi Chen, PhD, and Gustavo Stolovitzky, PhD, published in the August 16 online issue of Journal of Extracellular Vesicles [DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12481].
Dr. Dogra is an Assistant Professor of Pathology, Molecular, and Cell-Based Medicine, and a member of the Icahn Genomics Institute, and Dr. Gonzalez-Kozlova is an Assistant Professor of Immunology, both at Icahn Mount Sinai. Dr. Chen, a former PhD student in Dr. Dogra’s and Dr. Cordon-Cardo’s labs, is also affiliated with the Pathology, Molecular, and Cell-Based Medicine. Dr. Stolovitzky was formerly an Adjunct Professor at Icahn Mount Sinai and a researcher at the IBM Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York.
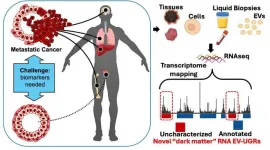
The research team named these RNA molecules "EV-UGRs" (short for Extracellular Vesicles-Associated Unannotated Genomic Regions) after discovering them in the blood and urine of prostate cancer patients. UGRs are often referred to as the “dark matter” of the human genome. They are believed to be crucial for controlling how genes are turned on and off and how genetic instructions are translated into proteins.
Extracellular vesicles and exosomes are tiny nanoparticles, approximately 1,000 times smaller than the thickness of a human hair, secreted by all cells into biofluids such as blood and urine. These nanoparticles are known to carry genetic material, which is protected from the external environment. A collaboration between the laboratory of Dr. Dogra and Dr. Stolovitzky discovered that EVs carry these small, previously unidentified pieces of RNA dark matter.
"Until now, the RNA 'dark matter' associated with extracellular vesicles and exosomes has been largely ignored. My team wanted to explore whether EV-UGRs could be valuable for disease monitoring. We tracked prostate cancer patients before and after prostate cancer surgery and were surprised to find that EV-UGR RNA expression changed following the surgery. This is, to our knowledge, the first study to detail these 'dark matter' RNA molecules, EV-UGRs, in unprecedented detail in the context of prostate cancer," says Dr. Dogra, lead author of the study. "Our findings indicate that blood EV-UGRs undergo changes in the presence of cancer, suggesting a less invasive approach for diagnosing prostate cancer through simple liquid biopsies, potentially eliminating the need for more complex, painful, and infection-prone biopsy procedures."
"Prostate cancer is a heterogeneous disease, often requiring only active monitoring rather than treatment. Our study uses extracellular vesicle-associated novel RNA molecules as a diagnostic tool. This technology holds significant potential for less invasive diagnosis and liquid biopsy in the near future," says Ash Tewari, MD, MBBS, MCh, co-author, and Professor and Chair of the Milton and Carroll Petrie Department of Urology at Icahn Mount Sinai.
As part of the research, the investigators used next-generation small RNA sequencing to rapidly analyze human tissues and fluids. In addition, they developed a cost-effective liquid biopsy test and created tools to isolate tiny EVs from the blood and urine. Finally, they devised a computer pipeline to identify the new types of RNA.
The discovery of EV-UGRs, reports Dr. Dogra, holds promise for non-invasive diagnosis not only for prostate cancer but potentially for other diseases as well. Next, the researchers plan to validate their findings through rigorous randomized clinical trials, which will involve testing the new approach on a broader scale to confirm its effectiveness.
"This is a significant and timely achievement. The potential impact of this research is vast, promising a future where diagnosing diseases like prostate cancer could be done quickly and less invasively. This advancement could revolutionize care by reducing the time and discomfort associated with current diagnostic procedures, potentially leading to earlier detection and more effective treatment strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life,” says Carlos Cordon-Cardo, MD, PhD, co-author, the Irene Heinz Given and John LaPorte Given Professor of Pathology, and Chair of the Department of Pathology, Molecular and Cell-Based Medicine at Icahn Mount Sinai.
The paper is titled “Extracellular Vesicles Carry Transcriptional ‘Dark Matter’ Revealing Tissue-Specific Information.”
The work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) awards P20CA264076 and R21 AGO78848.
-####-
About the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is internationally renowned for its outstanding research, educational, and clinical care programs. It is the sole academic partner for the eight- member hospitals* of the Mount Sinai Health System, one of the largest academic health systems in the United States, providing care to a large and diverse patient population.
Ranked 13th nationwide in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and among the 99th percentile in research dollars per investigator according to the Association of American Medical Colleges, Icahn Mount Sinai has a talented, productive, and successful faculty. More than 3,000 full-time scientists, educators, and clinicians work within and across 44 academic departments and 36 multidisciplinary institutes, a structure that facilitates tremendous collaboration and synergy. Our emphasis on translational research and therapeutics is evident in such diverse areas as genomics/big data, virology, neuroscience, cardiology, geriatrics, as well as gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
Icahn Mount Sinai offers highly competitive MD, PhD, and Master’s degree programs, with current enrollment of approximately 1,300 students. It has the largest graduate medical education program in the country, with more than 2,000 clinical residents and fellows training throughout the Health System. In addition, more than 550 postdoctoral research fellows are in training within the Health System.
A culture of innovation and discovery permeates every Icahn Mount Sinai program. Mount Sinai’s technology transfer office, one of the largest in the country, partners with faculty and trainees to pursue optimal commercialization of intellectual property to ensure that Mount Sinai discoveries and innovations translate into healthcare products and services that benefit the public.
Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to breakthrough science and clinical care is enhanced by academic affiliations that supplement and complement the School’s programs.
Through the Mount Sinai Innovation Partners (MSIP), the Health System facilitates the real-world application and commercialization of medical breakthroughs made at Mount Sinai. Additionally, MSIP develops research partnerships with industry leaders such as Merck & Co., AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, and others.
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is located in New York City on the border between the Upper East Side and East Harlem, and classroom teaching takes place on a campus facing Central Park. Icahn Mount Sinai’s location offers many opportunities to interact with and care for diverse communities. Learning extends well beyond the borders of our physical campus, to the eight hospitals of the Mount Sinai Health System, our academic affiliates, and globally.
-------------------------------------------------------
* Mount Sinai Health System member hospitals: The Mount Sinai Hospital; Mount Sinai Beth Israel; Mount Sinai Brooklyn; Mount Sinai Morningside; Mount Sinai Queens; Mount Sinai South Nassau; Mount Sinai West; and New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
END