Socioeconomics shape children’s connection to nature more than where they live
2024-08-23
(Press-News.org)
The income and education levels of a child’s environment determine their relationship to nature, not whether they live in a city or the countryside. This is the finding of a new study conducted by researchers at Lund University, Sweden. The results run counter to the assumption that growing up in the countryside automatically increases our connection to nature, and yet the study also shows that nature close to home increases children’s well-being.
There is a general concern that, with urbanisation, people have lost contact with nature. According to research, less contact means lower engagement with nature and poorer health outcomes as people spend less time outdoors. How we might strengthen or rediscover our connection to nature is therefore a topical question. This is particularly important for children, partly because of the impact on their health, but also because it is in childhood that our relationships with nature are formed.
The researchers wanted to study the relationships urban and rural schoolchildren have to nature and whether these vary with socioeconomic status. They also wanted to look into whether feeding birds could serve as a point of contact with wildlife, potentially strengthening children's knowledge of and feeling for nature, and by extension, improving their sense of well-being.
“Contrary to expectations, we have shown that children’s relationships with nature are not determined by whether they grow up in the countryside or in the city. Instead, socioeconomic factors play a decisive role. For example, children in areas with higher levels of education generally had better species knowledge, which in turn was linked to more positive attitudes towards wildlife. Higher incomes are linked to children participating more in nature-based activities, which also leads to a better connection to nature. This was true regardless of whether the children lived in a city centre or in the countryside,” says Dr Johan Kjellberg Jensen, researcher at Lund University, who led the study.
The study did find some differences between urban and rural children, however.
“It appears that children use natural environments in different ways, but this does not affect their attitudes towards nature in general. We could also see that children who have more direct access to nature close to home report a higher self-perceived sense of well-being. This shows how important contact with nature really is,” Dr Jensen says.
What was the outcome of the bird feeding project? The researchers from Lund found that children’s species knowledge increased, but they saw no effect on well-being or attitudes to nature.
“That said, we saw a very wide variation in results between schools, which points to the important role of teachers and schools in projects like this. We already know that our contact with nature is shaped through social interactions and that adults have considerable responsibility in acting as role models for how children relate to nature,” says Dr Johan Kjellberg Jensen, who also points out that this does not necessarily have to fall to teachers, who already have considerable responsibilities.
Another key finding of the study was that children with little access to nature close to home benefited most from the bird feeding project.
“This highlights the importance of green and equitable housing policies and urban planning. If we want future generations to have positive relationships with nature, enjoying all the health benefits that come with that, we may need targeted projects to increase children's contact with nature, both in urban and rural settings. This is particularly important in areas of low socioeconomic levels and little nature near residential housing,” Dr Johan Kjellberg Jensen concludes.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-23
An international study led by Institute of Natural Resources and Agrobiology of Seville (IRNAS-CSIC), of the Spanish National Research Council (CISC), has shown that as the number of global change factors increases, terrestrial ecosystems become more sensitive to the impacts of global change. The results, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience, show that the resistance of our ecosystems to global change decreases significantly as the number of environmental stressors increases, especially when this stress is sustained over time.
This is the conclusion reached by the Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning ...
2024-08-23
Researchers at Rutgers University in New Jersey have discovered that a protein produced by parasitic worms in the gut enhances wound healing in mice. The study, to be published August 23 in the journal Life Science Alliance (LSA), reveals that applying the protein to skin wounds speeds up wound closure, improves skin regeneration, and inhibits the formation of scar tissue. Whether the protein can be harnessed to enhance wound healing in human patients remains to be seen.
Skin wounds must be rapidly closed in order to prevent infection, but rapid wound closure can favor the development of scar tissue instead of properly regenerated skin. The balance between scarring ...
2024-08-23
In a recent comprehensive review published in Cyborg Bionic Systems, researchers led by Keyi Li from the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command in Shenyang, along with international collaborators, detail significant advances in the identification and application of biomarkers for prostate cancer (PCa). This critical insight is pivotal as prostate cancer remains one of the most common malignancies among men globally, emphasizing the urgent need for effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Prostate cancer is characterized by a multitude of molecular aberrations that complicate its early ...
2024-08-23
A team of researchers led by Professor Sebastian Deindl at Uppsala University has developed a pioneering method that vastly improves the ability to observe and analyse complex biological processes at the single-molecule level. Their work is set to be published in the upcoming issue of the journal Science.
“With our new technique, we can now extend single-molecule biophysics to the genome scale. This advance is expected to significantly deepen our understanding of how nucleic-acid interacting proteins function in ...
2024-08-23
The detection of individual particles and molecules has opened new horizons in analytical chemistry, cellular imaging, nanomaterials, and biomedical diagnostics. Traditional single-molecule detection methods rely heavily on fluorescence techniques, which require labeling of the target molecules. In contrast, photothermal microscopy has emerged as a promising label-free, non-invasive imaging technique. This method measures localized variations in the refractive index of a sample's surroundings, resulting from light absorption by sample components, which induces temperature changes in the surrounding region. Whispering ...
2024-08-23
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that is similar to both Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease but studies on long-term treatments are lacking. A new study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, highlights the potential cognitive benefits of cholinesterase inhibitor treatment.
Lewy body disease, which includes dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) and Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, following Alzheimer’s disease. DLB accounts for approximately ...
2024-08-23
NEW YORK, August 23, 2024 — In a groundbreaking advancement, researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have experimentally demonstrated that metasurfaces (two-dimensional materials structured at the nanoscale) can precisely control the optical properties of thermal radiation generated within the metasurface itself. This pioneering work, published in Nature Nanotechnology, paves the way for creating custom light sources with unprecedented capabilities, ...
2024-08-23
University of Leeds News
Embargoed until 23 August 10:00 BST
A selection of AQ Stripes graphic images are available here
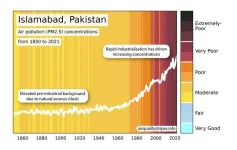
The global concentrations of one of the main air pollutants known to affect human health have been graphically illustrated for the first time by a team of scientists.
The Air Quality Stripes which were created by the University of Leeds, the University of Edinburgh, North Carolina State University, and the UK Met Office, starkly contrast the significant improvements in air quality across much of Europe with the alarming deterioration in parts ...
2024-08-23
Still unknown what causes neurological complications of COVID-19 including ‘long COVID,’ ‘brain fog’ and loss of taste and smell
Viruses with a deletion in the spike protein are better able to infect the brains of mice
‘These findings suggest there might be treatments that could work better to clear the virus from the brain’
CHICAGO --- Scientists have discovered a mutation in SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, that plays a key role in its ability to infect the central nervous system. The findings may help scientists understand its neurological symptoms and the mystery of “long COVID,” and ...
2024-08-23
A variety of vegetarian diets appear to protect against risk of mortality and contributing conditions, with a pesco-vegetarian diet — which includes fish — providing the most protection against risk in very elderly people, according to a new study.
Researchers at Loma Linda University Health found that vegetarian diets are associated with lower risk for all-cause mortality and many cause-specific mortalities, especially among males and in middle-aged subjects. However, slightly higher risks were observed among very elderly vegetarians for neurological conditions such as stroke, dementia, and Parkinson’s Disease. Despite this, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Socioeconomics shape children’s connection to nature more than where they live