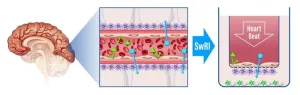
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO — August 22, 2024 —Scientists at Southwest Research Institute have developed a new screening method to identify drug formulations that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier (BBB), to facilitate treatment of brain diseases and conditions.
“The BBB protects the brain and central nervous system from potentially harmful substances in the bloodstream, regulating the transport of essential nutrients and ions while maintaining the stability of the central nervous system,” said Research Engineer Nicholas McMahon, from SwRI’s Bioengineering group. “However, the very characteristics that make the BBB such an effective protector also pose significant challenges to the delivery of therapeutic agents to treat various neurological disorders.”
SwRI has developed a technique to measure the permeation rates of molecules passing into the brain. By mimicking the interaction of pharmaceuticals with the BBB’s dynamic, highly regulated processes, researchers can understand how to override the brain’s natural defenses to support the development of targeted pharmaceutical treatments for neurological conditions and diseases.
“Our lab models offer an efficient, cost-effective and reproducible means of studying the molecular and cellular interactions at the BBB while avoiding the ethical and logistical issues associated with in vivo studies,” said Principal Scientist Dr. Mike Rubal, the lead on the project.
The Institute leverages multidisciplinary pharmaceutical and bioengineering research and development to provide every phase of drug development from initial concept through clinical trials. SwRI scientists have used the new BBB techniques to screen multiple compounds for internal research and government projects. The team also developed specific liposomes; lab-created cell membranes designed to penetrate the BBB.
“A liposome is essentially a Trojan horse that can deliver drugs to the brain,” said Darrel Johnston, director of SwRI’s Pharmaceutical and Bioengineering Department. “Using our microencapsulation expertise, we can disguise a drug to get around the brain’s robust protections.”
The team hopes the new approach will advance potential treatments for a variety of diseases and conditions.
“To treat diseases such as Alzheimer’s requires penetrating the blood-brain barrier,” said Rubal. “The Institute’s BBB work will open the door to new treatments and pharmaceuticals we can develop at Southwest Research Institute.”
SwRI will showcase the BBB analyses and other innovative research at booth No. 312 at the upcoming Military Health Systems Research Symposium, August 26-29, in Kissimmee, Florida.
For more information visit https://www.swri.org/industries/biochemistry-bioengineering.
END
SwRI develops novel methodology for measuring blood-brain barrier permeability
Understanding BBB may allow for the development of targeted treatments of neurological diseases
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Role of bitter polyphenols in the regulation of blood sugar
2024-08-22
Bioactive compounds like polyphenols and their health benefits have long captured public attention and interest. Commonly present in plant-based food like fruits, vegetables, seeds, coffee, and tea, the polyphenols have a strong bitter taste and, in the normal course, is excreted by our body due to poor absorption.
The polyphenols interact with human bitter taste receptors also known as Type 2 taste receptors (T2R) expressed within and outside the oral cavity. Notably, the activation of T2R expressed along the ...
Promising treatment for rectal cancer confirmed in major study
2024-08-22
A new treatment for locally advanced rectal cancer shows favourable results in that surgery can sometimes be avoided completely. It also reduces the risk of recurrence. The method has been confirmed as effective in a comprehensive study conducted at Uppsala University and published in eClinicalMedicine.
“The tumour disappears completely more often, thereby increasing the chance of avoiding surgery and retaining normal rectum and rectal function. Moreover, there are fewer metastases,” says Bengt Glimelius, Professor of Oncology ...
Chronic cough may be hereditary
2024-08-22
Chronic cough is among the most common reasons for seeking medical care, with middle-aged women the group most affected. New studies at Uppsala University also show that this condition appears to be a hereditary phenomenon. The studies have been published in ERJ Open Research and PLOS ONE.
“More than 10% of the population has a chronic cough, which has been shown to entail several negative consequences: reduced quality of life, reduced ability to work and voice problems. At present, we have insufficient knowledge about ...
Universal flu vaccine candidate protects against infection in mice
2024-08-22
Highlights:
Flu vaccine efficacy varies year to year.
A universal flu vaccine would protect people against all influenza strains that infect humans and last more than a season.
A new vaccine candidate incorporates proteins from 8 strains of influenza.
Recent tests of the candidate show efficacy in animal models, and the researchers hope to move to clinical trials soon.
Washington, D.C.—Annual flu vaccines protect against severe infection, but they vary in efficacy and may not match the most virulent strains ...
$20M community-driven research funding aims to reduce inequities, improve health outcomes
2024-08-22
DALLAS, August 22, 2024 — A new $20 million research initiative will engage the people most impacted by health disparities in developing solutions that may help improve their overall health and well-being. The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF), a leading national philanthropy dedicated to taking bold leaps to transform health, are ...
Novel redox-active metal-organic framework as an anode material for Li batteries operating in freezing conditions
2024-08-22
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has developed a redox-active metal-organic hybrid electrode material (SKIER-5) for Li batteries that remains stable in cold conditions as low as minus 20 degrees Celsius. By addressing the limitations of graphite as an anode material of conventional Li batteries under freezing conditions, SKIER-5 has the potential to be a superior alternative. This novel material can be used in Li batteries for a variety of applications, including electric vehicles, drones, and ultra-small electronic devices, even in low temperatures.
Currently, ...
Mental health and chronic diabetes complications strongly linked both ways, study finds
2024-08-22
Heart attack, stroke, nerve damage.
These are just some of the complications for which millions of Americans with diabetes are at greater risk.
When a person has any of these chronic diabetes complications, they are more likely to have a mental health disorder, and vice versa, according to a University of Michigan-led study.
That is, the relationship goes both ways: having a mental health condition also increases the risk of developing chronic complications of diabetes.
“We wanted to see if chronic diabetes complications ...
Endoscopic treatment approaches for inflammatory bowel diseases: old friends and new weapons
2024-08-22
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), comprising Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), are chronic inflammatory conditions affecting the gastrointestinal tract. These diseases can lead to various complications, including strictures, fistulas, and abscesses, significantly impacting patients' quality of life. Endoscopy plays a crucial role in diagnosing IBD, assessing disease activity, and monitoring treatment response. In recent years, advances in operative endoscopy have introduced ...
Bed-sharing has no impact on children’s psychological development
2024-08-22
Parental bed-sharing is unlikely to impact children’s psychological development, new research has found.
The study from the University of Essex looked at nearly 17,000 British babies and tracked them for 11 years – finding kids who shared beds were happy and healthy.
Dr Ayten Bilgin, from the Department of Psychology, found no association between bed-sharing at 9 months and childhood emotional or behavioural problems.
The practice is mired in controversy as some experts previously thought it negatively affected children’s development.
However, others say it helps both parents and children as they are nearby for feeding and if they wake in the night.
Dr Bilgin, said: ...
Self-improving AI method increases 3D-printing efficiency
2024-08-22
PULLMAN, Wash. – An artificial intelligence algorithm can allow researchers to more efficiently use 3D printing to manufacture intricate structures.
The Washington State University study, published in the journal Advanced Materials Technologies, could allow for more seamless use of 3D printing for complex designs in everything from artificial organs to flexible electronics and wearable biosensors. As part of the study, the algorithm learned to identify, and then print, the best versions of kidney and prostate organ models, printing out 60 continually improving versions.
“You can optimize the results, saving time, cost and labor,” said Kaiyan Qiu, co-corresponding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] SwRI develops novel methodology for measuring blood-brain barrier permeabilityUnderstanding BBB may allow for the development of targeted treatments of neurological diseases