miR-10b Inhibition: A strategy for treating metastatic breast cancer
“We have developed a nanodrug, termed MN-anti-miR10b, that delivers anti-miR-10b antisense oligomers to cancer cells.”
2024-08-28
(Press-News.org)
“We have developed a nanodrug, termed MN-anti-miR10b, that delivers anti-miR-10b antisense oligomers to cancer cells.”
BUFFALO, NY- August 28, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on August 26, 2024, entitled, “Inhibition of miR-10b treats metastatic breast cancer by targeting stem cell-like properties.”
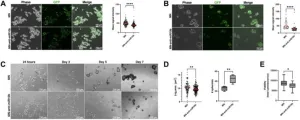
As stated within the Abstract of the paper, despite advances in breast cancer screening and treatment, the prognosis for metastatic disease remains dismal, with only a 30% five-year survival rate. This poor outcome is largely due to the failure of current therapeutics to target the unique properties of metastatic cells. One of the key drivers of metastasis is miR-10b, a small noncoding RNA implicated in cancer cell invasion, migration, viability, and proliferation.
Researchers Alan Halim, Nasreen Al-Qadi, Elizabeth Kenyon, Kayla N. Conner, Sujan Kumar Mondal, Zdravka Medarova, and Anna Moore from Michigan State University’s Precision Health Program, College of Human Medicine, and College of Veterinary Medicine, and Transcode Therapeutics Inc. in Newton, Massachusetts, provide transcriptional evidence that inhibiting miR-10b with MN-anti-miR10b—a nanodrug designed to deliver anti-miR-10b antisense oligomers to cancer cells—activates developmental processes in cancer cells. They observed increased miR-10b expression in stem-like cancer cells.
In mouse models of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, MN-anti-miR10b has been shown to prevent the onset of metastasis and eliminate existing metastases when combined with chemotherapy, even after treatment has been discontinued.
"Our results demonstrate that inhibition of miR-10b using MN-anti-miR10b decreases the stemness of breast cancer cells, supporting dedifferentiation as a mechanism through which the nanodrug may function as a therapy."
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28641
Correspondence to: Anna Moore - moorea57@msu.edu
Video short: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BtaZd_iV8dI
Keywords: breast cancer, metastasis, stem-like cells, nanoparticle, miR-10b
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-28
Male fruit flies will become oblivious to physical danger as they become more engaged in courtship and sex, new research shows.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have shown that pursuit of a coveted reward – in this case a female fly – will cause a male fruit fly to ignore threats such as predation.
In the study, published today (28 Aug) in Nature, the team was able to show for the first time the neural networks in the fly’s brain that direct this decision-making process, revealing the neurotransmitter dopamine has a leading role to play.
Lead researcher Dr Carolina Rezaval said: “Every day we make decisions that require us to ...
2024-08-28
The risk of death for people who donate a kidney for transplantation — already small a decade ago — has dropped by more than half since then, a new study shows.
Each year, roughly 6,000 Americans volunteer to donate a kidney, according to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Before undergoing the procedure, donors are informed of the potential risks, including death. Based on data from 1995 through 2009, experts had originally predicted that about three of every 10,000 donors were likely to die within three months of the procedure. The authors of the ...
2024-08-28
About The Study: Perioperative mortality after living donation declined substantially in the past decade compared with prior decades, to fewer than 1 event per 10,000 donations. Risk was higher for male donors and donors with a history of hypertension. Current guidelines for donor informed consent, based on 2009 data, should be updated to reflect this information.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dorry L. Segev, MD, PhD, email dorry.segev@nyulangone.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.14527)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
2024-08-28
About The Study: Patients with early-onset colorectal cancer (defined as colorectal cancer diagnosed in individuals younger than 50 years) living in rural areas had lower 5-year survival rates than their urban dwelling counterparts in this study. While it was not observed consistently for all age groups, persistent poverty in these rural areas may compound this association.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Meng-Han Tsai, PhD, metsai@augusta.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.30615)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
2024-08-28
About The Study: Prescriptions for first-generation antihistamines were associated with a 22.0% higher seizure risk in children, especially in those ages 6 to 24 months in this cohort study. These findings emphasize the need for careful and judicious prescription of first-generation antihistamines in young children and underline the need for further research to elucidate associations between antihistamine prescriptions and seizure risk.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Seonkyeong Rhie, MD, (starclusters@gmail.com) and Man Yong Han, MD, (drmesh@gmail.com).
To ...
2024-08-28
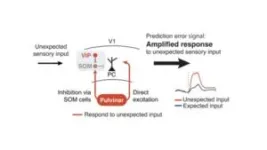
Researchers have discovered how two brain areas, neocortex and thalamus, work together to detect discrepancies between what animals expect from their environment and actual events. These prediction errors are implemented by selective boosting of unexpected sensory information. These findings enhance our understanding of predictive processing in the brain and could offer insights into how brain circuits are altered in autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and schizophrenia spectrum disorders (SSDs).
The research, published today in Nature, outlines how scientists at the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at UCL studied mice in a virtual reality ...
2024-08-28
More people in the UK are at risk of a hereditary form of cardiac amyloidosis, a potentially fatal heart condition, than previously thought, according to a new study led by researchers at UCL (University College London) and Queen Mary University of London.
The study, published in JAMA Cardiology, used data from the UK Biobank to analyse the genes of 469,789 people in the UK and found that one in 1,000 possessed genetic variants with a likely link to cardiac transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis.
Among ...
2024-08-28
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Artificial intelligence is a powerful tool for researchers, but with a significant limitation: The inability to explain how it came to its decisions, a problem known as the “AI black box.” By combining AI with automated chemical synthesis and experimental validation, an interdisciplinary team of researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has opened up the black box to find the chemical principles that AI relied on to improve molecules for harvesting solar energy.
The result produced light-harvesting molecules four times more stable than ...
2024-08-28
In a study that reshapes what we know about COVID-19 and its most perplexing symptoms, scientists have discovered that the blood coagulation protein fibrin causes the unusual clotting and inflammation that have become hallmarks of the disease, while also suppressing the body’s ability to clear the virus.
Importantly, the team also identified a new antibody therapy to combat all of these deleterious effects.
Published in Nature, the study by Gladstone Institutes and collaborators overturns the prevailing ...
2024-08-28
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina — New insights into the biology of kidney cancer, including those informed by scientific discoveries that earned a Nobel Prize, have led to advances in treatment and increased survival rates, according to a review by UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center’s William Kim, MD, and Tracy Rose, MD, MPH.
Their observations, drawn from a meta-analysis of 89 studies published between January 2013 and January 2024, were published in JAMA Aug. 28.
“The Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology in 2019 was awarded ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] miR-10b Inhibition: A strategy for treating metastatic breast cancer
“We have developed a nanodrug, termed MN-anti-miR10b, that delivers anti-miR-10b antisense oligomers to cancer cells.”