(Press-News.org) London, UK, 30 August 2024: Updated ESC Guidelines on the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension include a new elevated blood pressure category, more ambitious and intensive treatment targets, and, for the first time, recommendations on the use of renal denervation to treat various forms of hypertension. The Guidelines have been produced by an international panel of experts that include co-Chairpersons Professor Bill McEvoy of the University of Galway, Ireland, and Professor Rhian Touyz of McGill University, Canada.
Elevated blood pressure and hypertension are by far the most common and important risk factors for heart attack and stroke (otherwise known as cardiovascular disease). As many as 45% of European adults have hypertension.1
The new guidelines are designed to get more patients to an evidence-based blood pressure treatment target and to increase the eligibility for blood pressure lowering medications to match the best current evidence from clinical trials. The ESC Guidelines also provide numerous pragmatic recommendations to avoid patients becoming symptomatic from overtreatment.
The 2024 Guidelines maintain the existing definition for 'Hypertension' as a BP ≥140/90 mmHg. However, they introduce a new category of 'Elevated BP' which is defined as a BP 120-139/70-89 mmHg. This new 'Elevated BP' category is introduced to facilitate consideration of more intensive blood pressure treatment targets among persons at increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
“This new category of elevated blood pressure recognises that people do not go from normal BP to hypertensive overnight,” says Prof McEvoy. “It is in most cases a steady gradient of change, and different subgroups of patients – for example those at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease (e.g. people living with diabetes’) – could benefit from more intensive treatment before their BP reaches the traditional threshold of hypertension.” Moreover, adds Prof Touyz: “The risks associated with increased blood pressure start at systolic blood pressure levels even below 120 mmHg.”
In another major change, the 2024 ESC Guidelines introduce a new systolic BP treatment target range of 120-129 mmHg for most patients receiving BP-lowering medication, with the important proviso that the new target requires that treatment is well tolerated. The 2024 ESC Guidelines also provide pragmatic recommendations on a systolic BP target 'as low as reasonably achievable' (known as the ALARA principle) in frail and older persons and in those not tolerating the primary treatment target of 120-129 mmHg. The guidelines focus more on ‘frailty’ of individuals rather than chronological age.
This new systolic BP treatment target of 120-129 represents a paradigm shift from prior European guidelines, including the 2018 ESC/ESH Hypertension Guidelines, the 2021 ESC Prevention Guidelines, and the 2023 ESH Hypertension Guidelines. Specifically, whereas prior guidelines generally recommended patients be treated to a BP <140/90 mmHg in the first instance and only thereafter be considered for treatment to <130/80 mmHg (a 2-step approach) the new 2024 guidelines recommend that most patients be treated to a systolic BP of 120-129 mmHg in the first instance (those who cannot tolerate this target can have it relaxed). “This change is driven by new trial evidence confirming that more intensive BP treatment targets reduce CVD outcomes across a broad spectrum of eligible patients”, says Prof. McEvoy.
In part to accommodate this new more intensive systolic BP treatment target range, the 2024 ESC Guidelines provide stronger recommendations than prior guidelines for the use of out-of-office BP measurements (including ambulatory BP monitors and validated home BP monitors).
The 2024 Guidelines also, for the first time, make recommendations on the use of renal denervation for treatment of hypertension. Due to lack of evidence regarding cardiovascular outcomes benefit, the guidelines do not recommend this medical procedure as first line treatment, and nor is it recommended for patients with highly impaired renal function, (eGFR <40 mL/min/1.73 m2) or secondary causes of hypertension.
On renal denervation, the guidelines say: “To reduce BP, and if performed at a medium-to-high volume centre, catheter-based renal denervation may be considered for patients with resistant hypertension who have BP that is uncontrolled despite a three BP-lowering drug combination (including a thiazide or thiazide-like diuretic), and who express a preference to undergo renal denervation after a shared risk-benefit discussion and multidisciplinary assessment.”
Prof Touyz explains: “These evidence-based recommendations provide guidance for clinicians and their patients on the use of this important new technology. However, it must be stressed that this procedure needs to be undertaken in a centre where there is expertise and experience.”
These new ESC Guidelines also update dietary advice on sodium and potassium intake and further emphasise the importance of life-style modifications for patients in a range of different circumstances and stages of CVD and chronic kidney disease. They also highlight the importance of sex and gender differences in hypertension and integrate this throughout the document, rather than as a separate section, as in most other guidelines.
ENDS
Disclosures: Please see full guidelines for all disclosures.
References and notes
The Guidelines ‘2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of elevated blood pressure and hypertension’ will be discussed during the session “2024 ESC Guidelines overview”, Friday 30 August at 8:15am BST in room London.
2024 ESC Guidelines for the Management of Elevated Blood Pressure and Hypertension. European Heart Journal. 2024, https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehae178
1. JAMA. 2003;289(18):2363-2369
ESC Press Office
Tel: +33 6 61 40 18 84
Email: press@escardio.org
The hashtag for ESC Congress 2024 is #ESCCongress
Follow us on X @ESCardioNews
Journalists are invited to become accredited and register here.
Check out the ESC Media and Embargo Policy.
About ESC Congress 2024
It is the world’s largest gathering of cardiovascular professionals, disseminating ground-breaking science both onsite in London and online – from 30 August to 2 September. Explore the scientific programme. More information is available from the ESC Press Office at press@escardio.org.
About the European Society of Cardiology
The European Society of Cardiology brings together health care professionals from more than 150 countries, working to advance cardiovascular medicine and help people lead longer, healthier lives.
