(Press-News.org) On behalf of the Community Health Impact Coalition (CHIC), Dr. Madeleine Ballard, global health leader and CEO of CHIC, is the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s 2024 Roux Prize winner. The award recognizes Dr. Ballard’s work alongside thousands of community health workers (CHWs) to secure quality care for all, through evidence-based health systems benefiting millions of people across the world.
Half of the world's population lacks access to essential health services. Around the globe, CHWs have stepped up to address this critical gap and deliver care in a way that improves access, increases equity, and saves lives. Despite their vital work, many CHWs remain unsalaried, unsupervised, and unequipped, so they are not set up to succeed in global health goals. Co-founded by Dr. Ballard in 2019, CHIC has played a key role in influencing guidelines, increasing funding, and advancing the development of national policies needed to make professional CHWs the norm everywhere.
“Millions of community health workers play a critical role in regions where resources are scarce and where marginalized populations face significant barriers to care,” said Dr. Chris Murray, Director of IHME. “The Roux Prize seeks to recognize global health leaders like Dr. Ballard and organizations such as CHIC who drive innovation, ambition, and collaboration. Through meticulous research, advocacy, and activation work, CHIC is addressing health disparities and improving access to health care,” he added. Amidst a worsening shortage of health workers, major health institutions are aiming to expand their workforce by 2030. By building a multi-country coalition of CHWs, advocates, and researchers, Dr. Ballard has brought key stakeholders together to address critical health, data, and implementation challenges that no one organization could solve alone.
This collaborative effort has resulted in significant achievements, including the first-ever WHO guideline on CHWs, USAID’s flagship CHW program evaluation tool, and the first-ever guidance on creating national georeferenced community health worker master lists.
The impact of this work does not end at global guidelines. The Coalition also leverages evidence to win commitments from major development aid providers and policymakers.
“Community health workers are the backbone of our health systems, yet their critical contributions are systemically overlooked,” Dr. Ballard said. “Years of rigorous research have shown that CHWs are essential to improving health outcomes, lowering costs, and increasing equity. But only if they’re treated like professionals – with salaries, skills, supervision, and supplies. We must translate this research into action – our work is about setting up CHWs for success in providing quality care for all, including those who provide it,” she added.
Now in its 11th year, the Roux Prize has been recognizing individuals all over the globe who have leveraged evidence-based health data to improve population health. The Roux Prize is awarded by the IHME at the University of Washington’s School of Medicine.
Dr. Ballard has been a strong advocate for using routine data collected during programmatic care delivery in research, and she sees many parallels between the Global Burden of Disease study as a hub for informing global health initiatives and CHIC’s own proCHW Policy Dashboard, a scoreboard for the proCHW movement.
“The Roux Prize will help advance our collaborative research and CHIC’s use of evidence to influence guidelines, funding, and policy to improve population health in multiple countries around the world,” Dr. Ballard stated. “This recognition is transformative for the Coalition as it will help expand our work creating proCHW guidelines, increasing funding, and ultimately impacting the millions of CHWs and patients we serve,” she concluded.
Dr. Ballard is a Rhodes Scholar, recipient of the Harvard Women’s Leadership Award, and co-chair of the Anti-Racism Task Force at the Arnhold Institute for Global Health of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, where she is on faculty.
As the Roux Prize winner, Dr. Ballard will receive $100,000 that will be used to advance CHIC’s work on establishing professional CHW policies in 95 countries. CHIC and Dr. Ballard will be recognized at an award ceremony on October 15 in London.
IHME will begin accepting nominations for the 2025 Roux Prize on December 2, 2024. Nominations are accepted from all countries and can include, but are not limited to, staff in government agencies, leaders in charitable organizations, or community health providers.
For questions about the prize, contact info@rouxprize.org
For media interviews, contact ihmemedia@uw.edu
About the Roux Prize
The Roux Prize is sponsored by IHME’s founding board member David Roux and his wife, Barbara, to reward innovation in the application of disease burden research. The prize recognizes the person who has used health evidence in bold ways to make people healthier – and to highlight just what’s possible when visionaries use health evidence to change lives.
About IHME
An independent population health research organization based at the University of Washington School of Medicine, the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) works with collaborators around the world to develop timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence that illuminates the state of health everywhere. In making our research available and approachable, we aim to inform health policy and practice in pursuit of our vision: all people living long lives in full health.
END
IHME’s 2024 Roux Prize awarded to Community Health Impact Coalition CEO – recognized for contributions to improve population health
CHIC’s CEO and co-founder Dr. Madeleine Ballard will receive a $100,000 award for research and advocacy alongside community health workers to improve health outcomes in remote communities.
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New detectable gravitational wave source from collapsing stars predicted from simulations
2024-08-22
The death of a massive, rapidly spinning star can shake the universe. And the resulting ripples — known as gravitational waves — could be felt by instruments on Earth, according to new research published August 22 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters. These new sources of gravitational waves just await discovery, the scientists behind the research predict.
