(Press-News.org) New research using neural networks, a form of brain-inspired AI, proposes a solution to the tough challenge of modelling the states of molecules.
The research shows how the technique can help solve fundamental equations in complex molecular systems.
This could lead to practical uses in the future, helping researchers to prototype new materials and chemical syntheses using computer simulation before trying to make them in the lab.
Led by Imperial College London and Google DeepMind scientists, the study is published today in Science.
Excited molecules
The team investigated the problem of understanding how molecules transition to and from ‘excited states’. When molecules and materials are stimulated by a large amount of energy, such as being exposed to light or high temperatures, their electrons can get kicked into a temporary new configuration, known as an excited state.
The exact amount of energy absorbed and released as molecules transition between states creates a unique fingerprint for different molecules and materials. This affects the performance of technologies ranging from solar panels and LEDs to semiconductors and photocatalysts. They also play a critical role in biological processes involving light, including photosynthesis and vision.
However, this fingerprint is extremely difficult to model because the excited electrons are quantum in nature, meaning their positions within the molecules are never certain, and can only be expressed as probabilities.
Lead researcher Dr David Pfau, from Google DeepMind and the Department of Physics at Imperial, said: “Representing the state of a quantum system is extremely challenging. A probability has to be assigned to every possible configuration of electron positions.
“The space of all possible configurations is enormous — if you tried to represent it as a grid with 100 points along each dimension, then the number of possible electron configurations for the silicon atom would be larger than the number of atoms in the universe. This is exactly where we thought deep neural networks could help.”
Neural networks
The researchers developed a new mathematical approach and used it with a neural network called FermiNet (Fermionic Neural Network), which was the first example where deep learning was used to compute the energy of atoms and molecules from fundamental principles that was accurate enough to be useful.
The team tested their approach with a range of examples, with promising results. On a small but complex molecule called the carbon dimer, they achieved a mean absolute error (MAE) of 4 meV (millielectronvolt – a tiny measure of energy), which is five times closer to experimental results than prior gold standard methods reaching 20 meV.
Dr Pfau said: “We tested our method on some of the most challenging systems in computational chemistry, where two electrons are excited simultaneously, and found we were within around 0.1 eV of the most demanding, complex calculations done to date.
“Today, we’re making our latest work open source, and hope the research community will build upon our methods to explore the unexpected ways matter interacts with light.”
END
AI tackles one of the most difficult challenges in quantum chemistry
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
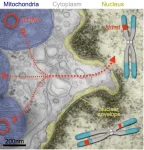
Mitochondria are flinging their DNA into our brain cells
2024-08-22
NEW YORK, NY (Aug. 22, 2024)--As direct descendants of ancient bacteria, mitochondria have always been a little alien.
Now a study shows that mitochondria are possibly even stranger than we thought.
Mitochondria in our brain cells frequently fling their DNA into the nucleus, the study found, where the DNA becomes integrated into the cells’ chromosomes. And these insertions may be causing harm: Among the study’s nearly 1,200 participants, those with more mitochondrial DNA insertions in their brain cells ...
Revealing DNA behavior in record time
2024-08-22
“DNA, RNA and proteins are the key players to regulate all processes in the cells of our body,” Leiden Professor John van Noort explains. “To understand the (mis-)functioning of these molecules, it is essential to uncover how their 3D structure depends on their sequence and for this it is necessary to measure them one molecule at a time. However, single-molecule measurements are laborious and slow, and the number of possible sequence variations is massive.”
From decades to days
Now the team of scientists developed an innovative tool, called SPARXS (Single-molecule Parallel Analysis for Rapid eXploration ...
Columbia receives $400 million gift for biomedical research
2024-08-22
NEW YORK, NY (Aug. 22, 2024)--Columbia University announced today a new $400 million gift from Roy and Diana Vagelos, which will secure Columbia’s leadership in biomedical science research and education and produce a vast array of compelling opportunities for improving society’s health and wellbeing. The gift is the single largest ever made to Columbia’s medical school and, taken together with their previous giving, establishes Roy and Diana as the most generous donors in the history of Columbia University.
