(Press-News.org) The kids were correct all along.
In the most comprehensive national study since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, a team of researchers that includes a Rutgers-organized consortium of pediatric sites has concluded that long COVID symptoms in children are tangible, pervasive, wide ranging and clinically distinct within specific age groups.
Results of the study, funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), are published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
“We have convincing evidence that COVID-19 is not just a mild, benign illness for children,” said Lawrence C. Kleinman, a professor of pediatrics and population health expert at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School (RWJMS) and the study’s third co-author. “There are children who are clearly disabled by long COVID for long periods of time.”
In the early stages of the pandemic, a myth arose and was perpetuated suggesting that because children often developed only mild cases of COVID-19, the risks for young patients were not serious. But this conjecture dissipated amid a rash of data demonstrating that a few children infected with COVID-19 will get very sick and others will suffer an array of health complications long after initial exposure.
Broadly defined, long COVID includes symptoms, signs, and conditions – such as aches, fatigue, memory loss and stomach pain – that develop, persist or relapse more than a month after a COVID-19 infection. Worldwide, an estimated 65 million people, including children, live with long COVID. Until recently, most research into COVID-19’s lingering effects focused on adults.
To quantify long COVID’s impact on children and determine whether symptoms experienced by the youngest COVID-19 patients differ by age group and from adults, Kleinman and more than 140 researchers throughout the United States crunched data from NIH’s Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery (RECOVER) Initiative, a national effort to survey COVID-19’s long-term impact.
As part of RECOVER, caregivers for 5,367 children (898 school-aged children and 4,469 adolescents) completed online surveys about their children’s health in time for this data analysis. Roughly 86 percent of the sample had previously been infected with COVID-19, while 14 percent – the control group – had not. The survey assessed 74 known and potential long COVID-19 symptoms across nine domains: eyes, ears, nose and throat; heart and lungs; gastrointestinal; dermatologic; musculoskeletal; neurologic; behavioral and psychological; menstrual; and general.
By analyzing the responses, researchers found 45 percent of COVID-19 infected school-age children (ages 6 to 11) reported at least one prolonged symptom after initial recovery versus 33 percent of uninfected children. Thirty-nine percent of COVID-19 infected adolescents (ages 12 to 17) reported one prolonged symptom, compared with 27 percent of uninfected adolescents. These differences implicate the virus as a likely causal factor, rather than just having lived through the pandemic.
Long COVID symptoms in children also were clustered in patterns distinct from adults and from each other. For instance, the most common symptom in adolescents was loss of smell and taste, followed by low energy, muscle aches and fatigue. For school-age children, memory and focus issues topped the list, followed by stomach pain, headaches and back or neck pain.
Children experienced prolonged symptoms after COVID-19 infection “in almost every organ system, with the vast majority having multisystem involvement,” the authors wrote.
By contrast, adults with COVID-19 report 37 symptoms more frequently than those who did not have COVID-19, including post-exertional malaise, brain fog, and gastrointestinal and heart symptoms, among others.
Recruitment for the RECOVER project is partially facilitated by an RWJMS collaboration of 10 national pediatric organizations. The Rutgers Collaborative Long-term study of Outcomes of COVID-19 in Kids (CLOCK), which Kleinman heads as lead investigator, was launched in 2021 and received an NIH grant of more than $30 million the following year. To date, CLOCK has recruited 2,200 children for the pediatric RECOVER study.
While more work is needed to understand long COVID’s symptoms in the youngest patients, and to develop effective treatment protocols, Kleinman said the latest findings leave no doubt that long COVID in children is real.
“Children do get long COVID, and it’s not rare,” he said. “Some children are severely affected; they are not faking it or making it up.
“This is a new chronic illness in children with all the unknowns that brings. We will need to be prepared to deal with it for a generation.”
END
Researchers aim to pull back the curtain on long COVID in kids
Rutgers Health partners in National Institutes of Health effort to characterize long-term effects of the virus on young patients
2024-08-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
RECOVER study determines most common long COVID symptoms in children and teens
2024-08-21
A research team led by the National Institutes of Health’s RECOVER Initiative and supported by its Clinical Science Core (CSC) at NYU Langone Health, has designed a new way to identify which school-age children and adolescents most likely have Long COVID.
Solely for the purpose of further study and not for use in clinical diagnoses, the team’s new measure (index) identifies children and teens with the highest chances of having Long COVID. The research index is based on long-term symptoms ...
UCLA-led study unveils new insights and potential treatments for pulmonary hypertension
2024-08-21
A new study from researchers with UCLA Health and collaborating organizations has found that asporin, a protein encoded by the ASPN gene, plays a protective role in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
Their findings, published on August 21 in the peer-reviewed journal Circulation, offer new insights into this incurable, often-fatal disease and suggest potential new ways to treat it.
