(Press-News.org) London, United Kingdom – 27 Aug 2024: New research presented at the ESC Congress 2024 in London, UK (30 August – 2 September) shows that women in the menopause transition period show changes in their blood cholesterol profiles which could have an adverse impact on their cardiovascular health.
“There is an increase in ‘bad’ low-density type lipoprotein (LDL) particles and a decrease in ‘good’ high-density lipoprotein particles (HDL) that takes place during and after the menopause transition,” says study author Dr Stephanie Moreno, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA. “Taken together, these changes suggest that menopause is associated with a transition to a higher-risk lipoprotein profile that could be more likely to cause cardiovascular disease, such as coronary artery disease.”
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the biggest killer of women, despite the misconceptionthat CVD is a 'man's disease’ - 40% of all deaths in women are from CVD. While women develop cardiovascular disease (CVD) approximately ten years later than men, risk of CVD in women rises after menopause. The mechanisms underlying this acceleration in CVD risk are not well understood, but adverse changes in blood fat (lipid) measures are known to occur during the perimenopause period. Previous investigations have been largely restricted to traditional lipid measures (LDL [bad] cholesterol, HDL [good] cholesterol, and triglycerides) and have not examined changes in advanced lipids, including lipid subfractions and particle number which have been shown to be more predictive of cardiovascular disease in various studies.
In this study, the authors examined the changes over time in lipoprotein particles that occur during the menopause transition. A total of 1246 participants in the Dallas Heart Study (DHS) with known menopause status underwent measurement of common lipoproteins associated with CVD, including atherogenic LDL-P and small dense-LDL. Using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology, at two time points (DHS1 and DHS2) they compared longitudinal changes in lipoprotein measures between pre-, peri-, post-menopausal women and men using statistical modelling. For their analysis peri- is the group that was pre-menopause at DHS I and post-menopause at DHS 2.
There were also 1346 men (reference group) included in the study with a mean age of 43 years. There was a total of 1246 women with a mean age of 42 years for the peri-group, 54 years for the post-group, and 34 years for the pre-group. Of the women 440 (35%) were pre-menopausal, 298 (24%) were peri-menopausal, and 508 (41%) were post-menopausal.
Over a median follow-up time of 7 years. All three female groups had an increase in LDL-P but the greatest percent change was found to be between peri and post groups at 8.3%. When compared to men the post-group has the greatest percent change of HDL-P with a negative change of 4.8%.
Small-dense LDL had a greater percent change in the peri- group when compared to men with a change of 213%. This percent change is ~15% higher than both pre- and post-menopause groups.
“We found that menopause is associated with adverse changes in lipoprotein profiles, with the most pronounced changes found to be in increases in ‘bad’ LDL-particles and subfractions observed for peri-menopausal women,” said Dr Moreno. “When looked at together, these changes could help explain the increase of cardiovascular disease in post-menopausal women and help determine if earlier interventions are warranted.”
She concludes: “More research is needed to investigate whether these adverse changes in lipoproteins translate to greater cardiovascular risk.”
ENDS
Notes to editors
Funding: NIH R-32
Disclosures: the authors declare no conflicts of interest
References and notes
The abstract ‘Lipid changes across menopause status point to increased cardiovascular risk’ will be presented at the session “Lipids as risk factors among different populations” which takes place on 2 September 2024, Station 4 in the Research Gateway.
ESC Press Office
Tel: +33 6 61 40 18 84
Email: press@escardio.org
The hashtag for ESC Congress 2024 is #ESCCongress
Follow us on X @ESCardioNews
Journalists are invited to become accredited and register here.
Check out the ESC Media and Embargo Policy.
About ESC Congress 2024
It is the world’s largest gathering of cardiovascular professionals, disseminating ground-breaking science both onsite in London and online – from 30 August to 2 September. Explore the scientific programme. More information is available from the ESC Press Office at press@escardio.org.
About the European Society of Cardiology
The European Society of Cardiology brings together health care professionals from more than 150 countries, working to advance cardiovascular medicine and help people lead longer, healthier lives.
END
Menopause potentially linked to adverse cardiovascular health through blood fat profile changes
Study shows than women going through menopause or post-menopause experience large adverse changes in blood fat profiles
2024-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Women in global fisheries industry fall through the safety net
2024-08-27
Millions of women who work in the fisheries industry are being left behind as technologies develop to counter the effects of climate change and economic pressures.
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) looks specifically at post-harvest fisheries and aquaculture, where women constitute 50 per cent of the total workforce. Despite their significant contributions women often remain invisible, are unpaid or underpaid, their work seen as an extension of household work.
The findings, ‘A systematic review of the impact of post-harvest aquatic food ...
In six new rogue worlds, Webb Telescope finds more star birth clues
2024-08-27
The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted six likely rogue worlds—objects with planetlike masses but untethered from any star’s gravity—including the lightest ever identified with a dusty disk around it.
The elusive objects offer new evidence that the same cosmic processes that give birth to stars may also play a common role in making objects only slightly bigger than Jupiter.