END
New ESC Hypertension Guidelines recommend intensified BP targets and introduce a novel elevated blood pressure category to better identify people at risk for heart attack and stroke
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New ESC Guidelines combine peripheral arterial and aortic diseases for first time, emphasising interconnectivity of whole arterial system
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: The 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of peripheral arterial and aortic diseases (PAAD) evaluate these vascular diseases together as part of same cardiovascular system, appreciating that patients with aortic diseases are at risk of having peripheral vascular diseases and vice versa. The Guidelines are aimed at cardiologists, but were coordinated for alignment with guidelines for surgeons by EACTS and endorsed by VASCERN and ESVM.
“These updated guidelines have been introduced now due to significant advancements and shifts in our understanding and management of aortic and peripheral ...
New Chronic Coronary Syndrome (CCS) Guidelines expand diagnostic tools and ways to prevent major adverse events and enhance quality of life
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: The 2024 ESC Guidelines on the management of chronic coronary syndromes (CCS) include a focus on both larger and smaller blood vessels of the heart; new models to estimate chances of blocked large arteries (so-called obstructive coronary artery disease); optimal selection and sequence of tests; drugs and interventions to prevent disease complications and improve symptoms, and the fundamental role of patient involvement.
“The new guidelines prompt cardiologists to rethink chronic coronary syndromes ...
Atrial fibrillation guidelines focus on shared and equal care, patient empowerment, comorbidities, evidence-based management and dynamic re-evaluation
2024-08-30
London, UK, 30 August 2024: The 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation, developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), contain a number of new approaches and treatment-specific recommendations to help manage the surging numbers of patients with AF worldwide.
“Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the most commonly encountered heart conditions, with a broad impact on all health services across primary, secondary and tertiary care,” says Guidelines Chair Professor Isabelle C. Van Gelder, University Medical Centre Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands. “The prevalence ...
Two thirds of deaths related to high BMI are due to cardiovascular diseases - ESC Clinical Consensus Statement on Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease
2024-08-30
London, United Kingdom – 30 August 2024: The ESC Clinical Consensus Statement on Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease, presented at this year’s ESC Congress (London, UK, 30 August to 2 September) summarises current evidence on the epidemiology and aetiology of obesity; the interplay between obesity, cardiovascular risk factors and cardiac conditions; the clinical management of patients with cardiac disease and obesity; and weight loss strategies including lifestyle changes, interventional procedures, and anti-obesity medications with particular focus ...
Prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
2024-08-30
About The Study: In patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, treatment with prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid did not reduce final infarct size after 3 months. However, the trial was likely underpowered as the final infarct size was smaller than anticipated. The glucocorticoid group had improved acute parameters compared with placebo.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jasmine Melissa Madsen, MD, email jasmine.melissa.madsen.01@regionh.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.2298)
Editor’s ...
Effects of sacubitril/valsartan on all-cause hospitalizations in heart failure
2024-08-30
About The Study: In this post hoc pooled analysis of 13,194 patients with chronic heart failure (HF) in the PARADIGM-HF and PARAGON-HF randomized clinical trials, sacubitril/valsartan significantly reduced hospitalization for any reason, with benefits most apparent in patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below normal. This reduction appeared to be principally driven by lower rates of cardiac and pulmonary hospitalizations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, email mvaduganathan@bwh.harvard.edu.
To ...
Promising antibiotic candidates discovered in microbes deep in the Arctic Sea
2024-08-30
Antibiotics are the linchpin of modern medicine: without them, anyone with open wounds or needing to undergo surgery would be at constant risk of dangerous infections. Yet we continue to face a global antibiotics crisis, as more and more resistant strains of bacteria are evolving, while the rate of discovery of fundamentally new antibiotics has been much slower.
But there is reason for hope: 70% of all currently licensed antibiotics have been derived from actinobacteria in the soil, and most environments on Earth have not yet ...
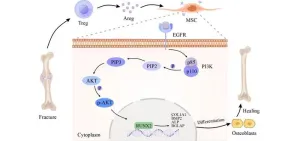
A distinct “repair” role of regulatory T cells in fracture healing
2024-08-30
The study uncovers a unique reparative function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the process of fracture healing, a discovery that adds a new dimension to our understanding of the immune response in tissue regeneration. Tregs, a subset of T cells known for their role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity, are now shown to play a critical part in the intricate interplay between the immune system and bone repair.
Fracture healing is a complex process that involves a sequence of events, including inflammation, repair, and remodeling. While the initial ...
Dancing galaxies make a monster at the cosmic dawn
2024-08-30
Astronomers have spotted a pair of galaxies in the act of merging 12.8 billion years ago. The characteristics of these galaxies indicate that the merger will form a monster galaxy, one of the brightest types of objects in the Universe. These results are important for understanding the early evolution of galaxies and black holes in the early Universe.
Quasars are bright objects powered by matter falling into a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy in the early Universe. The most accepted theory is that when two gas-rich galaxies merge to form a single larger galaxy, the gravitational interaction of the two galaxies causes gas to fall towards the supermassive ...
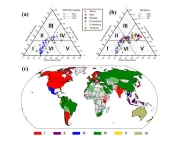
Drought risk and awareness gaps in global society
2024-08-30
Natural disasters have threatened to human beings and the ecosystem. Among the various natural disasters, drought is one of the most insidious and costliest, adversely affecting the global economy and livelihoods. Unlike sudden disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes, drought is a slow-onset phenomenon that gradually intensifies. This prolonged nature of drought often results in the shortage of drinking water and the disruption of local economies.
The Slow Onset and Impact of Drought
Drought creeps in gradually, often going unnoticed until it reaches a critical stage. This slow progression makes drought particularly challenging to manage and mitigate. Initially, ...