(Press-News.org) The Microbiology Society, one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe, is pleased to announce a new three year Publish and Read offering with German consortium ZB Med – Information Centre for Life Sciences, available to its 400 member institutions and 2,000 hospitals. This agreement was established in partnership with HARRASSOWITZ, the Society’s representative agency in Germany.
From 2025, member institutions can join this consortium-wide Publish and Read agreement to enjoy discounted pricing. For participating institutions, the Society’s Publish and Read model allows affiliated researchers:
Uncapped Open Access publishing: corresponding authors from a Publish and Read institution can publish Open Access with no Article Processing Charges (APCs).
Unlimited usage: any user associated with a Publish and Read institution can access the entire archive of Society content, back to 1947.
Publish and Read covers the Society’s entire portfolio, including hybrid titles Journal of General Virology, Journal of Medical Microbiology and International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology and fully Open Access titles Access Microbiology, Microbiology and Microbial Genomics.
Authors can check if their institution is signed up here.
Peter Cotgreave, Chief Executive of the Microbiology Society: “We are delighted to have established this offering for the ZB Med consortium to further support microbiologists across Germany with simple, APC-free Open Access publishing. Germany is a crucial region for the Society’s efforts to advance the field of microbiology and we are grateful for the support of our representatives at HARRASSOWITZ in arranging this wide-reaching, impactful agreement for the German research community.”
Petra Labriga, Head of Strategic Licensing and Acquisitions at ZB MED: “In our role as the German Information Centre for Life Sciences, ZB Med is strongly invested in helping German life scientists publish their work Open Access in an affordable yet highly professional environment. Focusing on the transition to Open Access and transformative agreements for German Life Sciences, we invite all interested German academic and research institutions and hospitals to join this Publish and Read consortium agreement with the Microbiology Society to take advantage of this non-APC based, uncapped author publishing opportunity across all of the Microbiology Society’s journals.”
Monika Schneider, Director of Sales Europe at HARRASSOWITZ: “We are extremely pleased to support German libraries in managing this new agreement. With HARRASSOWITZ's extensive experience in handling transformative agreements and understanding the specific requirements of consortia, we will provide the highest level of precision and align our services with the needs of our clients. We have a long and successful history of working closely with both Microbiology Society and ZB MED, and we are excited to continue this collaboration.”
Microbiology Society
The Microbiology Society is a membership charity for scientists interested in microbes, their effects and their practical uses. It is one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe with a worldwide membership based in universities, industry, hospitals, research institutes and schools.
Contact: Sarah Cooper, Journals Marketing and Development Lead, Microbiology Society – s.cooper@microbiologysociety.org
ZB Med – Information for Life Sciences
Z B Med – Information for Life Sciences is Germany’s national infrastructure and research hub for data and information in the life sciences. Our digital services support research projects that benefit people and the environment from medicine and biodiversity to environmental protection.
HARRASSOWITZ
Established in 1872, HARRASSOWITZ has been serving libraries around the world for more than 150 years. Customers value HARRASSOWITZ for the quality and accuracy of its services and for its industry-leading and innovative solutions. HARRASSOWITZ specializes in providing a comprehensive range of high-quality collection support services to academic and research libraries for e-content, periodicals, continuations, books, and music scores. For more information, see https://www.harrassowitz.de/.
Contact: Monika Schneider, Director of Sales Europe, HARRASSOWITZ – mschneider@harrassowitz.de
The Microbiology Society, one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe, is pleased to announce a new three year Publish and Read offering with German consortium ZB Med – Information Centre for Life Sciences, available to its 400 member institutions and 2,000 hospitals. This agreement was established in partnership with HARRASSOWITZ, the Society’s representative agency in Germany.
From 2025, member institutions can join this consortium-wide Publish and Read agreement to enjoy discounted pricing. For participating institutions, the Society’s Publish and Read model allows affiliated researchers:
Uncapped Open Access publishing: corresponding authors from a Publish and Read institution can publish Open Access with no Article Processing Charges (APCs).
Unlimited usage: any user associated with a Publish and Read institution can access the entire archive of Society content, back to 1947.
