(Press-News.org) The public could have days or months of warning about a major earthquake through identification of prior low-level tectonic unrest over large areas, according to research by a University of Alaska Fairbanks scientist who analyzed two major quakes in Alaska and California.
The work was led by research assistant professor Társilo Girona of the UAF Geophysical Institute.
Girona, a geophysicist and data scientist, studies precursory activity of volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. Geologist Kyriaki Drymoni of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität in Munich, Germany, is a co-author.
The detection method, based on machine learning, was published Aug. 28 in Nature Communications.
“Our paper demonstrates that advanced statistical techniques, particularly machine learning, have the potential to identify precursors to large-magnitude earthquakes by analyzing datasets derived from earthquake catalogs,” Girona said.
The authors wrote a computer algorithm to search the data to look for abnormal seismic activity. Algorithms are a set of computer instructions that teach a program to interpret data, learn from it and make informed predictions or decisions.
They focused on two major earthquakes: the 2018 magnitude 7.1 Anchorage earthquake and the 2019 Ridgecrest, California, earthquake sequence of magnitudes 6.4 to 7.1.
They found that approximately three months of abnormal low-magnitude regional seismicity had occurred across about 15% to 25% of Southcentral Alaska and Southern California prior to each of the two studied earthquakes.
Their research finds that unrest preceding major earthquakes is mostly captured by seismic activity with magnitude below 1.5.
The Anchorage earthquake occurred Nov. 30, 2018, at 8:29 a.m., with an epicenter located approximately 10.5 miles north of the city. It caused extensive damage to some roads and highways, and several buildings sustained damage.
Using their data-trained program, Girona and Drymoni found with the Anchorage earthquake that the probability that a major earthquake would happen in 30 days or fewer increased abruptly up to approximately 80% around three months before the Nov. 30 earthquake. The probability increased to approximately 85% just a few days before it occurred. They had similar probability findings for the Ridgecrest earthquake sequence for a period beginning about 40 days prior to the onset of the quake sequence.
Girona and Drymoni propose a geologic cause for the low-magnitude precursor activity: A significant increase in pore fluid pressure within a fault.
Pore fluid pressure refers to the pressure of fluid within a rock. High pore fluid pressures can potentially lead to fault slip if the pressure is sufficient to overcome the frictional resistance between the blocks of rock on either side of the fault.
“Increased pore fluid pressure in faults that lead to major earthquakes changes the faults’ mechanical properties, which in turn leads to uneven variations in the regional stress field,” Drymoni said. “We propose that these uneven variations … control the abnormal, precursory low-magnitude seismicity.”
Machine learning is having a major positive impact on earthquake research, Girona said.
“Modern seismic networks produce enormous datasets that, when properly analyzed, can offer valuable insights into the precursors of seismic events,” he said. “This is where advancements in machine learning and high-performance computing can play a transformative role, enabling researchers to identify meaningful patterns that could signal an impending earthquake.”
The authors state that their algorithm will be tested in near-real-time situations to identify and address potential challenges for earthquake forecasting. The method should not be employed in new regions without training the algorithm with that area’s historical seismicity, they add.
Producing reliable earthquake forecasts has a “deeply important and often controversial dimension,” Girona said.
“Accurate forecasting has the potential to save lives and reduce economic losses by providing early warnings that allow for timely evacuations and preparation,” he said. “However, the uncertainty inherent in earthquake forecasting also raises significant ethical and practical questions.”
“False alarms can lead to unnecessary panic, economic disruption, and a loss of public trust, while missed predictions can have catastrophic consequences,” he said.
CONTACTS:
• Társilo Girona, University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute, 907-474-5784, tarsilo.girona@alaska.edu
• Rod Boyce, University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute, 907-474-7185, rcboyce@alaska.edu
END
UAF scientist’s method could give months’ warning of major earthquakes
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Consensus paper: Carcinogenicity of gene therapies
2024-08-30
Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, Gene Therapy Program, and Moderna, have shown that repeated administration of lipid nanoparticle-encapsulated mRNA therapy significantly extended survival and reduced serum leucine levels in a mouse model of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Click here to read the article now.
The researchers, led by James Wilson, MD, PhD, from the University of Pennsylvania, Perelman School of Medicine, evaluated a lipid nanoparticle-based treatment approach to address all possible genetic mutations that can cause MSUD.
“Repeated intravenous delivery ...
