(Press-News.org) About The Study: In patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, treatment with prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid did not reduce final infarct size after 3 months. However, the trial was likely underpowered as the final infarct size was smaller than anticipated. The glucocorticoid group had improved acute parameters compared with placebo.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jasmine Melissa Madsen, MD, email jasmine.melissa.madsen.01@regionh.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2024.2298)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflicts of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2024.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/10.1001/jamacardio.2024.2298?guestAccessKey=a0145eff-4cd6-44be-ae67-9c736ee0ef94&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=083024
END
Prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
JAMA Cardiology
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Effects of sacubitril/valsartan on all-cause hospitalizations in heart failure
2024-08-30
About The Study: In this post hoc pooled analysis of 13,194 patients with chronic heart failure (HF) in the PARADIGM-HF and PARAGON-HF randomized clinical trials, sacubitril/valsartan significantly reduced hospitalization for any reason, with benefits most apparent in patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction below normal. This reduction appeared to be principally driven by lower rates of cardiac and pulmonary hospitalizations.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Muthiah Vaduganathan, MD, MPH, email mvaduganathan@bwh.harvard.edu.
To ...
Promising antibiotic candidates discovered in microbes deep in the Arctic Sea
2024-08-30
Antibiotics are the linchpin of modern medicine: without them, anyone with open wounds or needing to undergo surgery would be at constant risk of dangerous infections. Yet we continue to face a global antibiotics crisis, as more and more resistant strains of bacteria are evolving, while the rate of discovery of fundamentally new antibiotics has been much slower.
But there is reason for hope: 70% of all currently licensed antibiotics have been derived from actinobacteria in the soil, and most environments on Earth have not yet ...
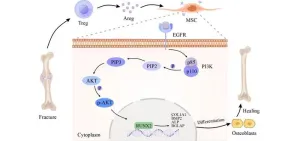
A distinct “repair” role of regulatory T cells in fracture healing
2024-08-30
The study uncovers a unique reparative function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the process of fracture healing, a discovery that adds a new dimension to our understanding of the immune response in tissue regeneration. Tregs, a subset of T cells known for their role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity, are now shown to play a critical part in the intricate interplay between the immune system and bone repair.
Fracture healing is a complex process that involves a sequence of events, including inflammation, repair, and remodeling. While the initial ...
Dancing galaxies make a monster at the cosmic dawn
2024-08-30
Astronomers have spotted a pair of galaxies in the act of merging 12.8 billion years ago. The characteristics of these galaxies indicate that the merger will form a monster galaxy, one of the brightest types of objects in the Universe. These results are important for understanding the early evolution of galaxies and black holes in the early Universe.
Quasars are bright objects powered by matter falling into a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy in the early Universe. The most accepted theory is that when two gas-rich galaxies merge to form a single larger galaxy, the gravitational interaction of the two galaxies causes gas to fall towards the supermassive ...
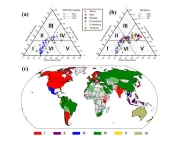
Drought risk and awareness gaps in global society
2024-08-30
Natural disasters have threatened to human beings and the ecosystem. Among the various natural disasters, drought is one of the most insidious and costliest, adversely affecting the global economy and livelihoods. Unlike sudden disasters such as earthquakes or hurricanes, drought is a slow-onset phenomenon that gradually intensifies. This prolonged nature of drought often results in the shortage of drinking water and the disruption of local economies.
The Slow Onset and Impact of Drought
Drought creeps in gradually, often going unnoticed until it reaches a critical stage. This slow progression makes drought particularly challenging to manage and mitigate. Initially, ...
UAF scientist’s method could give months’ warning of major earthquakes
2024-08-30
The public could have days or months of warning about a major earthquake through identification of prior low-level tectonic unrest over large areas, according to research by a University of Alaska Fairbanks scientist who analyzed two major quakes in Alaska and California.
The work was led by research assistant professor Társilo Girona of the UAF Geophysical Institute.
Girona, a geophysicist and data scientist, studies precursory activity of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. Geologist Kyriaki Drymoni of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität in Munich, Germany, is a co-author.
The ...
Consensus paper: Carcinogenicity of gene therapies
2024-08-30
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, Gene Therapy Program, and Moderna, have shown that repeated administration of lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated mRNA therapy significantly extended survival and reduced serum leucine levels in a mouse model of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Click here to read the article now.
The researchers, led by James Wilson, MD, PhD, from the University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, evaluated a lipid nanoparticle-based treatment approach to address all possible genetic mutations that can cause MSUD.
“Repeated intravenous delivery ...
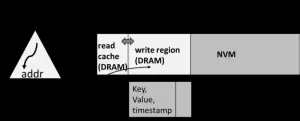
HeterMM: Applying in-DRAM index to heterogeneous memory-based key-value stores
2024-08-30
Emerging byte-addressable storage technologies, such as NVM, provide a more cost-effective and larger-capacity alternative to DRAM, presenting new opportunities to address the high cost, limited capacity, and volatility of in-memory key-value (KV) stores. Numerous efforts have been dedicated to redesigning conventional structures on NVM. However, they were challenged by the substantial engineering cost and increased complexity to be integrated into existing systems. Thus, a general framework to apply existing indexes to KV stores on NVM becomes more attractive.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Xuan Zhou published their new research on ...
Several advantages when medical abortion is started at home
2024-08-30
Being at home is as safe as at the hospital when a medical abortion after twelve weeks of pregnancy is initiated. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. When starting at home, day patient care is usually sufficient, and women are satisfied with the treatment.
In the case of medical abortion up to and including the tenth week of pregnancy, the procedure used is a so-called home abortion. At ten to twelve weeks, day patient care is most commonly used, while s medical abortion after twelve ...
Northwestern receives $55 million to advance health research
2024-08-30
Funding will enable discoveries for diverse populations to go from lab to clinical care settings
Will translate scientific research to treatments, therapies that can improve patients’ quality of life
Institute will infuse implementation-science methods into research to make public health improvements more scalable
‘Clinical and translational research does not happen in a bubble’
CHICAGO --- The Northwestern University Clinical and Translational Sciences (NUCATS) Institute has received $55 million in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding to accelerate the development, evaluation and implementation of improved health care interventions.
The seven-year ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
[Press-News.org] Prehospital pulse-dose glucocorticoid in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarctionJAMA Cardiology