Publish and Read covers the Society’s entire portfolio, including hybrid titles Journal of General Virology, Journal of Medical Microbiology and International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology and fully Open Access titles Access Microbiology, Microbiology and Microbial Genomics.
Authors can check if their institution is signed up here.
Peter Cotgreave, Chief Executive of the Microbiology Society: “We are delighted to have established this offering for the ZB Med consortium to further support microbiologists across Germany with simple, APC-free Open Access publishing. Germany is a crucial region for the Society’s efforts to advance the field of microbiology and we are grateful for the support of our representatives at HARRASSOWITZ in arranging this wide-reaching, impactful agreement for the German research community.”
Petra Labriga, Head of Strategic Licensing and Acquisitions at ZB MED: “In our role as the German Information Centre for Life Sciences, ZB Med is strongly invested in helping German life scientists publish their work Open Access in an affordable yet highly professional environment. Focusing on the transition to Open Access and transformative agreements for German Life Sciences, we invite all interested German academic and research institutions and hospitals to join this Publish and Read consortium agreement with the Microbiology Society to take advantage of this non-APC based, uncapped author publishing opportunity across all of the Microbiology Society’s journals.”
Monika Schneider, Director of Sales Europe at HARRASSOWITZ: “We are extremely pleased to support German libraries in managing this new agreement. With HARRASSOWITZ's extensive experience in handling transformative agreements and understanding the specific requirements of consortia, we will provide the highest level of precision and align our services with the needs of our clients. We have a long and successful history of working closely with both Microbiology Society and ZB MED, and we are excited to continue this collaboration.”
Microbiology Society
The Microbiology Society is a membership charity for scientists interested in microbes, their effects and their practical uses. It is one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe with a worldwide membership based in universities, industry, hospitals, research institutes and schools.
Contact: Sarah Cooper, Journals Marketing and Development Lead, Microbiology Society – s.cooper@microbiologysociety.org
ZB Med – Information for Life Sciences
Z B Med – Information for Life Sciences is Germany’s national infrastructure and research hub for data and information in the life sciences. Our digital services support research projects that benefit people and the environment from medicine and biodiversity to environmental protection.
HARRASSOWITZ
Established in 1872, HARRASSOWITZ has been serving libraries around the world for more than 150 years. Customers value HARRASSOWITZ for the quality and accuracy of its services and for its industry-leading and innovative solutions. HARRASSOWITZ specializes in providing a comprehensive range of high-quality collection support services to academic and research libraries for e-content, periodicals, continuations, books, and music scores. For more information, see https://www.harrassowitz.de/.
Contact: Monika Schneider, Director of Sales Europe, HARRASSOWITZ – mschneider@harrassowitz.de
END
New Microbiology Society Publish and Read consortium deal now available to science institutions and hospitals across Germany
2024-08-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Atomic force microscopy upgrade captures 3D images of calcite dissolving
2024-08-29
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, implement modifications to their high-speed atomic force microscopy that simultaneously improve resolution and speed, while enabling direct measurements of 3D structures to provide conclusive evidence of a contested hydration layer forming as calcite dissolves.
Understanding the dissolution processes of minerals can provide key insights into geochemical processes. Attempts to explain some of the observations during the dissolution of calcite (CaCO3) have led to the hypothesis that a hydration layer forms, although this has been contested. Hydration layers are also ...
New research unveils cellular pathways to Alzheimer’s and alternative brain aging
2024-08-29
A new study has found an answer for a long-lasting question in aging research - Is Alzheimer’s disease-dementia a form of accelerated aging or is there a different path that can lead us to healthier brain aging? In an international effort, the researchers mapped 1.65 million cells from 437 aging brains, and uncovered distinct paths of cellular change in the aging brains, with one leading to Alzheimer’s disease and the other to an alternative form brain aging. They also point to specific cell signatures predicted to advance disease once they appear in the aging ...
JMIR Medical Informatics is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled: "Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation"
2024-08-29
Toronto- August 27, 2024 - JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation” in JMIR Medical Informatics, a leading peer-reviewed journal indexed in PubMed with a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes.
