(Press-News.org) An international team of 45 researchers studying meteor showers has found that not all comets crumble the same way when they approach the Sun. In a paper published in the journal Icarus this week, they ascribe the differences to the conditions in the protoplanetary disk where comets formed 4.5 billion years ago.
“The meteoroids we see as meteors in the night sky are the size of small pebbles,” said lead author and SETI Institute and NASA Ames meteor astronomer Peter Jenniskens. “They are, in fact, the same size as the pebbles that collapsed into comets during the formation of our solar system.”
As our solar system formed, tiny particles in the disk around the young Sun gradually grew larger until they became the size of small pebbles.
“Once pebbles grow large enough to no longer travel along with the gas, they are destroyed by mutual collisions before they can grow much bigger,” said NASA Ames planetary scientist and co-author Paul Estrada. “Comets and primitive asteroids instead were formed when clouds of these pebbles locally collapsed into kilometer-sized and larger bodies.” /p>
Fast forward 4.5 billion years: when comets approach the Sun today, they crumble into smaller pieces called meteoroids. Those meteoroids co-orbit with the comet for a while and can later create meteor showers when they hit Earth’s atmosphere.
“We hypothesized that comets crumble into the sizes of the pebbles they are made of,” said Jenniskens. “In that case, the size distribution and the physical and chemical properties of young meteoroid streams still contain information about the conditions in the protoplanetary disk during this collapse.”
Jenniskens and his team of professional and amateur astronomers use special low-light video cameras in networks all over the world to track meteors in a NASA-sponsored project called “CAMS” – or Cameras for Allsky Meteor Surveillance (http://cams.seti.org).
“These cameras measure the meteoroids’ paths, how high they are when they first light up, and how they slow down in Earth’s atmosphere,” said Jenniskens. “Specialized cameras measured the composition of some of these meteoroids.”
The team studied 47 young meteor showers. Most are the crumbs of two types of comets: Jupiter-family comets from the Scattered Disk of the Kuiper Belt beyond Neptune and long-period comets from the Oort Cloud surrounding our solar system. Long-period comets move on much wider orbits than the Jupiter-family comets and are much more loosely held by the Sun’s gravity.
“We found that long-period (Oort Cloud) comets often crumble into sizes indicative of gentle accretion conditions,” said Jenniskens. “Their meteoroids have a low density. The meteoroid streams contain a fairly constant 4% of a type of solid meteoroids that were heated in the past and now only brighten deeper in Earth’s atmosphere and typically are poor in the element sodium.”
On the other hand, Jupiter-family comets usually crumble into smaller, denser meteoroids. They also have a higher 8% of solid materials on average and show more diversity in that content.
“We concluded that these Jupiter-family comets are composed of pebbles that had reached the point where fragmentation became important in their size evolution,” said Estrada. “The higher admixture of materials that were heated in the past are expected closer to the Sun.”
Primitive asteroids formed even closer to the Sun, although still outside the orbit of Jupiter. These asteroids produce meteor showers with even smaller particles, showing their pebble building blocks experienced even more aggressive fragmentation.
“While there are exceptions in both groups, the implication is that most long-period comets formed under more gentle particle growth conditions, possibly near the 30 AU edge of the Trans Neptunian Disk,” said Estrada. “Most Jupiter family comets formed closer to the Sun where pebbles reached or passed the fragmentation barrier, while primitive asteroids formed in the region where the cores of the giant planets formed.”
How is this possible? While the giant planets were growing, Neptune moved outward and scattered comets and asteroids out of the remaining protoplanetary disk. This outward movement likely created both the Scattered Disk of the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud. That would predict that both long period and Jupiter-family comets have the same properties, but the team found otherwise.
“It is possible that stars and molecular clouds in the birth region of the Sun perturbed the wide orbits of Oort Cloud comets early on, and the long-period comets we see today were scattered into such orbits only at a time when the Sun had moved out of this region,” said Jenniskens. “In contrast, Jupiter-family comets have always been on shorter orbits and sample all objects scattered by Neptune on its way out.”
Link to the paper:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0019103524002896
On arXiv:
https://arxiv.org/
About the SETI Institute
Founded in 1984, the SETI Institute is a non-profit, multi-disciplinary research and education organization whose mission is to lead humanity’s quest to understand the origins and prevalence of life and intelligence in the Universe and to share that knowledge with the world. Our research encompasses the physical and biological sciences and leverages expertise in data analytics, machine learning and advanced signal detection technologies. The SETI Institute is a distinguished research partner for industry, academia and government agencies, including NASA and NSF.
Contact information
Rebecca McDonald
Director of Communications
SETI Institute
rmcdonald@seti.org
END
Meteor showers shed light on where comets formed in the early solar system
An international team of 45 researchers studying meteor showers has found that not all comets crumble the same way when they approach the Sun
2024-08-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ChatGPT shows promise in answering patients' questions to urologists
2024-08-22
August 22, 2024 — The groundbreaking ChatGPT chatbot shows potential as a time-saving tool for responding to patient questions sent to the urologist's office, suggests a study in the September issue of Urology Practice®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The artificial intelligence (AI) tool generated "acceptable" responses to nearly one-half of a sample of real-life patient questions, according to the new research ...
