(Press-News.org) Research from Radboud university medical center reveals that T cells from the adaptive immune system can manipulate the memory of innate immune cells. Previously, it was believed that the memory of innate immune cells operated independently. This surprising connection opens up new possibilities for the treatment of various diseases. A mouse model shows that no immunosuppressive drugs are needed after an organ transplantation if this interaction between T cells and the innate immunity is temporarily blocked after the transplantation.
The adaptive immune system develops through infections that people experience. This immune response is slow to develop, highly specific against pathogens, and uses memory cells. In addition, there is the innate immune system, which responds much faster to invaders and serves as a first line of defense. About ten years ago, it was discovered that the cells of the innate system also have memory, allowing them to respond stronger and faster to repeated infections. This is called trained immunity.
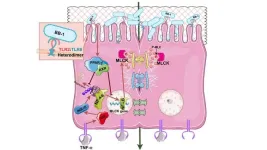
Until now, trained immunity was thought to be an independent process of innate immune cells. However, research from an international team led by Raphaël Duivenvoorden and researcher Maaike Jacobs from Radboudumc has now revealed that T cells from the adaptive immune system play a crucial role in regulating trained immunity. They discovered that this occurs through direct contact between cells via the CD40 molecule.
Transplantation
This finding offers new possibilities for the treatment of various conditions where trained immunity plays a role, such as autoimmune disorders, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and organ transplantation. The researchers demonstrated in a mouse model that a transplanted heart is accepted by the recipient for a long time when the interaction between T cells and the innate immune system is briefly blocked after the transplantation.
In this model, the researchers used nanoparticles with drugs incorporated that inhibit the CD40 signal. They combined three injections of these nanoparticles with a single injection of the existing drug CTLA4-Ig during the first week after the heart transplantation. This led to long-term acceptance of the transplanted heart, with no further need for other immunosuppressive drugs.
Memory
The fact that the innate immune system has memory is vital for the body's defense. However, sometimes the innate immune system is overactive, such as in autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and during organ transplants, and this memory can have harmful effects. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind this memory is therefore essential for developing new treatments.
This research shows that manipulating the memory of the innate immune system has potential as a new therapeutic strategy in organ transplantation. Duivenvoorden concludes: ‘In the coming years, we will continue this research with the aim of making this treatment strategy possible in humans.’
END
T cells manipulate the memory of innate immune cells
Remarkable finding offers potential for organ transplantation
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Immune cells have a metabolic backup plan for accessing their anti-cancer playbook
2024-08-22
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Aug. 22, 2024) — Immune cells use two different routes to produce acetyl-CoA, an essential metabolite required to fight infection and cancer, reports a study led by Van Andel Institute scientists.
The findings, published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, could help improve immunotherapies by revealing how diet can boost immune cell function.
“Like any good system, immune cells have a plan A and a plan B,” said Russell Jones, Ph.D., the study’s corresponding author and chair of VAI’s Department of Metabolism and Nutritional ...
A 3D ion Magnet, the new experimental frontier for quantum information processing
2024-08-22
Many quantum devices, from quantum sensors to quantum computers, use ions or charged atoms trapped with electric and magnetic fields as a hardware platform to process information.
However, current trapped-ion systems face important challenges. Most experiments are limited to one-dimensional chains or two-dimensional planes of ions, which constrain the scalability and functionality of quantum devices. Scientists have long dreamed of stacking these ions into three-dimensional structures, but this has been very difficult ...
A potential pathway may guide new therapies for inflammatory bowel disease and other inflammatory diseases
2024-08-22
Philadelphia, August 22, 2024 – There is a critical unmet need to help tighten and maintain a healthy intestinal barrier and treat a leaky gut. Researchers have now found that a unique strain of probiotic bacteria, Bifidobacterium bifidum BB1, enhances intestinal barrier function and protects against penetration of bacteria and various harmful agents in the intestine. The findings, detailed in an article in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, can help advance the development of novel, targeted, naturally occurring probiotic therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other inflammatory diseases, such as fatty liver disease or alcoholic liver ...
