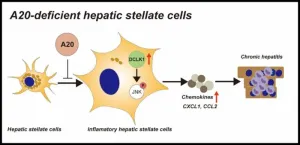
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) determine how a protein called A20 can regulate the inflammatory response to suppress chronic hepatitis
Tokyo, Japan – Many individuals worldwide suffer from chronic liver disease (CLD), which poses significant concerns for its tendency to lead to hepatocellular carcinoma or liver failure. CLD is characterized by inflammation and fibrosis. Certain liver cells, called hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), contribute to both these characteristics, but how they are specifically involved in the inflammatory response is not fully clear. In a recent article published in The FASEB Journal, a team led by researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) uncovered the role of tumor necrosis factor-α-related protein A20, shortened to A20, in this inflammatory signaling.
Previous studies have indicated that A20 has an anti-inflammatory role, as mice lacking this protein develop severe systemic inflammation. Additionally, certain genetic variants in the gene encoding A20 result in autoimmune hepatitis with cirrhosis. This and other published work made the TMDU team become interested in how A20 functions in HSCs to potentially affect chronic hepatitis.
“We developed an experimental line of mice called a conditional knockout, in which about 80% to 90% of the HSCs lacked A20 expression,” says Dr Sei Kakinuma, an author of the study. “We also simultaneously explored these mechanisms in a human HSC cell line called LX-2 to help corroborate our findings in the mice.”
When examining the livers of these mice, the team observed inflammation and mild fibrosis without treating them with any inducing agent. This indicated that the observed inflammatory response was spontaneous, suggesting that HSCs require A20 expression to suppress chronic hepatitis.
“Using a technique called RNA sequencing to determine which genes were expressed, we found that the mouse HSCs lacking A20 displayed expression patterns consistent with inflammation,” describes Dr Yasuhiro Asahina, one of the study’s senior authors. “These cells also showed atypical expression levels of chemokines, which are important inflammation signaling molecules.”
When working with the LX-2 human cells, the researchers made similar observations to those for the mouse HSCs. They then used molecular techniques to express high amounts of A20 in the LX-2 cells, which resulted in decreased chemokine expression levels. Through further investigation, the team identified the specific mechanism regulating this phenomenon.
“Our data suggest that a protein called DCLK1 can be inhibited by A20. DCLK1 is known to activate an important pro-inflammatory pathway, known as JNK signaling, that increases chemokine levels,” explains Dr Kakinuma.
Inhibiting DCLK1 in cells with A20 expression knocked down resulted in much lower chemokine expression, further supporting that A20 is involved in inflammation in HSCs through the DCLK1-JNK pathway.
Overall, this study provides impactful findings that emphasize the potential of A20 and DCLK1 in novel therapeutic development for chronic hepatitis.
###
The article, “A20 in hepatic stellate cells suppresses chronic hepatitis by inhibiting DCLK1-JNK pathway-dependent chemokines,” was published in The FASEB Journal at DOI: 10.1096/fj.202400109R
END
Finding new targets for blocking chronic hepatitis
2024-08-29
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New Microbiology Society Publish and Read consortium deal now available to science institutions and hospitals across Germany
2024-08-29
The Microbiology Society, one of the largest microbiology societies in Europe, is pleased to announce a new three year Publish and Read offering with German consortium ZB Med – Information Centre for Life Sciences, available to its 400 member institutions and 2,000 hospitals. This agreement was established in partnership with HARRASSOWITZ, the Society’s representative agency in Germany.
From 2025, member institutions can join this consortium-wide Publish and Read agreement to enjoy discounted pricing. For participating institutions, the ...
Atomic force microscopy upgrade captures 3D images of calcite dissolving
2024-08-29
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, implement modifications to their high-speed atomic force microscopy that simultaneously improve resolution and speed, while enabling direct measurements of 3D structures to provide conclusive evidence of a contested hydration layer forming as calcite dissolves.
Understanding the dissolution processes of minerals can provide key insights into geochemical processes. Attempts to explain some of the observations during the dissolution of calcite (CaCO3) have led to the hypothesis that a hydration layer forms, although this has been contested. Hydration layers are also ...
