(Press-News.org) James Tour’s lab at Rice University has developed a new method known as flash-within-flash Joule heating (FWF) that could transform the synthesis of high-quality solid-state materials, offering a cleaner, faster and more sustainable manufacturing process. The findings were published in Nature Chemistry on Aug. 8.
Traditionally, synthesizing solid-state materials has been a time-consuming and energy-intensive process, often accompanied by the production of harmful byproducts. But FWF enables gram-scale production of diverse compounds in seconds while reducing energy, water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions by more than 50%, setting a new standard for sustainable manufacturing.
The innovative research builds on Tour’s 2020 development of waste disposal and upcycling applications using flash Joule heating, a technique that passes a current through a moderately resistive material to quickly heat it to over 3,000 degrees Celsius (over 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit) and transform it into other substances.
“The key is that formerly we were flashing carbon and a few other compounds that could be conductive,” said Tour, the T.T. and W.F. Chao Professor of Chemistry and professor of materials science and nanoengineering. “Now we can flash synthesize the rest of the periodic table. It is a big advance.”
FWF’s success lies in its ability to overcome the conductivity limitations of conventional flash Joule heating methods. The team — including Ph.D. student Chi Hun “Will” Choi and corresponding author Yimo Han , assistant professor of chemistry, materials science and nanoengineering — incorporated an outer flash heating vessel filled with metallurgical coke and a semiclosed inner reactor containing the target reagents. FWF generates intense heat of about 2,000 degrees Celsius, which rapidly converts the reagents into high-quality materials through heat conduction.
This novel approach allows for the synthesis of more than 20 unique, phase-selective materials with high purity and consistency, according to the study. FWF’s versatility and scalability is ideal for the production of next-generation semiconductor materials such as molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2), tungsten diselenide and alpha phase indium selenide, which are notoriously difficult to synthesize using conventional techniques.
“Unlike traditional methods, FWF does not require the addition of conductive agents, reducing the formation of impurities and byproducts,” Choi said.
This advancement creates new opportunities in electronics, catalysis, energy and fundamental research. It also offers a sustainable solution for manufacturing a wide range of materials. Moreover, FWF has the potential to revolutionize industries such as aerospace, where materials like FWF-made MoSe2 demonstrate superior performance as solid-state lubricants.
“FWF represents a transformative shift in material synthesis,” Han said. “By providing a scalable and sustainable method for producing high-quality solid-state materials, it addresses barriers in manufacturing while paving the way for a cleaner and more efficient future.”
This study was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, U.S. Army Corp of Engineers, and Welch Foundation.
END
New twist on synthesis technique developed at Rice promises sustainable manufacturing
2024-08-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rare diseases point to connections between metabolism and immunity
2024-08-16
Inherited diseases of metabolism and immunity have more in common than previously recognized, according to a new study published in the journal Science Immunology. The findings point to a new set of metabolic genes that are important for the function of immune system T cells, and they offer insights that could improve care for patients with these disorders.
The study examined genes that cause inborn errors of metabolism (disorders of the processes that cells use to convert food to energy) and inborn errors of immunity (disorders that affect immune system function). These rare and complex diseases are not fully understood.
“There had previously ...
Nitrogen interventions as a key to better health and robust ecosystems
2024-08-16
The Earth’s nitrogen cycle is among the most heavily exceeded planetary boundaries. Agricultural production and fossil fuel burning release nitrogen pollutants like ammonia (NH3), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and nitrous oxide (N2O), which contribute to air pollution and damage ecosystems. These pollutants harm human health, crops, and ecosystems. Given the growing global energy and food demand, this damage is expected to increase even further.
The potential of nitrogen pollution mitigation technologies ...
Knocking out one key gene leads to autistic traits
2024-08-16
More than 70 genes have been linked to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), a developmental condition in which differences in the brain lead to a host of altered behaviors, including issues with language, social communication, hyperactivity, and repetitive movements. Scientists are attempting to tease out those specific associations gene by gene, neuron by neuron.