CU researchers awarded $1.35 million grant to develop decision support technology for long-term care facilities
2024-08-22
Researchers from the University of Colorado College of Nursing and CU School of Medicine on the Anschutz Medical Campus were awarded a $1.35 million grant from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) to design and implement technologies that improve resident safety and employee wellbeing at long-term care facilities.
“Long-term care facilities in the United States are in crisis, they’re facing low resources and high staff turnover,” CU Nursing Associate Professor and ...
Alzheimer’s drug may someday help save lives by inducing a state of “suspended animation”
2024-08-22
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University report that they were able to successfully put tadpoles of Xenopus laevis frogs into a hibernation-like torpor state using donepezil (DNP), a drug approved by the FDA to treat Alzheimer’s. The team had previously used another drug, SNC80, to achieve similar results in tadpoles and enhance the survival of whole mammalian hearts for transplants, but SNC80 is not approved for clinical use in humans because it can cause seizures. By contrast, DNP is already being used in the clinic, meaning it potentially could be rapidly repurposed ...
New NSF Center for Pandemic Insights
2024-08-22
Preventing the next pandemic begins before diseases emerge. This “pre-emergence” phase is the focus of a new center funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and led by the University of California, Davis.
Supported with $18 million over seven years, the U.S. National Science Foundation Center for Pandemic Insights (NSF CPI) includes partnering institutions from across the United States. It aims to harness new technologies and develop sensing to detect, investigate, and ultimately prevent ...
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering research shows how insulin, zinc and pH can block harmful protein clumps linked to Type 2 diabetes
2024-08-22
An estimated 462 million people around the world suffer from Type 2 diabetes, a chronic disease in which the body has problems using sugar as a fuel, leading to a buildup of sugar in the blood and chronic health issues.
New research led by Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy, a professor at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, shows how zinc, pH levels and insulin work together to inhibit the buildup of protein clumps that contribute to this disease. The work, which points toward promising avenues for innovative treatments, ...
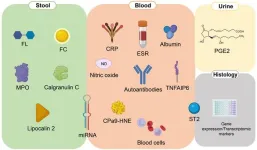
Fecal, blood, and urinary biomarkers in inflammatory bowel diseases
2024-08-22
The global burden of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), primarily Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), continues to rise. Recent data show incidence rates of up to 17.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for CD and even higher for UC, reaching 28.4 per 100,000 person-years. These diseases primarily affect older populations and vary geographically, with higher prevalence rates in highly developed countries. Currently, endoscopic assessment through ileo-colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing and monitoring IBD. However, this approach is invasive and often has limited availability, leading to long ...
ARDD 2024 | What can we do before the "cliff" of aging arrives?
2024-08-22
When exactly does the aging process start? With the aging mechanisms unclear, no consensus has been reached about aging “cliffs”, where our body functions and biological processes just change dramatically, as if overnight.
In 2019, a study published in the authoritative peer-reviewed journal Nature Medicine, based on plasma proteomics data, identified 34, 60, and 78 years old as key time points of aging. In August 2024, Nature Aging, a Nature portfolio journal focusing on aging mechanisms, published the latest findings incorporating comprehensive data including transcriptomics and metabolomics, pinpointing the aging cliffs to the 40s and 60s.
In the biomedical field, multi-omics ...
Hydrogels can play Pong by “remembering” previous patterns of electrical simulation
2024-08-22
Non-living hydrogels can play the video game Pong and improve their gameplay with more experience, researchers report August 23 in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports Physical Science. The researchers hooked hydrogels up to a virtual game environment and then applied a feedback loop between the hydrogel’s paddle—encoded by the distribution of charged particles within the hydrogel—and the ball’s position—encoded by electrical stimulation. With practice, the hydrogel’s accuracy improved by up to 10%, resulting in longer rallies. The researchers say that this demonstrates ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
[Press-News.org] T cells manipulate the memory of innate immune cellsRemarkable finding offers potential for organ transplantation