A ...
Air pollution harms mental health worse in New York’s historically redlined neighborhoods
2024-08-22
BUFFALO, N.Y. — Air pollution is bad for mental health. That much is clear. Now, new research shows the impact may be even worse in neighborhoods that were historically redlined.
University at Buffalo researchers looked at 17 cities across New York State where longstanding federal housing policies once denied neighborhoods with people of color from receiving mortgages. Although this practice was outlawed in 1968, the researchers found that elevated levels of air pollutants in these neighborhoods of the state ...
Meteor showers shed light on where comets formed in the early solar system
2024-08-22
An international team of 45 researchers studying meteor showers has found that not all comets crumble the same way when they approach the Sun. In a paper published in the journal Icarus this week, they ascribe the differences to the conditions in the protoplanetary disk where comets formed 4.5 billion years ago.
“The meteoroids we see as meteors in the night sky are the size of small pebbles,” said lead author and SETI Institute and NASA Ames meteor astronomer Peter Jenniskens. “They are, in fact, the same size as the pebbles that collapsed into comets during the formation of ...
ChatGPT shows promise in answering patients' questions to urologists
2024-08-22
August 22, 2024 — The groundbreaking ChatGPT chatbot shows potential as a time-saving tool for responding to patient questions sent to the urologist's office, suggests a study in the September issue of Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The artificial intelligence (AI) tool generated "acceptable" responses to nearly one-half of a sample of real-life patient questions, according to the new research ...
T cells manipulate the memory of innate immune cells
2024-08-22
Research from Radboud university medical center reveals that T cells from the adaptive immune system can manipulate the memory of innate immune cells. Previously, it was believed that the memory of innate immune cells operated independently. This surprising connection opens up new possibilities for the treatment of various diseases. A mouse model shows that no immunosuppressive drugs are needed after an organ transplantation if this interaction between T cells and the innate immunity is temporarily blocked after the transplantation.
The adaptive immune ...
Immune cells have a metabolic backup plan for accessing their anti-cancer playbook
2024-08-22
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Aug. 22, 2024) — Immune cells use two different routes to produce acetyl-CoA, an essential metabolite required to fight infection and cancer, reports a study led by Van Andel Institute scientists.
The findings, published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, could help improve immunotherapies by revealing how diet can boost immune cell function.
“Like any good system, immune cells have a plan A and a plan B,” said Russell Jones, Ph.D., the study’s corresponding author and chair of VAI’s Department of Metabolism and Nutritional ...
A 3D ion Magnet, the new experimental frontier for quantum information processing
2024-08-22
Many quantum devices, from quantum sensors to quantum computers, use ions or charged atoms trapped with electric and magnetic fields as a hardware platform to process information.
However, current trapped-ion systems face important challenges. Most experiments are limited to one-dimensional chains or two-dimensional planes of ions, which constrain the scalability and functionality of quantum devices. Scientists have long dreamed of stacking these ions into three-dimensional structures, but this has been very difficult ...
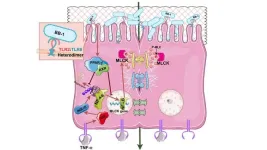
A potential pathway may guide new therapies for inflammatory bowel disease and other inflammatory diseases
2024-08-22
Philadelphia, August 22, 2024 – There is a critical unmet need to help tighten and maintain a healthy intestinal barrier and treat a leaky gut. Researchers have now found that a unique strain of probiotic bacteria, Bifidobacterium bifidum BB1, enhances intestinal barrier function and protects against penetration of bacteria and various harmful agents in the intestine. The findings, detailed in an article in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, can help advance the development of novel, targeted, naturally occurring probiotic therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other inflammatory diseases, such as fatty liver disease or alcoholic liver ...