One such gene is Astrotactin 2 (ASTN2). In 2018, researchers from the Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology at Rockefeller University discovered how defects in the protein produced by the gene disrupted ...
What does the EU's recent AI Act mean in practice?
2024-08-16
The European Union's law on artificial intelligence came into force on 1 August. The new AI Act essentially regulates what artificial intelligence can and cannot do in the EU. A team led by computer science professor Holger Hermanns from Saarland University and law professor Anne Lauber-Rönsberg from Dresden University of Technology has examined how the new legislation impacts the practical work of programmers. The results of their analysis will be published in the autumn.
'The AI Act shows ...
A visionary approach: How an Argonne team developed accessible maps for colorblind scientists
2024-08-16
Imagine having to do your job, but not being able to visually process the data right in front of you. Nearly eight percent of genetic males and half a percent of genetic females have some form of Color Vision Deficiency (CVD), or the decreased ability to discern between particular colors. CVD is commonly referred to as color blindness.
Scientists use colors to convey information. Many scientists in the weather radar community have CVD and the use and interpretation of color is an important aspect of their work. Most colormaps ...
Unveiling the power of hot carriers in plasmonic nanostructures
2024-08-16
A new scientific review explores the exciting potential of hot carriers, energetic electrons generated by light in plasmonic nanostructures. These tiny structures hold immense promise for future technologies due to their unique way of interacting with light and creating hot carriers.
Hot carriers are electrons with a surplus of energy. When light strikes a plasmonic nanostructure, it can excite these electrons, pushing them out of equilibrium. This non-equilibrium state unlocks a range of fascinating phenomena. Hot carriers can be used to control light itself, potentially leading to ...
New research shows agricultural impacts on soil microbiome and fungal communities
2024-08-16
New research from Smithsonian’s Bird Friendly Coffee program highlights a type of biodiversity that often gets overlooked: soil bacteria and fungal communities. For over twenty years, Smithsonian research has shown that coffee farms with shade trees protect more biodiversity than intensified, monoculture coffee farms. The new research, published today in Applied Soil Ecology, shows that soil bacteria and fungi on coffee farms also respond to the intensity of coffee farm management. To conduct this research, the team collected soils samples on coffee farms in Colombia, El Salvador, and Peru and used DNA analysis to profile bacterial and fungal soil on ...
Tracking down the asteroid that sealed the fate of the dinosaurs
2024-08-16
Geoscientists from the University of Cologne have led an international study to determine the origin of the huge piece of rock that hit the Earth around 66 million years ago and permanently changed the climate. The scientists analysed samples of the rock layer that marks the boundary between the Cretaceous and Paleogene periods. This period also saw the last major mass extinction event on Earth, in which around 70 percent of all animal species became extinct. The results of the study published in Science indicate that the asteroid formed outside Jupiter’s orbit during the ...
IOP Publishing hosts Progress In Physics 2024 – a two-day hybrid conference focused on condensed matter physics
2024-08-16
The Institute of Physics and IOP Publishing (IOPP) are launching Progress In Physics 2024, a two-day hybrid workshop hosted at the Institute of Physics’ office in London from 9-10 October 2024. The event will cover topics on condensed matter and will bring together leading physics researchers to exchange knowledge in both an in-person and online format.
Progress in Physics 2024 aligns with the mission of IOPP’s new Progress In seriesTM of journals. The series builds on the success of IOPP’s flagship journal Reports on Progress in PhysicsTM which celebrates its 90th anniversary this year.
With ...
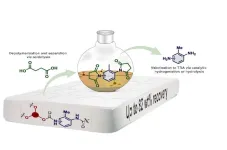
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
2024-08-16
Researchers discover smarter way to recycle polyurethane
Researchers at Aarhus University have found a better method to recycle polyurethane foam from items like mattresses. This is great news for the budding industry that aims to chemically recover the original components of the material – making their products cheaper and better.
Polyurethane (PUR) is an indispensable plastic material used in mattresses, insulation in refrigerators and buildings, shoes, cars, airplanes, wind turbine blades, cables, and much more. It could be called a wonder material if it weren’t also an environmental ...