T cells manipulate the memory of innate immune cells
2024-08-22
Research from Radboud university medical center reveals that T cells from the adaptive immune system can manipulate the memory of innate immune cells. Previously, it was believed that the memory of innate immune cells operated independently. This surprising connection opens up new possibilities for the treatment of various diseases. A mouse model shows that no immunosuppressive drugs are needed after an organ transplantation if this interaction between T cells and the innate immunity is temporarily blocked after the transplantation.
The adaptive immune ...
Immune cells have a metabolic backup plan for accessing their anti-cancer playbook
2024-08-22
GRAND RAPIDS, Mich. (Aug. 22, 2024) — Immune cells use two different routes to produce acetyl-CoA, an essential metabolite required to fight infection and cancer, reports a study led by Van Andel Institute scientists.
The findings, published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, could help improve immunotherapies by revealing how diet can boost immune cell function.
“Like any good system, immune cells have a plan A and a plan B,” said Russell Jones, Ph.D., the study’s corresponding author and chair of VAI’s Department of Metabolism and Nutritional ...
A 3D ion Magnet, the new experimental frontier for quantum information processing
2024-08-22
Many quantum devices, from quantum sensors to quantum computers, use ions or charged atoms trapped with electric and magnetic fields as a hardware platform to process information.
However, current trapped-ion systems face important challenges. Most experiments are limited to one-dimensional chains or two-dimensional planes of ions, which constrain the scalability and functionality of quantum devices. Scientists have long dreamed of stacking these ions into three-dimensional structures, but this has been very difficult ...
A potential pathway may guide new therapies for inflammatory bowel disease and other inflammatory diseases
2024-08-22
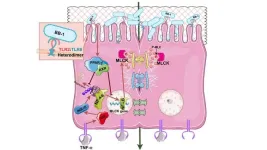
Philadelphia, August 22, 2024 – There is a critical unmet need to help tighten and maintain a healthy intestinal barrier and treat a leaky gut. Researchers have now found that a unique strain of probiotic bacteria, Bifidobacterium bifidum BB1, enhances intestinal barrier function and protects against penetration of bacteria and various harmful agents in the intestine. The findings, detailed in an article in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, can help advance the development of novel, targeted, naturally occurring probiotic therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other inflammatory diseases, such as fatty liver disease or alcoholic liver ...
CU researchers awarded $1.35 million grant to develop decision support technology for long-term care facilities
2024-08-22
Researchers from the University of Colorado College of Nursing and CU School of Medicine on the Anschutz Medical Campus were awarded a $1.35 million grant from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) to design and implement technologies that improve resident safety and employee wellbeing at long-term care facilities.
“Long-term care facilities in the United States are in crisis, they’re facing low resources and high staff turnover,” CU Nursing Associate Professor and ...
Alzheimer’s drug may someday help save lives by inducing a state of “suspended animation”
2024-08-22
Researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University report that they were able to successfully put tadpoles of Xenopus laevis frogs into a hibernation-like torpor state using donepezil (DNP), a drug approved by the FDA to treat Alzheimer’s. The team had previously used another drug, SNC80, to achieve similar results in tadpoles and enhance the survival of whole mammalian hearts for transplants, but SNC80 is not approved for clinical use in humans because it can cause seizures. By contrast, DNP is already being used in the clinic, meaning it potentially could be rapidly repurposed ...
New NSF Center for Pandemic Insights
2024-08-22
Preventing the next pandemic begins before diseases emerge. This “pre-emergence” phase is the focus of a new center funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation and led by the University of California, Davis.
Supported with $18 million over seven years, the U.S. National Science Foundation Center for Pandemic Insights (NSF CPI) includes partnering institutions from across the United States. It aims to harness new technologies and develop sensing to detect, investigate, and ultimately prevent ...
FAMU-FSU College of Engineering research shows how insulin, zinc and pH can block harmful protein clumps linked to Type 2 diabetes
2024-08-22
An estimated 462 million people around the world suffer from Type 2 diabetes, a chronic disease in which the body has problems using sugar as a fuel, leading to a buildup of sugar in the blood and chronic health issues.
New research led by Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy, a professor at the FAMU-FSU College of Engineering and the Florida State University-headquartered National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, shows how zinc, pH levels and insulin work together to inhibit the buildup of protein clumps that contribute to this disease. The work, which points toward promising avenues for innovative treatments, ...
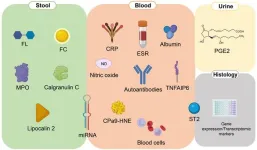
Fecal, blood, and urinary biomarkers in inflammatory bowel diseases
2024-08-22
The global burden of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), primarily Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), continues to rise. Recent data show incidence rates of up to 17.8 cases per 100,000 person-years for CD and even higher for UC, reaching 28.4 per 100,000 person-years. These diseases primarily affect older populations and vary geographically, with higher prevalence rates in highly developed countries. Currently, endoscopic assessment through ileo-colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing and monitoring IBD. However, this approach is invasive and often has limited availability, leading to long ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
[Press-News.org] Meteor showers shed light on where comets formed in the early solar systemAn international team of 45 researchers studying meteor showers has found that not all comets crumble the same way when they approach the Sun