A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240061, discusses soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes.
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a coherent light source consisting of a series of discrete, equally spaced and phase-locked frequency lines, which is crucial for practical applications in building optical clocks, searching Earth-like exoplanets, exploring quantum optics, optical frequency synthesis, high-resolution optical spectroscopy, lidar, high-speed telecom communication, microwave photonics, and many others.
In recent years, on-chip soliton microcomb, which finely balances the dispersion with Kerr nonlinearity, has become one of the most important members of the comb family due to their high energy efficiency, compact size, robustness, high repetition rate, and low-cost manufacturing, providing new opportunities in device miniaturizing and having an immediate impact on the fields of information processing, time–frequency metrology and sensing. And various material platforms such as silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, calcium fluoride, magnesium fluoride, silica, silicon, silicon carbide, AlGaAs, chalcogenide glass, high-index doped silica, and lithium niobate have been employed for microcomb generation, utilizing the second-order (quadratic comb) or third-order (Kerr comb) nonlinear optical properties of the involved materials.
To form a stable soliton pulse train in time for miniaturized comb generation, the cavity is required to operate in an anomalous dispersion regime to balance Kerr nonlinearity. And such a requirement has been successfully fulfilled through structural dispersion engineering of the cavity whispering gallery mode (WGM), which is highly sensitive to geometrical dispersion and fabrication imperfection, inevitably leading to degraded Q-factors and higher pump threshold. Moreover, in popular material platforms such as thin-film lithium niobate (LN), which has high second-order nonlinearity and strong electro-optic effect, soliton comb generation has been demonstrated, offering distinct functionalities for generating soliton microcombs featuring high-speed modulation, self-referencing and self-starting. However, soliton comb generation in LN platform can be easily impaired by the competing stimulated Raman scattering due to its high Raman activities, causing even higher pump threshold power for soliton formation. For these reasons, the Kerr soliton microcomb has not yet been observed in single normal dispersion microcavities, allowing low pump power operation by leveraging the ultra-high Q factors.
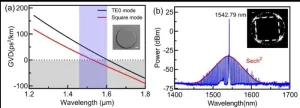
The authors of this article demonstrated a soliton microcomb excited by cavity polygon modes. The cavity polygon modes were formed through the coherent combination of quasi-degenerate WGMs in a normal-dispersion LN disk microcavity with the assistance of weak perturbations introduced by a coupled tapered fiber. Unlike the WGM counterpart, light in polygon modes propagates in a trajectory that is mostly away from the rough cavity edge and light coupling element. Consequently, the edge induced scattering loss is significantly reduced and the coupling loss is low even the tapered fiber is place in contact with the cavity, leading to a high loaded Q factor of 4.1´106, which is higher than that of fundamental WGM of 3.0´106. Meanwhile, the spatial distribution characteristics of polygon modes have small modal overlaps with other mode families, which further suppresses Raman effects and mode crossings. More importantly, compared with WGMs, polygon mode induced by weak perturbation is protected by the classical orbit, thus a lower dispersion occurs in polygon mode due to its stable geometrical conditions. As a result, polygon modes possess anomalous group velocity dispersion (GVD) of -4.9 ps2/km even the LN material displays a normal dispersion of 25.5ps2/km in the telecom band, as shown in Fig. 1(a). Consequently, by scanning the input wavelength across the resonance from the red-detuned side to the blue-detuned side of the polygon mode around 1542.8 nm, soliton microcomb with a spectrum spanning from 1450 nm to 1620 nm was observed, which is confirmed by a smooth sech2 shaped spectrum envelop, as depicted in Fig. 1 (b). Due to these advantages, an on-chip record-low pump power of 11.1 mW is demonstrated in LN platform.
Therefore, ultra-high Q polygon modes have been coherently formed through coherent mode recombination and utilized to provide anomalous dispersion, which facilitate soliton comb generation with low pump power operation and greatly suppress the mode crossing and stimulated Raman scattering. This technique makes the Kerr soliton microcomb generation insensitive to the geometric dispersion of the microcavities and allows higher Q factors for low pump power operation, which has profound implication because otherwise there is an inevitable high price to pay for achieving a qualified microcavity that has an ultra-high Q factors and anomalous dispersion property, allowing soliton microcomb generated with low pump power.
In this work, the research team fabricated ultra-high Q (>3´106) LN microcavities using femtosecond laser photolithography assisted chemo-mechanical etching technique invented by Prof. Ya Cheng et al.. Benefitting from the studies in the formation and manipulation of polygon modes in weakly perturbed LN microcavities previously carried out by the research group, Jintian Lin et al. discovered a novel phenomenon that the soliton comb could be generated by polygon modes in the normal-dispersion LN microcavities. Botao Fu performed theoretical simulation. Prof. Ya Cheng, Jintian Lin, and Ni Yao analyzed and discussed the experimental and simulation results and revealed the novel dispersion tailoring mechanics for the soliton comb generated by cavity polygon mode.
Keywords: thin-film lithium niobate / nonlinear optics / microresonators
# # # # # #
This work was led by Prof. Ya Cheng, who earned his B.S. degree in Physics from Fudan University in 1993 and his Ph.D. from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (SIOM), Chinese Academy of Sciences in 1998. He is currently a professor at both East China Normal University and SIOM. His research primarily focuses on ultrafast photonics, femtosecond laser micromachining, and integrated photonics. Prof. Cheng is a Fellow of both the Institute of Physics (London) and Optica.
# # # # # #
Opto-Electronic Advances (OEA) is a rapidly growing high-impact, open access, peer reviewed monthly SCI journal with an impact factor of 15.3 (Journal Citation Reports for IF2023). OEA has been indexed in SCI, EI, DOAJ, Scopus, CA and ICI databases, and expanded its Editorial Board to 31 members from 17 countries with an average h-index of 62.
The journal is published by The Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, aiming at providing a platform for researchers, academicians, professionals, practitioners, and students to impart and share knowledge in the form of high quality empirical and theoretical research papers covering the topics of optics, photonics and optoelectronics.
# # # # # #
More information: http://www.oejournal.org/oea
Editorial Board: http://www.oejournal.org/oea/editorialboard/list
All issues available in the online archive (http://www.oejournal.org/oea/archive).
Submissions to OEA may be made using ScholarOne (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/oea).
ISSN: 2096-4579
CN: 51-1781/TN
Contact Us: oea@ioe.ac.cn
Twitter: @OptoElectronAdv (https://twitter.com/OptoElectronAdv?lang=en)
WeChat: OE_Journal
# # # # # #
Fu BT, Gao RH, Yao N et al. Soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes. Opto-Electron Adv 7, 240061 (2024). doi: 10.29026/oea.2024.240061
END