(Press-News.org) Non-living hydrogels can play the video game Pong and improve their gameplay with more experience, researchers report August 23 in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports Physical Science. The researchers hooked hydrogels up to a virtual game environment and then applied a feedback loop between the hydrogel’s paddle—encoded by the distribution of charged particles within the hydrogel—and the ball’s position—encoded by electrical stimulation. With practice, the hydrogel’s accuracy improved by up to 10%, resulting in longer rallies. The researchers say that this demonstrates the ability of non-living materials to use “memory” to update their understanding of the environment, though more research is needed before it could be said that hydrogels can “learn.”
“Ionic hydrogels can achieve the same kind of memory mechanics as more complex neural networks,” says first author and robotics engineer Vincent Strong of the University of Reading. “We showed that hydrogels are not only able to play Pong; they can actually get better at it over time.”
The researchers were inspired by a previous study that showed that brain cells in a dish can learn to play Pong if they are electrically stimulated in a way that gives them feedback on their performance.
“Our paper addresses the question of whether simple artificial systems can compute closed loops similar to the feedback loops that allow our brains to control our bodies,” says corresponding author and biomedical engineer Yoshikatsu Hayashi of the University of Reading. “The basic principle in both neurons and hydrogels is that ion migration and distributions can work as a memory function that can correlate with sensory-motor loops in the Pong world. In neurons, ions run within the cells; in the gel, they run outside.”
Hydrogels are complex polymers that become jelly like when hydrated—gelatin and agar are natural examples. In this case, the researchers used an “electro-active polymer,” meaning a hydrogel that can respond to electrical stimulation thanks to the presence of ions (charged particles) in the media surrounding its polymer matrix. When the hydrogel is electrically stimulated, the ions move, dragging water molecules with them, and this movement causes the hydrogel to temporarily change shape.
“The rate at which the hydrogel de-swells takes much longer than the time it takes for it to swell in the first place, meaning that the ions’ next motion is influenced by its previous motion, which is sort of like memory occurring,” says Strong. “The continued rearrangement of ions within the hydrogel is based off of previous rearrangements within the hydrogel, continuing back to when it was first made and had a homogeneous distribution of ions.”
To test whether the hydrogel’s physical “memory” could enable it to play Pong, the researchers used electrodes to connect the hydrogel to a virtual game environment and started up the game by sending the ball in a random direction. They used electrical stimulation to inform the hydrogel of the ball’s position and measured the movement of ions within the hydrogel to determine the position of its paddle.
As the Pong games played out, the researchers measured the gel’s hit rate and examined whether its accuracy improved. They showed that, with more experience, the hydrogel was able to hit the ball more frequently, resulting in longer rallies. Whereas the Pong-playing neurons achieved their optimal ball-skills within around 10 minutes, the hydrogel took closer to 20 minutes to reach its maximum Pong potential.
“Over time, as the ball moves, the gel gathers a memory of all motion. And then the paddle moves to accommodate that ball within the simulated environment,” says Strong. “The ions move in a way that maps a memory of all motion over time, and this “memory” results in improved performance.”
Because most existing AI algorithms are derived from neural networks, the researchers say that hydrogels represent a different kind of “intelligence” that could be used to develop new, simpler algorithms. In the future, the researchers plan to further probe the hydrogel’s “memory” by examining the mechanisms behind its memory and by testing its ability to perform other tasks.
“In our follow-up projects, we are thinking about how to extract the algorithm from the hydrogels that allows memory acquisition,” says co-author William Holderbaum of the University of Reading.
“We’ve shown that memory is emergent within the hydrogels, but the next step is to see whether we can also show specifically that learning is occurring,” says Strong.
###
This research was supported by Process Vision Ltd.
Cell Reports Physical Science, Strong, Holderbaum, and Hayashi, “Electro-Active Polymer Hydrogels Exhibit Emergent Memory When Embodied in a Simulated Game-Environment” https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-physical-science/fulltext/S2666-3864(24)00436-3
Cell Reports Physical Science (@CellRepPhysSci), published by Cell Press, is a broad-scope, open access journal that publishes cutting-edge research across the spectrum of the physical sciences, including chemistry, physics, materials science, energy science, engineering, and related interdisciplinary work. Visit: https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-physical-science/home. To receive Cell Press media alerts, please contact press@cell.com.
END
The anti-cancer drug olaparib may be effective in treating biochemically recurrent prostate cancer without accompanying hormone therapy for men who have mutations in genes such as BRCA2, according to results of a phase II clinical trial of 51 patients conducted at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and three other sites.
