(Press-News.org) Inherited diseases of metabolism and immunity have more in common than previously recognized, according to a new study published in the journal Science Immunology. The findings point to a new set of metabolic genes that are important for the function of immune system T cells, and they offer insights that could improve care for patients with these disorders.
The study examined genes that cause inborn errors of metabolism (disorders of the processes that cells use to convert food to energy) and inborn errors of immunity (disorders that affect immune system function). These rare and complex diseases are not fully understood.
“There had previously been only a small number of genes that were on both lists of diseases, but we found that many more have overlap,” said Andrew Patterson, PhD, who led the study as a postdoctoral fellow working with Jeffrey Rathmell, PhD, at Vanderbilt University Medical Center. “Our study showed that a large number of genes associated with inborn errors of metabolism can also potentially affect T cell function when they are mutated.”
The findings suggest that patients with an inborn error of metabolism may also have immune defects that could impact their care, and conversely that metabolic defects may contribute to symptoms in patients with inborn errors of immunity.
“There’s a lot more that will have to be learned, but these connections might point to different therapies,” said Rathmell, Cornelius Vanderbilt Professor of Immunobiology and director of the Vanderbilt Center for Immunobiology. “Rather than different categories, these diseases are part of a continuum; there’s a gray zone between them and a potential new class of inborn errors of immunometabolism that intersects the two.”
Patterson and the research team used a gene-editing CRISPR approach to screen the inborn errors of metabolism genes for immune defects and the inborn errors of immunity genes for metabolic defects. They further analyzed one example from each set — one metabolic gene that had an immune defect; one immunity gene that had a metabolic defect — to more carefully examine the mechanistic impact.
Overall, Rathmell’s team is interested in discovering how metabolic pathways regulate T cell function, with the goal of developing targeted therapies for immune-mediated disorders.
“What we’ve done is lay the foundation for further investigation,” Patterson said. “The two examples we studied in detail point to new biology and new mechanisms, and there are hundreds of other genes we identified to analyze for their roles in T cell function.”
The findings are available on a website for other researchers to use.
“If you’re trying to understand the connections between metabolism and immunity, this is a great place to start,” Rathmell said.
Patterson recently joined the faculty of the University of Louisville as an assistant professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics. Vanderbilt collaborators Vivian Gama, PhD, associate professor of Cell and Developmental Biology, and Janet Markle, PhD, assistant professor of Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology, were important contributors to the study.
The current project started as part of the Human Immunology Discovery Initiative of the Vanderbilt Center for Immunobiology, which focused on developing approaches to study inborn errors of immunity and was supported by a Trans-Institutional Program grant from Vanderbilt University. Other funding support included grants from the National Institutes of Health (T32AR059039, T32CA009582, R01DK105550, R01HL136664, R01CA217987, R01AI153167, R35GM128915, RF1MH123971, R01AI165722, F99NS125829) and the Lupus Research Alliance.
END
Rare diseases point to connections between metabolism and immunity
Overlap in genes suggests a potential new class of inborn errors of immunometabolism
2024-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Nitrogen interventions as a key to better health and robust ecosystems
2024-08-16
The Earth’s nitrogen cycle is among the most heavily exceeded planetary boundaries. Agricultural production and fossil fuel burning release nitrogen pollutants like ammonia (NH3), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which contribute to air pollution and damage ecosystems. These pollutants harm human health, crops, and ecosystems. Given the growing global energy and food demand, this damage is expected to increase even further.
The potential of nitrogen pollution mitigation technologies ...
Knocking out one key gene leads to autistic traits
2024-08-16
More than 70 genes have been linked to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a developmental condition in which differences in the brain lead to a host of altered behaviors, including issues with language, social communication, hyperactivity, and repetitive movements. Scientists are attempting to tease out those specific associations gene by gene, neuron by neuron.
One such gene is Astrotactin 2 (ASTN2). In 2018, researchers from the Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology at Rockefeller University discovered how defects in the protein produced by the gene disrupted ...
What does the EU's recent AI Act mean in practice?
2024-08-16
The European Union's law on artificial intelligence came into force on 1 August. The new AI Act essentially regulates what artificial intelligence can and cannot do in the EU. A team led by computer science professor Holger Hermanns from Saarland University and law professor Anne Lauber-Rönsberg from Dresden University of Technology has examined how the new legislation impacts the practical work of programmers. The results of their analysis will be published in the autumn.
