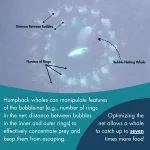
(Press-News.org) In a study published today in Royal Society Open Science, researchers at the Marine Mammal Research Program (MMRP) at UH Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) and Alaska Whale Foundation (AWF) consider a new designation of the humpback whales they study: tool wielders. Researchers have known that humpback whales create “bubble-nets” to hunt, but they have learned that the animals don’t just create the bubble-nets; they manipulate this unique tool in a variety of ways to maximize their food intake in Alaskan feeding grounds. This novel research demystifies a behavior key to the whales’ survival and offers a compelling case for including humpbacks among the rare animals that manufacture and wield their own tools.
“Many animals use tools to help them find food,” explains Professor Lars Bejder, co-lead author of the study and Director of MMRP, “but very few actually create or modify these tools themselves. We discovered that solitary humpback whales in southeast (SE) Alaska craft complex bubble nets to catch krill, which are tiny shrimp-like creatures. These whales skillfully blow bubbles in patterns that form nets with internal rings, actively controlling details like the number of rings, the size and depth of the net, and the spacing between bubbles. This method lets them capture up to seven times more prey in a single feeding dive without using extra energy. This impressive behavior places humpback whales among the rare group of animals that both make and use their own tools for hunting.”
Success in hunting is key for the whalesʻ survival. The population of humpback whales in SE Alaska overwinters in Hawaiʻi, and their energy budget for the entire year depends on their ability to capture enough food during summer and fall in SE Alaska. Unraveling the nuances of their carefully honed hunting technique sheds light on how migratory humpback whales consume enough calories to traverse the Pacific Ocean.
Advanced Tools & Partnerships are Key to Demystifying Whale Behavior
Marine mammals known as cetaceans include whales, dolphins, and porpoises, and they are notoriously difficult to study. Advances in research tools are making it easier to track and understand their behavior, and in this instance, researchers employed specialty tags and drones to study the whalesʻ movements from above and below the water.
“We deployed non-invasive suction-cup tags on whales and flew drones over solitary bubble-netting humpback whales in SE Alaska, collecting data on their underwater movements,” shares co-author and MMRP researcher William Gough. The tools have incredible capability, but honing them takes practice. Gough reflects, “Whales are a difficult group to study, requiring skill and precision to successfully tag and/or drone them.”
The logistics of working in a remote location in SE Alaska brought its own challenges to the research. “We are so grateful to our research partners at the Alaska Whale Foundation (AWF) for their immense knowledge of the local area and the whales in that part of the world,” emphasizes Bejder. “This research would not have been possible without the strong collaborative effort with AWF.”
More Insights and Improved Management to Come
Cetaceans throughout the globe face a slough of threats that range from habitat degradation, climate change, fisheries, to chemical and noise pollution. One quarter of the 92 known cetacean species are at risk of extinction, and there is a clear and urgent need to implement effective conservation strategies on their behalf. How the animals hunt is key to their survival, and understanding this essential behavior makes resource managers better poised to adeptly monitor and conserve the feeding grounds that are critical to their survival.
“This little-studied foraging behavior is wholly unique to humpback whales,” notes Gough. “It’s so incredible to see these animals in their natural habitat, performing behaviors that only a few people ever get to see. And it’s rewarding to be able to come back to the lab, dive into the data, and learn about what they’re doing underwater once they disappear from view.”
With powerful new tools in researchersʻ hands, many more exciting cetacean behavioral discoveries lie on the horizon. “This is a rich dataset that will allow us to learn even more about the physics and energetics of solitary bubble-netting,” shares Bejder. “There is also data coming in from humpback whales performing other feeding behaviors, such as cooperative bubble-netting, surface feeding, and deep lunge feeding, allowing for further exploration of this population’s energetic landscape and fitness.”
“What I find exciting is that humpbacks have come up with complex tools allowing them to exploit prey aggregations that otherwise would be unavailable to them,” says Dr. Andy Szabo, AWF Executive Director and study co-lead. “It is this behavioral flexibility and ingenuity that I hope will serve these whales well as our oceans continue to change.”
This groundbreaking work was made possible with support from Lindblad Expeditions - National Geographic Fund, the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa, and a Department of Defense (DOD) Defense University Research Instrumentation Program (DURIP) grant.
This study was conducted under a NOAA permit issued to Alaska Whale Foundation (no. 19703). All research was conducted under institution IACUC approvals.
END
Humpbacks are among animals who manufacture and wield tools
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTA federal research expenditures doubled in 2023
2024-08-20
In 2023, federally sponsored research at The University of Texas at Arlington accounted for $77 million in expenditures, with about $40.7 million spent on research-related goods and services in Texas. That more than doubles the total for 2022, when federally sponsored research at UTA contributed $38 million to the economy.
The $77 million is a portion of UTA’s $122 million in total research expenditures from all sources last year. This number includes federally sponsored research awards as well as those from local and state governments, private institutions, and other sources. Overall, UT Arlington and its 270,000 alumni contribute $29 billion ...