The study was done of men experiencing signs of cancer recurrence after surgical removal of the prostate, as measured by a high level of the protein prostate-specific antigen (PSA). Following treatment with olaparib, 13 participants, including all 11 who had BRCA2 mutations, had a decrease in PSA of at least 50% ...
Tens of millions of Americans are being exposed to tobacco content on streaming services, according to new research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The researchers found that the odds of encountering tobacco products being advertised, marketed or promoted on these platforms increased based on race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status and smoking habits.
The nationally representative study, published today in JAMA Network, revealed an estimated 12.4% of American adults were exposed to tobacco promotion on streaming services. Exposure was highest among those with a high school education or less (16.4%), Black/African American respondents (19.4%), ...
About The Study: In two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials, elinzanetant, a selective neurokinin-1,3 receptor antagonist, demonstrated statistically significant reductions in vasomotor symptoms (VMS) frequency and severity vs placebo in postmenopausal individuals with moderate to severe VMS. Elinzanetant also significantly improved sleep disturbances and menopause-related quality of life vs placebo; the safety profile was favorable.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, JoAnn V. Pinkerton, ...
About The Study: In this repeated cross-sectional study of children’s exposure to food-related television advertisements, exposure via children’s programming decreased substantially. However, most advertisements seen were still for unhealthy products, and exposure from all programming remained substantial. Findings of more than 90% of advertising exposure not from children’s programming and more than 1,000 food-related advertisements seen per year suggest the need for government regulations based on time of day rather than programming.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lisa M. Powell, PhD, email powelll@uic.edu.
To ...
About The Study: In this study of the prevalence of exposure to tobacco advertisements on TV or streaming platforms among U.S. adults, disparities in exposure by race or ethnicity, education level, and smoking status were identified. These findings underscore the need for targeted public health interventions and regulation to address these disparities and reduce the impact of tobacco advertisements on vulnerable populations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sanjay Shete, PhD, email sshete@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27781)
Editor’s ...
Thyroid hormone plays a key role in regulating a range of physiologic functions, including metabolism, temperature, heart rate, and growth. It accomplishes this impressive array of activities by interacting with almost every organ system in the body. Yet despite a long history of research on how thyroid hormone influences different organs, its effects on arguably the most crucial organ — the brain — have remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, scientists at Harvard Medical School have gained ...
Higher thiazide doses are associated with greater reductions in urine calcium, which in turn correlate with fewer symptomatic kidney stone events, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
Thiazide diuretics, commonly prescribed to prevent kidney stone recurrence, are drugs that act directly on the kidneys to promote diuresis (urine flow) by inhibiting the sodium/chloride cotransporter located in the distal convoluted tubule of a nephron ...
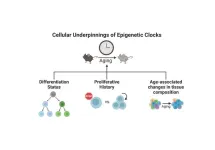
How old are you, really? Your chronological age is the number of years you have been alive. Your biological age is how old your cells are which scientists believe may better assess one’s age-related health and disease risk. People biologically age at different rates, depending on genetic and environmental factors, so that a person’s chronological age does not necessarily match their biological age. In recent years, direct-to-consumer biological age tests have become increasingly accessible and popular as interest has increased ...
In a study published today (22 August) in Cell Reports Physical Science, a team led by Dr Yoshikatsu Hayashi demonstrated that a simple hydrogel - a type of soft, flexible material - can learn to play the simple 1970s computer game ‘Pong’. The hydrogel, interfaced with a computer simulation of the classic game via a custom-built multi-electrode array, showed improved performance over time.
Dr Hayashi, a biomedical engineer at the University of Reading’s School of Biological Sciences, said: "Our research shows that even very simple materials can exhibit complex, adaptive behaviours typically associated with living systems or sophisticated AI.
"This ...
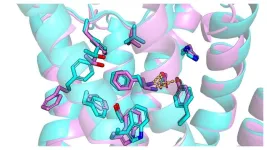
Artificial intelligence (AI) can help identify molecules that could serve as new drugs for mental health disorders. AI can be used to predict the three-dimensional structures of important receptors and thereby speed up the development of potential drugs. This is the result of a new study from Uppsala University published in Science Advances.
In drug development, experimental methods are often used to determine the three-dimensional structures of target proteins and to understand how molecules bind to them. This information is needed to design drug molecules efficiently. However, the process to determine structures can be demanding, meaning this ...