New research unveils cellular pathways to Alzheimer’s and alternative brain aging
2024-08-29
A new study has found an answer for a long-lasting question in aging research - Is Alzheimer’s disease-dementia a form of accelerated aging or is there a different path that can lead us to healthier brain aging? In an international effort, the researchers mapped 1.65 million cells from 437 aging brains, and uncovered distinct paths of cellular change in the aging brains, with one leading to Alzheimer’s disease and the other to an alternative form brain aging. They also point to specific cell signatures predicted to advance disease once they appear in the aging ...
JMIR Medical Informatics is inviting submissions for a new theme issue titled: "Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation"
2024-08-29
Toronto- August 27, 2024 - JMIR Publications invites submissions to a new theme issue titled “Advancing Digital Health: Real-World Implementation and Strategic Insights from Industry-Driven Innovation” in JMIR Medical Informatics, a leading peer-reviewed journal indexed in PubMed with a unique focus on clinical informatics and the digitization of care processes.
The health care landscape is transforming rapidly, driven by technological innovation and the pressing need for more efficient, accessible and patient-centric health care solutions.
Yet, the health IT industry grapples with ...
Terasaki Institute scientist awarded 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant
2024-08-29
LOS ANGELES, August 29, 2024 — Yangzhi Zhu, Ph.D., Assistant Professor at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), has been awarded the prestigious 2024 NARSAD Young Investigator Grant for his groundbreaking work on a lab-on-a-contact lens (LoCL) system. This innovative technology is designed to monitor mental health by providing real-time, non-invasive tracking of panels of key biomarkers, from the wearer’s tears.
Mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, affect nearly a billion ...
A breakthrough in diagnosing hydrocephalus: Multimodality approaches enhance accuracy and reduce costs
2024-08-29
A recent case report published in Cyborg Bionic Systems details the diagnosis of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (iNPH) using multimodality diagnostic approaches, highlighting significant advancements in medical diagnostics and patient care. The study conducted by a team of researchers from Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, Tianjin, China, presents a comprehensive case study of a 68-year-old male patient diagnosed with iNPH, showcasing the effectiveness of these advanced diagnostic techniques.
iNPH is a condition characterized by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) causing ventricular dilation, ...
This tiny backyard bug does the fastest backflips on earth
2024-08-29
Move over, Sonic. There’s a new spin-jumping champion in town – the globular springtail (Dicyrtomina minuta). This diminutive hexapod backflips into the air, spinning to over 60 times its body height in the blink of an eye, and a new study features the first in-depth look at its jumping prowess.
Globular springtails are tiny, usually only a couple millimeters in body length. They don’t fly, bite or sting. But they can jump. In fact, jumping is their go-to (and only) plan for avoiding predators. And they excel at it – to the naked eye it seems as though they vanish entirely when they take off.
“When globular springtails ...
Climate change increases foodborne illness risk from raw produce
2024-08-29
Highlights:
Salmonella enterica causes disease in 1.2 million people in the U.S. annually.
The most common way people get infected is by consuming contaminated fresh produce.
New research shows that bacterial leaf spot of lettuce and high humidity promote S. enterica growth in lettuce, and climate change is predicted to increase humid periods.
Washington, D.C.—Climate change will increase the risk of the foodborne illness from Salmonella enterica, according to a new study. The research was published today in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
S. enterica causes disease in 1.2 million people in the ...
NSF Grant empowers FAU to explore Caribbean climate crisis with ethnography
2024-08-29
Transformations in the global climate system are profoundly destabilizing ecosystems across the Caribbean, with South Florida and Puerto Rico experiencing notable impacts. To address this challenge, researchers from Florida Atlantic University and the University of Puerto Rico (UPR) in Cayey, are turning to ethnography – an in-depth, immersive research method that involves observing and interviewing people in their natural settings.
FAU’s Dorothy F. Schmidt College of Arts and Letters, in collaboration with UPR Cayey, has received a $650,000 grant from ...
A bacterial defense with potential application in genome editing
2024-08-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists who have described in a new study the step-by-step details of a bacterial defense strategy see the mechanism as a promising platform for development of a new genome-editing method.
The system involves two proteins that team up to disable plasmids, small DNA molecules that exchange genetic information among different bacterial strains. While plasmids provide evolutionary benefits, they can also be seen by host bacteria as threats.
The research team determined that one protein uses a short piece of DNA – known as a DNA guide – to ...