(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. - Ensuring that scientific funding goes to states and territories that have typically received smaller fractions of federal research dollars in the past, the Department of Energy (DOE) today announced $36 million in funding for 39 research projects in 19 states via the Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR). The grants connect innovative ideas from scientists at eligible institutions with leading-edge capabilities at the DOE national laboratories.
Supporting scientists while building the expertise and capabilities critical for performing leading research in areas of high importance for the country is a top priority. This program advances both scientific knowledge and the geographic diversity of researchers conducting competitive energy-relevant research.
“Making sure that scientific funding benefits and delivers results to the entire country in a more equitable fashion is a top priority for DOE,” said Harriet Kung, Acting Director of the DOE Office of Science. “The EPSCoR program is an important component of the effort to ensure that all regions of the country can perform competitive and impactful energy-relevant research. These projects will enhance the scientific expertise and capabilities at the EPSCoR institutions and strengthen their connections to the unique capabilities and expertise at the DOE national laboratories.”
The new projects span a wide range of energy research topics, including fundamental work in chemistry and materials science for clean energy, fusion energy, advanced computing, biological and environmental research, high energy and nuclear physics, as well as early-stage R&D for advanced manufacturing, solar energy, vehicles, wind, nuclear power, and carbon management.
Projects were chosen by competitive peer review under a DOE Funding Opportunity Announcement for Building EPSCoR-State/National Laboratory Partnerships. Each project is funded for four years.
The EPSCoR program is managed by the Department’s Office of Science through its Office of Basic Energy Sciences (BES).
The list of awards and more information can be found at science.osti.gov/funding-opportunities/award.
Selection for award negotiations is not a commitment by DOE to issue an award or provide funding. Before funding is issued, DOE and the applicants will undergo a negotiation process, and DOE may cancel negotiations and rescind the selection for any reason during that time.
END
Department of Energy announces $36 million to support energy-relevant research in underrepresented regions of America
Projects support partnerships with DOE national laboratories to perform early-stage, fundamental energy research and scientific workforce development
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Analysis of 1,500 climate policies reveals only a small fraction achieved significant emission reductions
2024-08-22
A new machine learning analysis has revealed the most effective climate policies out of 1,500 implemented worldwide over the last two decades. Some of the success stories – numbered at about 63 – involve rarely studied policies and unappreciated policy combinations. “Our results provide a clear yet sobering perspective on the policy effort necessary for closing the remaining emissions gap of 23 billion tons carbon dioxide (CO2) by 2023,” write the authors. To achieve the Paris Agreement’s climate targets, it is essential to know which ...
Fatty-acid derived polymers yield recyclable and highly versatile adhesives
2024-08-22
Researchers have presented a new family of polymer adhesives that offer a sustainable and recyclable alternative to conventional polymer adhesives and can be used across a wide range of applications, from industrial adhesives to surgical superglues. The new chemical approach to aLA polymerization addresses the performance and environmental challenges of traditional polymers, providing environmentally friendly adhesive solutions. Polymer adhesives are ubiquitous in modern life and are widely used in many medical, consumer, and industrial products. Given this diversity, each adhesive material is often tailored ...
Governance needed to ensure biosecurity of biological AI models
2024-08-22
Concerns over the biosecurity risks posed by artificial intelligence (AI) models in biology continue to grow. Amid this concern, Doni Bloomfield and colleagues argue, in a Policy Forum, for improved governance and pre-release safety evaluations of new models in order to mitigate potential threats. “We propose that national governments, including the United States, pass legislation and set mandatory rules that will prevent advanced biological models from substantially contributing to large-scale dangers, such as the creation of novel or enhanced pathogens ...
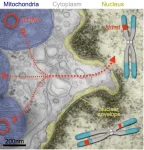
Spontaneous transfer of mitochondrial DNA into the nuclear genomes in the human brain over the individual’s lifespan
2024-08-22
Somatic nuclear mitochondrial DNA (Numt) insertions are mito-nuclear gene transfer events that can arise in the germline and in cancer. This study shows that Numt insertions arise spontaneously and accumulate in brain tissues during development or over the human lifespan.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002723
Article Title: Somatic nuclear mitochondrial DNA insertions are prevalent in the human brain and accumulate over time in fibroblasts
Author Countries: United States
Funding: see manuscript END ...
Cancer drug could treat early-stage Alzheimer’s disease, study shows
2024-08-22
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A type of drug developed for treating cancer holds promise as a new treatment for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s, according to a recent study by researchers at Penn State, Stanford University and an international team of collaborators.
The researchers discovered that by blocking a specific enzyme called indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1, or IDO1 for short, they could rescue memory and brain function in models that mimic Alzheimer’s disease. The findings, published today (Aug. 22) in the journal Science, suggest that IDO1 inhibitors currently ...
Drugs that improve brain metabolism could help Alzheimer’s patients
2024-08-22
Among the many ways neuroscientists think Alzheimer’s disease may strip away brain function is by disrupting the glucose metabolism needed to fuel the healthy brain. In essence, declining metabolism robs the brain of energy, impairing thinking and memory.
Against that backdrop, a team of neuroscientists at the Knight Initiative for Brain Resilience at Stanford’s Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute have zeroed in on a critical regulator of brain metabolism known as the kynurenine pathway. They hypothesize that that the kynurenine pathway is overactivated as a result of ...
Life after (feigned) death
2024-08-22
A new study led by scientists from the University of Bristol has revealed what animals do after they have feigned death in order to avoid being killed by a predator and what the context of this behaviour is.
Many animals, as a last-ditch defence, become motionless after being contacted by a predator.
This behaviour is so common that it's recognised in such phrases as “playing possum”. It is even said to occur in humans in extreme circumstances.
In previous studies, carried out by the same team using antlion larvae, scientists noticed that they become motionless after being individually handled.
At one point ...
Fisheries research overestimates fish stocks
2024-08-22
Many fish stocks around the world are either threatened by overfishing or have already collapsed. One of the main reasons for this devastating trend is that policymakers have often ignored the catch limits calculated by scientists, which were intended to be strict thresholds to protect stocks. But it has now become clear that even these scientific recommendations were often too high.
In the European Union (EU), for example, fisheries are primarily managed through allowable catch limits, known as quotas, which are set by the European ...
AI tackles one of the most difficult challenges in quantum chemistry
2024-08-22
New research using neural networks, a form of brain-inspired AI, proposes a solution to the tough challenge of modelling the states of molecules.
The research shows how the technique can help solve fundamental equations in complex molecular systems.
This could lead to practical uses in the future, helping researchers to prototype new materials and chemical syntheses using computer simulation before trying to make them in the lab.
Led by Imperial College London and Google DeepMind scientists, the study is published today in Science.
Excited molecules
The team investigated the problem of understanding ...
Mitochondria are flinging their DNA into our brain cells
2024-08-22
NEW YORK, NY (Aug. 22, 2024)--As direct descendants of ancient bacteria, mitochondria have always been a little alien.
Now a study shows that mitochondria are possibly even stranger than we thought.
Mitochondria in our brain cells frequently fling their DNA into the nucleus, the study found, where the DNA becomes integrated into the cells’ chromosomes. And these insertions may be causing harm: Among the study’s nearly 1,200 participants, those with more mitochondrial DNA insertions in their brain cells ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Department of Energy announces $36 million to support energy-relevant research in underrepresented regions of AmericaProjects support partnerships with DOE national laboratories to perform early-stage, fundamental energy research and scientific workforce development