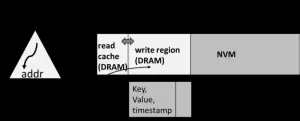
HeterMM: Applying in-DRAM index to heterogeneous memory-based key-value stores
2024-08-30
Emerging byte-addressable storage technologies, such as NVM, provide a more cost-effective and larger-capacity alternative to DRAM, presenting new opportunities to address the high cost, limited capacity, and volatility of in-memory key-value (KV) stores. Numerous efforts have been dedicated to redesigning conventional structures on NVM. However, they were challenged by the substantial engineering cost and increased complexity to be integrated into existing systems. Thus, a general framework to apply existing indexes to KV stores on NVM becomes more attractive.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Xuan Zhou published their new research on ...
Several advantages when medical abortion is started at home
2024-08-30
Being at home is as safe as at the hospital when a medical abortion after twelve weeks of pregnancy is initiated. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. When starting at home, day patient care is usually sufficient, and women are satisfied with the treatment.
In the case of medical abortion up to and including the tenth week of pregnancy, the procedure used is a so-called home abortion. At ten to twelve weeks, day patient care is most commonly used, while s medical abortion after twelve ...
Northwestern receives $55 million to advance health research
2024-08-30
Funding will enable discoveries for diverse populations to go from lab to clinical care settings
Will translate scientific research to treatments, therapies that can improve patients’ quality of life
Institute will infuse implementation-science methods into research to make public health improvements more scalable
‘Clinical and translational research does not happen in a bubble’
CHICAGO --- The Northwestern University Clinical and Translational Sciences (NUCATS) Institute has received $55 million in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding to accelerate the development, evaluation and implementation of improved health care interventions.
The seven-year ...
The Lancet: Managing early stages of abortion care at home after 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe and reduces time spent in hospital, study finds
2024-08-30
The Lancet: Managing early stages of abortion care at home after 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe and reduces time spent in hospital, study finds
A randomised controlled trial of 435 women having a medical abortion after 12 weeks of pregnancy found 71% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at home spent fewer than 9 hours in hospital, compared to 46% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at hospital.
There was no difference in safety outcomes observed between the two groups, however, of the women who took the first ...
Billions worldwide consume inadequate levels of micronutrients critical to human health
2024-08-30
Embargoed for release: Thursday, August 29, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and E, according to new estimations.
Micronutrient inadequacies may be more severe than previously thought and may differ between males and females.
The results provide a roadmap for taking action by showing which population groups are at risk of deficiency for specific nutrients.
Boston, MA—More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and ...
Lack of competition between petrol stations hits households most in poorest areas
2024-08-30
Households in low-income areas face significantly higher increases in petrol prices when rival fuel stations close compared to high-income areas, according to new research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
At the same time, low-income areas do not benefit from a higher drop in prices when new stations open.
The study is published today in the Journal of Industrial Economics. It shows that it matters who operates the petrol stations: large chains respond with higher price increases following the exit of one of their rivals.
Other factors, such as reliance on cars, commuting distance, age, or education also drive some of this ...
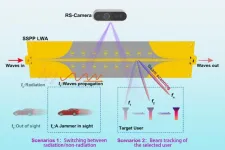
An externally perceivable smart leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240040, discusses an externally perceivable smart leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons.
Smart antennas have garnered significant attention for their ability to enable both communication and perception functions simultaneously, commonly with complicated control and high cost though. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) has led to new applications across disciplines, and a range of flexible and miniaturized perceptive devices. Therefore, smart antennas that can ...
MSU researchers find regional variations in concussion diagnoses
2024-08-30
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Researchers in Michigan State University’s Department of Kinesiology found significant geographic variations in concussion diagnoses in United States emergency departments — with the highest rates in the South and lower rates in the Midwest and Northeast.
The study, published by the Journal of Safety Research, analyzed a public database of emergency department visits from 2010 to 2018, focusing on sport-related concussions, or SRC, and nonsport-related concussions, or NSRC.
The study authors, from MSU’s College of Education and ...
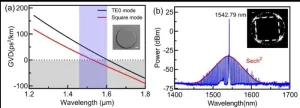
Soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240061, discusses soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes.
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a coherent light source consisting of a series of discrete, equally spaced and phase-locked frequency lines, which is crucial for practical applications in building optical clocks, searching Earth-like exoplanets, exploring quantum optics, optical frequency synthesis, high-resolution optical spectroscopy, lidar, high-speed telecom communication, microwave photonics, and many others.
In recent years, on-chip soliton microcomb, which finely balances ...