“We were surprised to find that asporin, which previously had not been linked to PAH, gets upregulated to increased levels as a response to ...
MD Anderson research highlights for August 21, 2024
2024-08-21
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Targeting an enzyme as part of combination therapy disrupts gastric cancer progression
Many patients with gastric cancer have metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis, ...
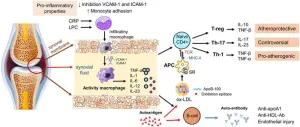
Proatherogenic disorders of blood lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
2024-08-21
In the realm of chronic inflammation, lipid abnormalities are well-recognized as pivotal contributors to the progression and clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis. Particularly in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a systemic autoimmune disorder, the immune response leads to the generation of inflammatory cytokines that profoundly alter lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. This review article delves into the latest research exploring the impact of inflammation on proatherogenic disorders of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in RA patients, with a focus on proinflammatory cytokines.
Role of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Lipid and Lipoprotein Dysregulation
Inflammatory ...
Pioneering study shows effective regulation and monitoring is key to tackling emissions of a super-greenhouse gas
2024-08-21
New research has revealed factories globally are not properly destroying one of the most potent greenhouse gases emitted from the production of fluoropolymers like Teflon, and refrigerants.
The study investigated a known disparity between real and reported emissions of this gas, prompting calls for more countries to sign up to official agreements to limit emissions and for their Teflon factories to be independently audited to ensure compliance.
The study, published today in the journal Nature, scrutinised emissions of one of the most potent hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) greenhouse gases called trifluoromethane, also ...
Inflammation during childhood linked to onset of mental health issues in early adulthood – study reveals
2024-08-21
Children who have persistently raised inflammation are at a higher risk of experiencing serious mental health disorders including psychosis and depression in early adulthood, according to a study published today in JAMA Psychiatry.
The research lead by the University of Birmingham also found that those who had experienced inflammation at a young age were at a higher risk of developing cardiometabolic diseases such as insulin resistance - an early form of diabetes.
The study used data collected by the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) – also known as Children of the 90s – and included a total of 6,556 participants of whom 50.4% ...
Study finds sex-based disparities in outcomes after cardiac surgery
2024-08-21
Mass General Brigham researchers found that women had a lower risk of developing postoperative atrial fibrillation after surgery compared to men, but a higher risk of long-term mortality
New research suggests that women who develop postoperative atrial fibrillation (poAF) after cardiac surgery are at greater risk of death than men. A study led by Mass General Brigham researchers found that women may have protective factors against the development of poAF, but once it develops, they may be more vulnerable to its associated long-term morbidities. The researchers suggest that more vigilant monitoring and long-term ...
Study of 18 million people finds increased mental illnesses incidence following severe COVID-19, especially in unvaccinated people
2024-08-21
A new study that examined health data on 18 million people reveals higher incidence of mental illnesses for up to a year following severe COVID-19 in unvaccinated people. Vaccination appeared to mitigate the adverse effects of COVID-19 on mental illnesses. The University of Bristol-led study, published in JAMA Psychiatry today [21 August], investigated associations of COVID-19 with mental illnesses according to time since diagnosis and vaccination status.
COVID-19 is associated with mental illnesses in both hospital and population-based studies. However, until now, there was limited evidence about the association of COVID-19 with ...
Nearly 90 percent of NYC transit workers have been harassed or assaulted
2024-08-21
The COVID-19 pandemic brought an increase in crime to New York City’s subways and buses. The transit system’s employees—especially female workers—have frequently been on the receiving end of attacks, according to a new study published in the Journal of Urban Health.
The study, led by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health, found that 89 percent of public-facing transit workers in New York City experienced harassment or violence on the job during the pandemic (2020-2023).
“Transit workers are our city’s unsung heroes—they kept New York City functioning during the COVID-19 pandemic, ...
COVID-19 and mental illnesses in vaccinated and unvaccinated people
2024-08-21
About The Study: In this cohort study, depression, serious mental illness, general anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, eating disorders, addiction, self-harm, and suicide were elevated during weeks 1 through 4 after COVID-19 diagnosis compared with before or without COVID-19. Incidence was lower in people who were vaccinated when they had COVID-19 and incidence was higher, and persisted longer, after hospitalization for COVID-19. The findings support recommendation of COVID-19 vaccination in the general population and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Researchers aim to pull back the curtain on long COVID in kidsRutgers Health partners in National Institutes of Health effort to characterize long-term effects of the virus on young patients