The gravitational waves emerge following the violent deaths of rapidly rotating stars 15 to 20 times the mass of the sun. Upon running ...
New study examines use of opioids for chronic cough
2024-08-22
INDIANAPOLIS – Chronic cough, with symptoms lasting more than eight weeks, affects approximately one in 10 adults. Cough is among the most common reasons for seeking medical care in the United States, yet chronic cough is difficult to treat. One of the largest studies of chronic cough and one of the first to explore the use of opioids, which are known to suppress cough, to treat these patients, has found that 20 percent of patients with chronic cough received a prescription for a cough suppressant containing an opioid.
With the goals of estimating opioid prescription in the chronic cough population and of informing alternative treatment ...
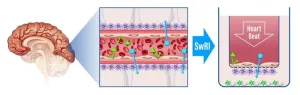
SwRI develops novel methodology for measuring blood-brain barrier permeability
2024-08-22
SAN ANTONIO — August 22, 2024 —Scientists at Southwest Research Institute have developed a new screening method to identify drug formulations that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB), to facilitate treatment of brain diseases and conditions.
“The BBB protects the brain and central nervous system from potentially harmful substances in the bloodstream, regulating the transport of essential nutrients and ions while maintaining the stability of the central nervous system,” said Research Engineer Nicholas McMahon, from SwRI’s Bioengineering group. “However, the very characteristics that make the BBB such an ...
Role of bitter polyphenols in the regulation of blood sugar
2024-08-22
Bioactive compounds like polyphenols and their health benefits have long captured public attention and interest. Commonly present in plant-based food like fruits, vegetables, seeds, coffee, and tea, the polyphenols have a strong bitter taste and, in the normal course, is excreted by our body due to poor absorption.
The polyphenols interact with human bitter taste receptors also known as Type 2 taste receptors (T2R) expressed within and outside the oral cavity. Notably, the activation of T2R expressed along the ...
Promising treatment for rectal cancer confirmed in major study
2024-08-22
A new treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer shows favourable results in that surgery can sometimes be avoided completely. It also reduces the risk of recurrence. The method has been confirmed as effective in a comprehensive study conducted at Uppsala University and published in eClinicalMedicine.
“The tumour disappears completely more often, thereby increasing the chance of avoiding surgery and retaining normal rectum and rectal function. Moreover, there are fewer metastases,” says Bengt Glimelius, Professor of Oncology ...
Chronic cough may be hereditary
2024-08-22
Chronic cough is among the most common reasons for seeking medical care, with middle-aged women the group most affected. New studies at Uppsala University also show that this condition appears to be a hereditary phenomenon. The studies have been published in ERJ Open Research and PLOS ONE.
“More than 10% of the population has a chronic cough, which has been shown to entail several negative consequences: reduced quality of life, reduced ability to work and voice problems. At present, we have insufficient knowledge about ...
Universal flu vaccine candidate protects against infection in mice
2024-08-22
Highlights:
Flu vaccine efficacy varies year to year.
A universal flu vaccine would protect people against all influenza strains that infect humans and last more than a season.
A new vaccine candidate incorporates proteins from 8 strains of influenza.
Recent tests of the candidate show efficacy in animal models, and the researchers hope to move to clinical trials soon.
Washington, D.C.—Annual flu vaccines protect against severe infection, but they vary in efficacy and may not match the most virulent strains ...
$20M community-driven research funding aims to reduce inequities, improve health outcomes
2024-08-22
DALLAS, August 22, 2024 — A new $20 million research initiative will engage the people most impacted by health disparities in developing solutions that may help improve their overall health and well-being. The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), a leading national philanthropy dedicated to taking bold leaps to transform health, are ...
Novel redox-active metal-organic framework as an anode material for Li batteries operating in freezing conditions
2024-08-22
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has developed a redox-active metal-organic hybrid electrode material (SKIER-5) for Li batteries that remains stable in cold conditions as low as minus 20 degrees Celsius. By addressing the limitations of graphite as an anode material of conventional Li batteries under freezing conditions, SKIER-5 has the potential to be a superior alternative. This novel material can be used in Li batteries for a variety of applications, including electric vehicles, drones, and ultra-small electronic devices, even in low temperatures.
Currently, ...
Mental health and chronic diabetes complications strongly linked both ways, study finds
2024-08-22
Heart attack, stroke, nerve damage.
These are just some of the complications for which millions of Americans with diabetes are at greater risk.
When a person has any of these chronic diabetes complications, they are more likely to have a mental health disorder, and vice versa, according to a University of Michigan-led study.
That is, the relationship goes both ways: having a mental health condition also increases the risk of developing chronic complications of diabetes.
“We wanted to see if chronic diabetes complications ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] IHME’s 2024 Roux Prize awarded to Community Health Impact Coalition CEO – recognized for contributions to improve population healthCHIC’s CEO and co-founder Dr. Madeleine Ballard will receive a $100,000 award for research and advocacy alongside community health workers to improve health outcomes in remote communities.