Protect your teeth with fruit: antimicrobial effects found in biomass compounds
A nonirritant, antibacterial solution to prevent oral inflammation may lie in citrus and coconut chemical compounds
2024-08-28
(Press-News.org)
Periodontal disease is an inflammatory disease caused by a periodontal pathogenic bacteria infection that affects oral and internal health. Good oral care is essential for prevention, but most over-the-counter oral hygiene products are disinfectants that can be highly irritating. This makes them unsuitable for use by young children and the elderly, who are susceptible to periodontal disease.
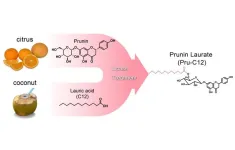
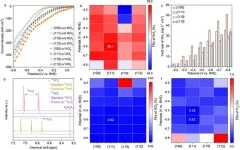
To find an antibacterial that is easy to use and effective in preventing periodontal disease at all ages, Professor Shigeki Kamitani of Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology led a research team in verifying the antibacterial effect of seven different compounds. Prunin laurate (Pru-C12) and its analogs were tested against the periodontal pathogenic bacteria, Porphyromonas gingivalis.
The results showed that while several of the compounds inhibited bacterial growth, Pru-C12, which can be derived from biomass such as that of citrus plants and coconut-derived components, had the highest antimicrobial effect.
“Pru-C12 is tasteless and hypoallergenic,” Professor Kamitani stated. “If its safety in humans is confirmed in the future, it could be an inexpensive antimicrobial solution.”
The findings were published in Foods.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-28
Since their release, AI tools like ChatGPT have had a huge impact on content creation. In schools and universities, a debate about whether these tools should be allowed or prohibited is ongoing.
Now, researchers in Sweden have investigated the relationship between adolescents’ EF and their use and perceived usefulness of generative AI chatbots for schoolwork. They published their results in Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence.
“Students with more EF challenges found these tools particularly useful, especially for completing assignments,” said Johan Klarin, a school psychologist and research assistant at the Department of Psychology ...
2024-08-28
Researchers have made a significant breakthrough in the development of catalysts for the electrochemical nitrate reduction reaction (eNO₃RR) to ammonia, a process that has broad implications for sustainable energy, agriculture, and industrial applications.
Ammonia, a critical component in global food production, also holds promise as a zero-carbon fuel due to its high energy density, clean combustion products, and established infrastructure for storage and transportation. However, the current method of producing ...
2024-08-28
Indigenous students pursuing nursing careers at the University of Arizona College of Nursing will benefit from additional financial support thanks to a $1.6 million grant from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ Indian Health Service.
The grant will fund the successful Indians in Nursing: Career Advancement and Transition Scholars, or INCATS, program for another five years. The program provides Indigenous students at the U of A College of Nursing with financial support for tuition, fees and a living stipend.
Additionally, the grant provides resources for dedicated time and personnel to partner with tribal ...
2024-08-28
How does one species become two? If you’re a biologist, that’s a loaded question. The consensus is that, in most cases, the process of speciation occurs when individuals from a single population become geographically isolated. If they remain separate long enough, they lose the ability to interbreed.
A new study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences demonstrates what happens when a less common form of speciation occurs. Rather than being separated by a physical barrier, such as a mountain range or an ocean, members of a species can become ...
2024-08-28
UVDF Funding, Henna
Henna Secures $30,000 from PSU’s University Venture Development Fund to Enhance AI Fairness & Safety
Portland, OR – August 13, 2024 – Henna, a startup with deep ties to Portland State University (PSU), has successfully secured $30,000 in funding from the University Venture Development Fund (UVDF). This grant will support Henna's mission to make AI adoption fairer and safer.
Henna was founded earlier this year by Arsh Haque (they/them), Chair of the Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion ...
2024-08-28
Work has started on a new Quantum Communications Hub Optical Ground Station (HOGS), a state-of-the-art telescope which is being built on Heriot-Watt University’s Research Park.
The new facility will demonstrate and test satellite quantum secure communications, maintaining and growing the UK’s strength in the field of quantum technologies. It is scheduled to be fully operational by late Autumn [2024].
As well as helping to tackle future cyberattacks by researching methods to send secure transmissions via satellites, it will unlock new research on space environmentalism alongside innovative R&D activities for future laser communication ...
2024-08-28
New York, NY – The State University of New York Board of Trustees today appointed Dr. David Troilo as president of SUNY College of Optometry. He is the 4th president to serve the state’s only college of optometry, following the retirement of Dr. David A. Heath after 17 years of dedicated service to the campus. Dr. Troilo’s appointment is effective immediately.
The SUNY Board of Trustees said, “SUNY College of Optometry is a center of research and academic excellence, and Dr. Troilo is a collaborative and thoughtful leader who is ready to move the campus forward growing ...
2024-08-28
A new applied mathematical theory could enhance our understanding of how sea ice affects global climate, potentially improving the accuracy of climate predictions.
The authors of a new paper published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society A on 28 August, offer new insights into how heat travels through sea ice, a crucial factor in regulating Earth's polar climate.
Dr Noa Kraitzman, Senior Lecturer in Applied Mathematics at Macquarie University and lead author of the study, says the research addresses a key gap in current climate modelling.
“Sea ice covers about 15 per cent of the ocean’s surface during ...
2024-08-28
Individuals with type 2 diabetes who are at higher risk of certain cancers could be identified by a simple blood test, this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September) will hear.
People with type 2 diabetes are known to be at higher risk of developing cancers associated with obesity (OR cancers), including breast, kidney, womb, thyroid and ovarian cancer, as well as gastrointestinal cancers, including colorectal and pancreatic ...
2024-08-27
The University of Texas School of Public Health San Antonio (UT School of Public Health San Antonio), a collaboration between The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA), proudly welcomes its inaugural class and the official launch of the region’s first Master of Public Health (MPH) graduate degree program.
Beginning Monday, Aug. 26, the first cohort of 40 students will attended classes at the new UT School of Public Health San Antonio, located on the Greehey Campus at UT Health San Antonio. Many of the students in the program ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Protect your teeth with fruit: antimicrobial effects found in biomass compounds
A nonirritant, antibacterial solution to prevent oral inflammation may lie in citrus and coconut chemical compounds