(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study of the prevalence of exposure to tobacco advertisements on TV or streaming platforms among U.S. adults, disparities in exposure by race or ethnicity, education level, and smoking status were identified. These findings underscore the need for targeted public health interventions and regulation to address these disparities and reduce the impact of tobacco advertisements on vulnerable populations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sanjay Shete, PhD, email sshete@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27781)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27781?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=082224
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Disparities in exposure to tobacco on television or streaming platforms
JAMA Network Open
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How thyroid hormone fuels the drive to explore
2024-08-22
Thyroid hormone plays a key role in regulating a range of physiologic functions, including metabolism, temperature, heart rate, and growth. It accomplishes this impressive array of activities by interacting with almost every organ system in the body. Yet despite a long history of research on how thyroid hormone influences different organs, its effects on arguably the most crucial organ — the brain — have remained shrouded in mystery.
Now, scientists at Harvard Medical School have gained ...
Higher thiazide doses shown to reduce kidney stone events
2024-08-22
Higher thiazide doses are associated with greater reductions in urine calcium, which in turn correlate with fewer symptomatic kidney stone events, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
Thiazide diuretics, commonly prescribed to prevent kidney stone recurrence, are drugs that act directly on the kidneys to promote diuresis (urine flow) by inhibiting the sodium/chloride cotransporter located in the distal convoluted tubule of a nephron ...
Reading your biological age in your blood or saliva? It’s not as simple as that
2024-08-22
How old are you, really? Your chronological age is the number of years you have been alive. Your biological age is how old your cells are which scientists believe may better assess one’s age-related health and disease risk. People biologically age at different rates, depending on genetic and environmental factors, so that a person’s chronological age does not necessarily match their biological age. In recent years, direct-to-consumer biological age tests have become increasingly accessible and popular as interest has increased ...
Pong prodigy: Hydrogel material shows unexpected learning abilities
2024-08-22
In a study published today (22 August) in Cell Reports Physical Science, a team led by Dr Yoshikatsu Hayashi demonstrated that a simple hydrogel - a type of soft, flexible material - can learn to play the simple 1970s computer game ‘Pong’. The hydrogel, interfaced with a computer simulation of the classic game via a custom-built multi-electrode array, showed improved performance over time.
Dr Hayashi, a biomedical engineer at the University of Reading’s School of Biological Sciences, said: "Our research shows that even very simple materials can exhibit complex, adaptive behaviours typically associated with living systems or sophisticated AI.
"This ...
AI can speed up drug development
2024-08-22
Artificial intelligence (AI) can help identify molecules that could serve as new drugs for mental health disorders. AI can be used to predict the three-dimensional structures of important receptors and thereby speed up the development of potential drugs. This is the result of a new study from Uppsala University published in Science Advances.
In drug development, experimental methods are often used to determine the three-dimensional structures of target proteins and to understand how molecules bind to them. This information is needed to design drug molecules efficiently. However, the process to determine structures can be demanding, meaning this ...
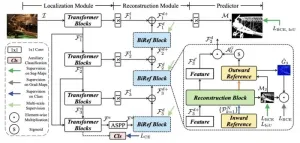
Bilateral reference framework for high-resolution dichotomous image segmentation
2024-08-22
A research team has developed a computer vision technique that can perform dichotomous image segmentation, high-resolution salient object detection, and concealed object detection in the same framework. Their novel bilateral reference framework (BiRefNet) is able to capture tiny-pixel features and holds potential for a wide range of practical computer vision applications.
The work is published in the journal CAAI Artificial Intelligence Research on August 22.
In computer vision research, ...
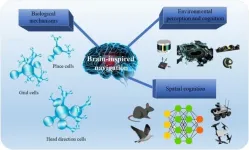
The future of robotics: Brain-inspired technologies paving the way
2024-08-22
In the ever-evolving field of robotics, a groundbreaking approach has emerged, revolutionizing how robots perceive, navigate, and interact with their environments. This new frontier, known as brain-inspired navigation technology, integrates insights from neuroscience into robotics, offering enhanced capabilities and efficiency.
Brain-inspired navigation technologies are not just a mere improvement over traditional methods; they represent a paradigm shift. By mimicking the neural mechanisms of animals, these technologies provide robots with the ability to navigate through complex and unknown terrains with unprecedented accuracy ...
IHME’s 2024 Roux Prize awarded to Community Health Impact Coalition CEO – recognized for contributions to improve population health
2024-08-22
On behalf of the Community Health Impact Coalition (CHIC), Dr. Madeleine Ballard, global health leader and CEO of CHIC, is the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s 2024 Roux Prize winner. The award recognizes Dr. Ballard’s work alongside thousands of community health workers (CHWs) to secure quality care for all, through evidence-based health systems benefiting millions of people across the world.
Half of the world's population lacks access to essential health services. Around the globe, CHWs have stepped up to address this critical gap and deliver care in a way that improves access, increases equity, and saves lives. Despite their ...
New detectable gravitational wave source from collapsing stars predicted from simulations
2024-08-22
The death of a massive, rapidly spinning star can shake the universe. And the resulting ripples — known as gravitational waves — could be felt by instruments on Earth, according to new research published August 22 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. These new sources of gravitational waves just await discovery, the scientists behind the research predict.
The gravitational waves emerge following the violent deaths of rapidly rotating stars 15 to 20 times the mass of the sun. Upon running ...
New study examines use of opioids for chronic cough
2024-08-22
INDIANAPOLIS – Chronic cough, with symptoms lasting more than eight weeks, affects approximately one in 10 adults. Cough is among the most common reasons for seeking medical care in the United States, yet chronic cough is difficult to treat. One of the largest studies of chronic cough and one of the first to explore the use of opioids, which are known to suppress cough, to treat these patients, has found that 20 percent of patients with chronic cough received a prescription for a cough suppressant containing an opioid.
With the goals of estimating opioid prescription in the chronic cough population and of informing alternative treatment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] Disparities in exposure to tobacco on television or streaming platformsJAMA Network Open