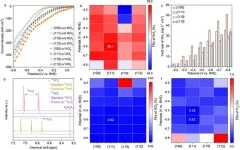
Researchers develop novel organic redox-active molecules for flow batteries
2024-08-28
(Press-News.org)
Organic redox-active molecules (ORAMs) are abundant and diverse, offering significant potential for cost-effective and sustainable energy storage, particularly in aqueous organic flow batteries (AOFBs). However, ensuring the stability of the ORAMs during the charge and discharge process is critical, as side reactions can deactivate them and eliminate their redox activity. Air stability remains a challenge for many ORAMs, complicating their practical use.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LI Xianfeng and Prof. ZHANG Changkun from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DlCP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed novel naphthalene derivatives with active hydroxyls and dimethylamine scaffolds that were stable in air and served as effective catholytes for AOFBs. This study, published in Nature Sustainability, demonstrates that these novel ORAMs can achieve long-term stable cycling even under air-atmosphere conditions.
ORAMs are challenged with instability and high cost, particularly when used without inert gas protection. This can lead to irreversible capacity loss and a reduced battery lifespan.
In this study, the researchers synthesized active naphthalene derivatives using a scalable approach that combined chemical and in situ electrochemical methods. This approach simplified the purification process and significantly reduced the cost of molecular synthesis.
Moreover, the researchers demonstrated specific structure changes in the naphthalene derivatives during the electrochemical process. The as-prepared naphthalene derivatives feature a multisubstituted framework with hydrophilic alkylamine scaffolds, which not only protect against potential side reactions but also improve their solubility in aqueous electrolytes.
The 1.5 mol/L naphthalene-based AOFB displayed stable cycling performance for 850 cycles (about 40 days) with a capacity of 50 Ah L-1. Remarkably, even with continuous air flow in the catholyte, the naphthalene-based AOFB could run smoothly for approximately 600 cycles (about 22 days) without capacity and efficiency decay. This demonstrated that the naphthalene-based catholyte had excellent air stability.
Furthermore, the researchers scaled up the preparation of naphthalene derivatives to the kilogram scale (5 kg per pot). Pilot-scale battery stacks containing these naphthalene derivatives achieved an average system capacity of approximately 330 Ah. They exhibited remarkable cycling stability over 270 cycles (about 27 days), with a capacity retention of 99.95% per cycle.
"This study is expected to open a new field in the design of air-stable molecular for sustainable and air-stable electrochemical energy storage," said Prof. LI.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-28
Imperial College London press release
Under strict embargo until:
Wednesday 28 August 2024
10am UK time/5am Eastern
Study finds limits to storing CO2 underground to combat climate change
Imperial research has found limits to how quickly we can scale up technology to store gigatonnes of carbon dioxide under the Earth’s surface.
Current international scenarios for limiting global warming to less than 1.5 degrees by the end of the century rely on technologies that remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the Earth’s atmosphere faster than humans release it. This means removing ...
2024-08-28
Pain may be the most prevalent and severe symptom reported by individuals with long Covid, according to a new study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The study, published in JRSM Open, analysed data from over 1,000 people in England and Wales who logged their symptoms on an app between November 2020 and March 2022.
Pain, including headache, joint pain and stomach pain, was the most common symptom, reported by 26.5% of participants.
The other most common symptoms were neuropsychological ...
2024-08-28
[Vienna, August 26 2024] – Since the end of the last Ice Age, growth of human population was far from uniform, marked instead by periods of rapid expansion followed by sharp declines. The reasons behind these fluctuations remain only partially understood. Previous research by CSH scientists Peter Turchin, Daniel Kondor, and an international team of collaborators, demonstrated that social conflicts, rather than – or in addition to – environmental factors, could have significantly impacted these patterns. Now, they add another piece to the puzzle.
Wars and conflicts not only cause direct casualties but also create an atmosphere of distress ...
2024-08-28
A new paper in the Journal of Public Health, published by Oxford University Press, finds that highlighting the harms of not getting vaccinated is a more effective message than emphasizing the benefits of vaccination for individual patients or the benefits to public health.
Vaccination remains the most economical and effective public health strategy for reducing morbidity and mortality. But some vaccines, such as those for flu, pneumonia and HPV, are given voluntarily. Often due to misinformation or ignorance many people are reluctant to get vaccinated for various diseases (or to vaccinate their children). For years researchers have been investigating various strategies ...
2024-08-28
Periodontal disease is an inflammatory disease caused by a periodontal pathogenic bacteria infection that affects oral and internal health. Good oral care is essential for prevention, but most over-the-counter oral hygiene products are disinfectants that can be highly irritating. This makes them unsuitable for use by young children and the elderly, who are susceptible to periodontal disease.
To find an antibacterial that is easy to use and effective in preventing periodontal disease at all ages, Professor Shigeki Kamitani of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology led a research team in verifying the antibacterial effect of seven ...
2024-08-28
Since their release, AI tools like ChatGPT have had a huge impact on content creation. In schools and universities, a debate about whether these tools should be allowed or prohibited is ongoing.
Now, researchers in Sweden have investigated the relationship between adolescents’ EF and their use and perceived usefulness of generative AI chatbots for schoolwork. They published their results in Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence.
“Students with more EF challenges found these tools particularly useful, especially for completing assignments,” said Johan Klarin, a school psychologist and research assistant at the Department of Psychology ...
2024-08-28
Researchers have made a significant breakthrough in the development of catalysts for the electrochemical nitrate reduction reaction (eNO₃RR) to ammonia, a process that has broad implications for sustainable energy, agriculture, and industrial applications.
Ammonia, a critical component in global food production, also holds promise as a zero-carbon fuel due to its high energy density, clean combustion products, and established infrastructure for storage and transportation. However, the current method of producing ...
2024-08-28
Indigenous students pursuing nursing careers at the University of Arizona College of Nursing will benefit from additional financial support thanks to a $1.6 million grant from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Indian Health Service.
The grant will fund the successful Indians in Nursing: Career Advancement and Transition Scholars, or INCATS, program for another five years. The program provides Indigenous students at the U of A College of Nursing with financial support for tuition, fees and a living stipend.
Additionally, the grant provides resources for dedicated time and personnel to partner with tribal ...
2024-08-28
How does one species become two? If you’re a biologist, that’s a loaded question. The consensus is that, in most cases, the process of speciation occurs when individuals from a single population become geographically isolated. If they remain separate long enough, they lose the ability to interbreed.
A new study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences demonstrates what happens when a less common form of speciation occurs. Rather than being separated by a physical barrier, such as a mountain range or an ocean, members of a species can become ...
2024-08-28
UVDF Funding, Henna
Henna Secures $30,000 from PSU’s University Venture Development Fund to Enhance AI Fairness & Safety
Portland, OR – August 13, 2024 – Henna, a startup with deep ties to Portland State University (PSU), has successfully secured $30,000 in funding from the University Venture Development Fund (UVDF). This grant will support Henna's mission to make AI adoption fairer and safer.
Henna was founded earlier this year by Arsh Haque (they/them), Chair of the Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop novel organic redox-active molecules for flow batteries