Researchers teaching artificial intelligence about frustration in protein folding
2024-08-20
Scientists have found a new way to predict how proteins change their shape when they function, which is important for understanding how they work in living systems. While recent artificial intelligence (AI) technology has made it possible to predict what proteins look like in their resting state, figuring out how they move is still challenging because there is not enough direct data from experiments on protein motions to train the neural networks.
In a new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on Aug.20, ...
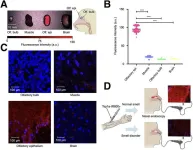
Novel molecular imaging tool objectively measures and diagnoses smell disorders
2024-08-20
Reston, VA (August 20, 2024) -- A new fluorescent imaging probe can for the first time objectively and non-invasively measure loss of smell, clinically known as anosmia. Targeting the olfactory nerve, the new tool has potential to eliminate biopsies used to diagnose certain anosmia conditions and to aid in the development of therapeutic interventions. This research was published in the August issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Research shows that an estimated 13.3 million adults in the United States have a vast range of smell disorders and that ...
Tiny killers: How autoantibodies attack the heart in lupus patients
2024-08-20
New York, NY—August 20, 2024—Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in patients suffering from lupus, an autoimmune disease in which our immune system attacks our own tissues and organs, the heart, blood, lung, joints, brain, and skin. Lupus myocarditis--inflammation of the heart muscle-- can be very serious because the inflammation alters the regularity of the rhythm and strength of the heartbeat. However, the mechanisms underlying this complex disease are poorly understood and difficult to study.
A long-standing question about lupus is why some patients develop myocarditis while others remain unaffected. And why the clinical manifestations of affected ...
Study: Temporarily removing firearms from people at risk of harm saves lives
2024-08-20
DURHAM, N.C. – An estimated one life was saved for every 17 times an extreme risk protection order removed guns from people who presented a risk of harming themselves or others, according to a Duke Health-led analysis of the laws in four states.
Extreme risk protection orders -- known as ERPOs or “red flag laws" -- are civil court orders that temporarily prevent people from accessing firearms after a judge determines that they pose an imminent risk of harming themselves or others. Twenty-one states and the District of Columbia have enacted ERPO laws, mostly in ...
Study finds Americans want pandemic-era ease of applying for Medicaid
2024-08-20
More than 23 million Americans who were granted Medicaid coverage during the COVID-19 pandemic lost their coverage starting in March 2023 after the pandemic was declared no longer a public health emergency. Many likely will not successfully re-enroll on their own given Medicaid’s administrative burden—the frustrations and challenges people often encounter in seeking or complying with coverage.
Now, a study of the so-called Medicaid Great Unwinding by Dr. Simon F. Haeder with the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, ...
It only takes 15 minutes to change your health
2024-08-20
Corporate Cup, lunchtime yoga, or even ‘walk and talks’, organisations come up with all sorts of wellness initiatives to encourage people to be more active in the workplace. But before you duck and hide, new research shows that all it takes is 15 minutes and a touch of gamification to put you on the path to success.
Assessing results from 11,575 participants, across 73 Australian, New Zealand, and UK companies, University of South Australia researchers found that a gamified workplace wellness program – the 15 Minute Challenge* - leads to substantial increases in physical activity levels, with 95% of participants meeting (36%) or exceeding (59%) ...
Nadia Drake joins SETI Institute Board of Directors as observer
2024-08-20
August 20, 2024, Mountain View, CA –The SETI Institute announced that Dr. Nadia Drake is joining the SETI Institute's Board of Directors as an observer. The SETI Institute's board guides its strategic direction, finances, and various committees. As a journalist, Drake will be an active, non-voting member, bringing her broad expertise to the team.
"I am thrilled by this appointment to the SETI Institute's board, which comes at an exciting time for the SETI Institute and for the search for life beyond Earth," said Drake. "For most of my career as a science journalist, I've covered astrobiology ...
Organized youth sports are increasingly for the privileged
2024-08-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A sweeping study of U.S. youth sports participation over the past 60 years found that there has been a significant increase over time in kids playing organized sports – but particularly among more privileged, educated families.
A national survey found that about 70% of Americans born in the ’90s and reaching age 18 by 2015-16 said they took part in organized sports through recreational, school, or club teams. This finding showed a rather steady increase in organized sports participation across generations. Slightly more than half of those ...
UCF researcher develops lotus-inspired tech to convert CO2 to fuels, chemicals
2024-08-20
Video available here.
In an effort to reduce the environmental impact of carbon dioxide emissions, a University of Central Florida researcher has developed a new technology that captures carbon dioxide and outputs useful fuels and chemicals.
Yang Yang, an associate professor in UCF’s NanoScience Technology Center, created an innovative device that captures carbon dioxide with a microsurface comprised of a tin oxide film and fluorine layer. The device then extracts gaseous carbon dioxide via a bubbling electrode and selectively converts ...