'The AI Act shows ...
A visionary approach: How an Argonne team developed accessible maps for colorblind scientists
2024-08-16
Imagine having to do your job, but not being able to visually process the data right in front of you. Nearly eight percent of genetic males and half a percent of genetic females have some form of Color Vision Deficiency (CVD), or the decreased ability to discern between particular colors. CVD is commonly referred to as color blindness.
Scientists use colors to convey information. Many scientists in the weather radar community have CVD and the use and interpretation of color is an important aspect of their work. Most colormaps ...
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures
2024-08-16
A new scientific review explores the exciting potential of hot carriers, energetic electrons generated by light in plasmonic nanostructures. These tiny structures hold immense promise for future technologies due to their unique way of interacting with light and creating hot carriers.
Hot carriers are electrons with a surplus of energy. When light strikes a plasmonic nanostructure, it can excite these electrons, pushing them out of equilibrium. This non-equilibrium state unlocks a range of fascinating phenomena. Hot carriers can be used to control light itself, potentially leading to ...
New research shows agricultural impacts on soil microbiome and fungal communities
2024-08-16
New research from Smithsonian’s Bird Friendly Coffee program highlights a type of biodiversity that often gets overlooked: soil bacteria and fungal communities. For over twenty years, Smithsonian research has shown that coffee farms with shade trees protect more biodiversity than intensified, monoculture coffee farms. The new research, published today in Applied Soil Ecology, shows that soil bacteria and fungi on coffee farms also respond to the intensity of coffee farm management. To conduct this research, the team collected soils samples on coffee farms in Colombia, El Salvador, and Peru and used DNA analysis to profile bacterial and fungal soil on ...
Tracking down the asteroid that sealed the fate of the dinosaurs
2024-08-16
Geoscientists from the University of Cologne have led an international study to determine the origin of the huge piece of rock that hit the Earth around 66 million years ago and permanently changed the climate. The scientists analysed samples of the rock layer that marks the boundary between the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods. This period also saw the last major mass extinction event on Earth, in which around 70 percent of all animal species became extinct. The results of the study published in Science indicate that the asteroid formed outside Jupiter’s orbit during the ...
IOP Publishing hosts Progress In Physics 2024 – a two-day hybrid conference focused on condensed matter physics
2024-08-16
The Institute of Physics and IOP Publishing (IOPP) are launching Progress In Physics 2024, a two-day hybrid workshop hosted at the Institute of Physics’ office in London from 9-10 October 2024. The event will cover topics on condensed matter and will bring together leading physics researchers to exchange knowledge in both an in-person and online format.
Progress in Physics 2024 aligns with the mission of IOPP’s new Progress In seriesTM of journals. The series builds on the success of IOPP’s flagship journal Reports on Progress in PhysicsTM which celebrates its 90th anniversary this year.
With ...
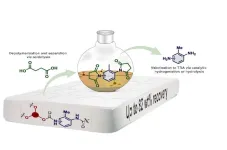
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
2024-08-16
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
Researchers at Aarhus University have found a better method to recycle polyurethane foam from items like mattresses. This is great news for the budding industry that aims to chemically recover the original components of the material – making their products cheaper and better.
Polyurethane (PUR) is an indispensable plastic material used in mattresses, insulation in refrigerators and buildings, shoes, cars, airplanes, wind turbine blades, cables, and much more. It could be called a wonder material if it weren’t also an environmental ...
Right on schedule: Physicists use modeling to forecast a black hole's feeding patterns with precision
2024-08-16
Powerful telescopes like NASA’s Hubble, James Webb, and Chandra X-ray Observatory provide scientists a window into deep space to probe the physics of black holes. While one might wonder how you can “see” a black hole, which famously absorbs all light, this is made possible by tidal disruption events (TDEs) - where a star is destroyed by a supermassive black hole and can fuel a “luminous accretion flare.” With luminosities thousands of billions of times brighter than the Sun, accretion events enable astrophysicists to study supermassive black holes (SMBHs) at cosmological distances.
TDEs occur when a star is violently ripped ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Rare diseases point to connections between metabolism and immunityOverlap in genes suggests a potential new class of inborn errors of immunometabolism