(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University report that they were able to successfully put tadpoles of Xenopus laevis frogs into a hibernation-like torpor state using donepezil (DNP), a drug approved by the FDA to treat Alzheimer’s. The team had previously used another drug, SNC80, to achieve similar results in tadpoles and enhance the survival of whole mammalian hearts for transplants, but SNC80 is not approved for clinical use in humans because it can cause seizures. By contrast, DNP is already being used in the clinic, meaning it potentially could be rapidly repurposed for use in emergency situations to prevent irreversible organ injury while a person is being transported to a hospital.
“Cooling a patient’s body down to slow its metabolic processes has long been used in medical settings to reduce injuries and long-term problems from severe conditions, but it can only currently be done in a well-resourced hospital,” said co-author Michael Super, Ph.D., Director of Immuno-Materials at the Wyss Institute. “Achieving a similar state of ‘biostasis’ with an easily administered drug like DNP could potentially save millions of lives every year.”
This research, published today in ACS Nano, was supported as part of the DARPA Biostasis Program, which funds projects that aim to extend the time for lifesaving medical treatment, often referred to as “the Golden Hour,” following traumatic injury or acute infection. The Wyss Institute has been a participant in the Biostasis Program since 2018, and has achieved several important milestones over the last few years.
Using a combination of predictive machine learning algorithms and animal models, the Wyss’ Biostasis team previously identified and tested existing drug compounds that had the potential to put living tissues into a state of suspended animation. Their first successful candidate, SNC80, significantly reduced oxygen consumption (a proxy for metabolism) in both a beating pig heart and in human organ chips, but has a known side effect of causing seizures when injected systemically.
In the new study, they once again turned to their algorithm, NeMoCad, to identify other compounds whose structures are similar to SNC80. Their top candidate was DNP, which has been approved since 1996 to treat Alzheimer’s.
“Interestingly, clinical overdoses of DNP in patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease have been associated with drowsiness and a reduced heart rate - symptoms that are torpor-like. However, this is the first study, to our knowledge, that focuses on leveraging those effects as the main clinical response, and not as side effects,” said the study’s first author María Plaza Oliver, Ph.D., who was a Postdoctoral Fellow at the Wyss Institute when the work was conducted.
The team used X. laevis tadpoles to evaluate DNP’s effects on a whole living organism, and found that it did successfully induce a torpor-like state that could be reversed when the drug was removed. The drug, however, did seem to cause some toxicity, and accumulated in all of the animals’ tissues. To solve that problem, the researchers encapsulated DNP inside lipid nanocarriers, and found that this both reduced toxicity and caused the drug to accumulate in the animals’ brain tissue. This is a promising result, as the central nervous system is known to mediate hibernation and torpor in other animals as well.
Although DNP has been shown to protect neurons from metabolic stress in models of Alzheimer’s disease, the team cautions that more work is needed to understand exactly how it torpor, as well as scale up production of the encapsulated DNP for use in larger animals and, potentially, humans.
“Donepezil has been used worldwide by patients for decades, so its properties and manufacturing methods are well-established. Lipid nanocarriers similar to the ones we used are also now approved for clinical use in other applications. This study demonstrates that an encapsulated version of the drug could potentially be used in the future to buy patients critical time to survive devastating injuries and diseases, and it could be easily formulated and produced at scale on a much shorter time scale than a new drug,” said senior author Donald Ingber, M.D., Ph.D. Ingber is the Founding Director of the Wyss Institute, the Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, and the Hansjörg Wyss Professor of Bioinspired Engineering at Harvard’s John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences.
Additional authors of the paper include former Wyss members Erica Gardner, Takako Takeda, Shruti Kaushal, Vaskar Gnyawali, and Richard Novak; current Wyss members Tiffany Lin, Katherine Sheehan, Megan Sperry, Shanda Lightbown, Ramsés Martínez, Daniela del Campo, Haleh Fotowat, Michael Lewandowski, and Alexander Pauer; and Maria V. Lozano and Manuel J. Santander Ortega from the University of Castilla-La Mancha, Spain.
This research was supported by DARPA under Cooperative Agreement Number W911NF-19-2-0027, the Margarita Salas postdoctoral grant co-funded by the Spanish Ministry of Universities, and the University of Castilla-La Mancha (NextGeneration EU UNI/551/2021).
END
Alzheimer’s drug may someday help save lives by inducing a state of “suspended animation”
New research in tadpoles reveals that FDA-approved donepezil puts the animals in reversible torpor-like state
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New NSF Center for Pandemic Insights
2024-08-22
Preventing the next pandemic begins before diseases emerge. This “pre-emergence” phase is the focus of a new center funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and led by the University of California, Davis.
Supported with $18 million over seven years, the U.S. National Science Foundation Center for Pandemic Insights (NSF CPI) includes partnering institutions from across the United States. It aims to harness new technologies and develop sensing to detect, investigate, and ultimately prevent ...