The health care landscape is transforming rapidly, driven by technological innovation and the pressing need for more efficient, accessible and patient-centric health care solutions.
Yet, the health IT industry grapples with ...
Terasaki Institute scientist awarded 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant
2024-08-29
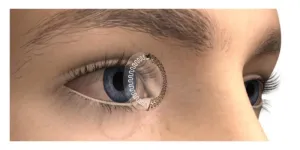
LOS ANGELES, August 29, 2024 — Yangzhi Zhu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), has been awarded the prestigious 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant for his groundbreaking work on a lab-on-a-contact lens (LoCL) system. This innovative technology is designed to monitor mental health by providing real-time, non-invasive tracking of panels of key biomarkers, from the wearer’s tears.
Mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, affect nearly a billion ...
A breakthrough in diagnosing hydrocephalus: Multimodality approaches enhance accuracy and reduce costs
2024-08-29
A recent case report published in Cyborg Bionic Systems details the diagnosis of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (iNPH) using multimodality diagnostic approaches, highlighting significant advancements in medical diagnostics and patient care. The study conducted by a team of researchers from Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China, presents a comprehensive case study of a 68-year-old male patient diagnosed with iNPH, showcasing the effectiveness of these advanced diagnostic techniques.
iNPH is a condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) causing ventricular dilation, ...
This tiny backyard bug does the fastest backflips on earth
2024-08-29
Move over, Sonic. There’s a new spin-jumping champion in town – the globular springtail (Dicyrtomina minuta). This diminutive hexapod backflips into the air, spinning to over 60 times its body height in the blink of an eye, and a new study features the first in-depth look at its jumping prowess.
Globular springtails are tiny, usually only a couple millimeters in body length. They don’t fly, bite or sting. But they can jump. In fact, jumping is their go-to (and only) plan for avoiding predators. And they excel at it – to the naked eye it seems as though they vanish entirely when they take off.
“When globular springtails ...
Climate change increases foodborne illness risk from raw produce
2024-08-29
Highlights:
Salmonella enterica causes disease in 1.2 million people in the U.S. annually.
The most common way people get infected is by consuming contaminated fresh produce.
New research shows that bacterial leaf spot of lettuce and high humidity promote S. enterica growth in lettuce, and climate change is predicted to increase humid periods.
Washington, D.C.—Climate change will increase the risk of the foodborne illness from Salmonella enterica, according to a new study. The research was published today in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
S. enterica causes disease in 1.2 million people in the ...
NSF Grant empowers FAU to explore Caribbean climate crisis with ethnography
2024-08-29
Transformations in the global climate system are profoundly destabilizing ecosystems across the Caribbean, with South Florida and Puerto Rico experiencing notable impacts. To address this challenge, researchers from Florida Atlantic University and the University of Puerto Rico (UPR) in Cayey, are turning to ethnography – an in-depth, immersive research method that involves observing and interviewing people in their natural settings.
FAU’s Dorothy F. Schmidt College of Arts and Letters, in collaboration with UPR Cayey, has received a $650,000 grant from ...
A bacterial defense with potential application in genome editing
2024-08-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists who have described in a new study the step-by-step details of a bacterial defense strategy see the mechanism as a promising platform for development of a new genome-editing method.
The system involves two proteins that team up to disable plasmids, small DNA molecules that exchange genetic information among different bacterial strains. While plasmids provide evolutionary benefits, they can also be seen by host bacteria as threats.
The research team determined that one protein uses a short piece of DNA – known as a DNA guide – to ...
Labor day crowds temporarily impact local streams, research shows
2024-08-29
Crowds flocking to rivers and streams over Labor Day weekend are doing more than cooling off and having fun. They’re temporarily introducing chemicals and microscopic organisms into their local waterways, according to new research from Johns Hopkins University.
The research, published today in ACS ES&T Water, is the first holistic assessment of how recreation impacts streams. Findings also provide insight into the compounds and chemicals people are splashing around in when their favorite swimming spots are packed.
“Residue from ...