“We are probing the very limits of the star forming process,” said lead author Adam Langeveld, an astrophysicist at Johns Hopkins University. “If you have an object that looks like a young Jupiter, is it possible that ...
Star lives and afterlives
2024-08-27
A two-faced star, a star as massive as the Sun but as compact as the Moon, and star ‘corpses’ that engulf entire planets and disrupt planetary orbits. Ilaria Caiazzo, an astrophysicist who has made stunning discoveries, joins the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) as a new assistant professor. Her path led her from philosophy to studying stellar evolution and death while managing her broad interests including movie production.
Ilaria Caiazzo has always had a broad spectrum of interests. Her path to astrophysics started in philosophy and ...
Dungeons and Dragons can help autistic people gain confidence and find their inner hero
2024-08-27
Dungeons and Dragons is a hugely popular roleplaying game enjoyed by millions of people all over the world, both in person and online, every day.
However, new research has found it could be particularly beneficial for people with autism, giving them a safe space to engage in social interactions away from some of the challenges they face in their daily lives.
The study, published in the journal Autism, was led by researchers from the University of Plymouth’s School of Psychology along with colleagues at Edge ...
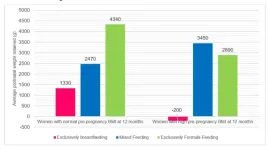
KKH study: Exclusive breastfeeding leads to greater weight loss in women with high body mass index as compared to women with normal weight
2024-08-27
27 August 2024, Singapore – A KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital (KKH) study[1] on breastfeeding practices revealed that among the women who exclusively breastfed, those with high body mass index[2] (BMI) before pregnancy lost more weight than women with a healthy BMI pre-pregnancy.
Women with high BMI who exclusively breastfed, in addition to losing their pregnancy weight, lost an extra 200 grammes on average, 12 months after childbirth. Women with normal BMI who exclusively breastfed lost weight ...
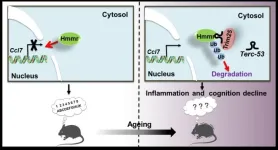
Noncoding RNA Terc-53 and hyaluronan receptor Hmmr regulate aging in mice
2024-08-27
The authors investigate the physiological functions of Terc-53 by creating transgenic mice that overexpress this noncoding RNA. They observe that Terc-53 overexpression affects normal aging in mammals, contributing to cognitive decline and shortened lifespan. Mechanistically, they find that Terc-53 binds to and promotes the degradation of Hmmr, leading to enhanced inflammation in tissues and accelerated aging. They also note that Hmmr levels decrease with age in certain brain regions, similar to Terc-53's pattern, and that restoring Hmmr levels can improve cognitive abilities ...
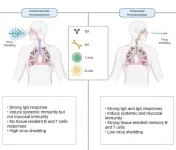
Game-changing needle-free COVID-19 intranasal vaccine
2024-08-27
A next-generation COVID-19 mucosal vaccine is set to be a gamechanger not only when delivering the vaccine itself, but also for people who are needle-phobic.
New Griffith University research, published in Nature Communications, has been testing the efficacy of delivering a COVID-19 vaccine via the nasal passages.
Professor Suresh Mahalingam from Griffith’s Institute for Biomedicine and Glycomics has been working on this research for the past four years.
“This is a live attenuated intranasal vaccine, called CDO-7N-1, designed ...
Preventing counterfeiting by adding dye to liquid crystals to create uncrackable coded tags
2024-08-27
A research group led by Nagoya University has developed an innovative approach to creating anti-counterfeiting labels for high-value goods. Their findings, published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, enhance the security of the currently used cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) by adding fluorescent dyes to produce florescent CLCs (FCLCs).
Using this unique technology, the group created unique labels with almost impossible-to-counterfeit security features. These advanced labels are designed to protect valuable items, important documents, and sensitive products ...
Beckman announces 2024 research seed grant awardees
2024-08-27
The Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology funded two research projects in 2024 as part of its research seed grant program. The program supports interdisciplinary research projects and is now in its second year.
This year, two research projects beginning in May 2024 received $75,000 per year for up to two years.
Research projects seeded by the Beckman Institute anticipate growth and typically lead to external funding proposals after the two-year seeding term.
Exploring how ASD-related genes influence brain networks that guide behavior
The CDC estimates that “1 in 36 children has been identified with autism spectrum disorder,” or ASD.
ASDs ...
Are crops worldwide sufficiently pollinated?
2024-08-27
A team of researchers led by Rutgers University-New Brunswick scientists has analyzed crop yields of more than 1,500 fields on six continents, and found that production worldwide of important, nutritionally dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts and legumes is being limited by a lack of pollinators.
The results, detailed in Nature Ecology & Evolution, showed that across diverse crops and locations, one-third to two-thirds of farms contain fields that aren’t producing at the levels they should be due to a lack of pollinators. The phenomenon of a low crop yield because of insufficient visits by insects is known as pollinator limitation.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] Menopause potentially linked to adverse cardiovascular health through blood fat profile changesStudy shows than women going through menopause or post-menopause experience large adverse changes in blood fat profiles