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering research shows how insulin, zinc and pH can block harmful protein clumps linked to Type 2 diabetes
2024-08-22
An estimated 462 million people around the world suffer from Type 2 diabetes, a chronic disease in which the body has problems using sugar as a fuel, leading to a buildup of sugar in the blood and chronic health issues.
New research led by Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy, a professor at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, shows how zinc, pH levels and insulin work together to inhibit the buildup of protein clumps that contribute to this disease. The work, which points toward promising avenues for innovative treatments, ...
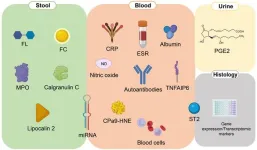
Fecal, blood, and urinary biomarkers in inflammatory bowel diseases
2024-08-22
The global burden of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), primarily Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), continues to rise. Recent data show incidence rates of up to 17.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for CD and even higher for UC, reaching 28.4 per 100,000 person-years. These diseases primarily affect older populations and vary geographically, with higher prevalence rates in highly developed countries. Currently, endoscopic assessment through ileo-colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing and monitoring IBD. However, this approach is invasive and often has limited availability, leading to long ...
ARDD 2024 | What can we do before the "cliff" of aging arrives?
2024-08-22
When exactly does the aging process start? With the aging mechanisms unclear, no consensus has been reached about aging “cliffs”, where our body functions and biological processes just change dramatically, as if overnight.
In 2019, a study published in the authoritative peer-reviewed journal Nature Medicine, based on plasma proteomics data, identified 34, 60, and 78 years old as key time points of aging. In August 2024, Nature Aging, a Nature portfolio journal focusing on aging mechanisms, published the latest findings incorporating comprehensive data including transcriptomics and metabolomics, pinpointing the aging cliffs to the 40s and 60s.
In the biomedical field, multi-omics ...
Hydrogels can play Pong by “remembering” previous patterns of electrical simulation
2024-08-22
Non-living hydrogels can play the video game Pong and improve their gameplay with more experience, researchers report August 23 in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports Physical Science. The researchers hooked hydrogels up to a virtual game environment and then applied a feedback loop between the hydrogel’s paddle—encoded by the distribution of charged particles within the hydrogel—and the ball’s position—encoded by electrical stimulation. With practice, the hydrogel’s accuracy improved by up to 10%, resulting in longer rallies. The researchers say that this demonstrates ...
Precision drug olaparib may be effective without hormone therapy for some men with biochemically recurrent prostate cancer
2024-08-22
The anti-cancer drug olaparib may be effective in treating biochemically recurrent prostate cancer without accompanying hormone therapy for men who have mutations in genes such as BRCA2, according to results of a phase II clinical trial of 51 patients conducted at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and three other sites.
The study was done of men experiencing signs of cancer recurrence after surgical removal of the prostate, as measured by a high level of the protein prostate-specific antigen (PSA). Following treatment with olaparib, 13 participants, including all 11 who had BRCA2 mutations, had a decrease in PSA of at least 50% ...
Americans face disparities in exposure to tobacco on streaming platforms
2024-08-22
Tens of millions of Americans are being exposed to tobacco content on streaming services, according to new research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The researchers found that the odds of encountering tobacco products being advertised, marketed or promoted on these platforms increased based on race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status and smoking habits.
The nationally representative study, published today in JAMA Network, revealed an estimated 12.4% of American adults were exposed to tobacco promotion on streaming services. Exposure was highest among those with a high school education or less (16.4%), Black/African American respondents (19.4%), ...
Elinzanetant for the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause
2024-08-22
About The Study: In two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials, elinzanetant, a selective neurokinin-1,3 receptor antagonist, demonstrated statistically significant reductions in vasomotor symptoms (VMS) frequency and severity vs placebo in postmenopausal individuals with moderate to severe VMS. Elinzanetant also significantly improved sleep disturbances and menopause-related quality of life vs placebo; the safety profile was favorable.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, JoAnn V. Pinkerton, ...
Trends in children’s exposure to food and beverage advertising on television
2024-08-22
About The Study: In this repeated cross-sectional study of children’s exposure to food-related television advertisements, exposure via children’s programming decreased substantially. However, most advertisements seen were still for unhealthy products, and exposure from all programming remained substantial. Findings of more than 90% of advertising exposure not from children’s programming and more than 1,000 food-related advertisements seen per year suggest the need for government regulations based on time of day rather than programming.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lisa M. Powell, PhD, email powelll@uic.edu.
To ...
Disparities in exposure to tobacco on television or streaming platforms
2024-08-22
About The Study: In this study of the prevalence of exposure to tobacco advertisements on TV or streaming platforms among U.S. adults, disparities in exposure by race or ethnicity, education level, and smoking status were identified. These findings underscore the need for targeted public health interventions and regulation to address these disparities and reduce the impact of tobacco advertisements on vulnerable populations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sanjay Shete, PhD, email sshete@mdanderson.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.27781)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] Alzheimer’s drug may someday help save lives by inducing a state of “suspended animation”New research in tadpoles reveals that FDA-approved donepezil puts the animals in reversible torpor-like state