(Press-News.org) The Lancet: Managing early stages of abortion care at home after 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe and reduces time spent in hospital, study finds
A randomised controlled trial of 435 women having a medical abortion after 12 weeks of pregnancy found 71% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at home spent fewer than 9 hours in hospital, compared to 46% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at hospital.
There was no difference in safety outcomes observed between the two groups, however, of the women who took the first dose of misoprostol at home, 1% (2/220) completed the abortion before admission to hospital.
In a survey after the abortion, more participants in the home group (78%) said they preferred their allocated treatment compared with the hospital group (49%).
The authors say the option of taking the first dose of misoprostol at home would give women having abortions after 12 weeks greater autonomy and reduce the need for overnight hospital stays.
Pregnant people who took the first dose of misoprostol (a pill given as part of the procedure for medical abortions) at home had a 71% chance of completing their care in hospital within 9 hours with no overnight stay when having an abortion after 12 weeks of pregnancy, compared to 46% of those who took the first dose of misoprostol at hospital, finds a randomised controlled trial published in The Lancet.
A medical abortion (also known as abortion with pills) involves taking two types of pills to end a pregnancy: mifepristone, which blocks the hormone progesterone therefore causing the lining of the uterus to break down, and misoprostol, which makes the womb contract. For abortions after 12 weeks of pregnancy, mifepristone is often given at a clinic to which the patient returns one to two days later to receive a first dose of misoprostol followed by additional doses of misoprostol every few hours until the abortion is complete. In this trial, all patients received the first dose of mifepristone in the clinic as usual, but some patients then took the first dose of misoprostol at home. Previous studies indicate that most medical abortions after 12 weeks of pregnancy are completed within eight to 12 hours after the first misoprostol dose and require an average of two to three misoprostol doses, with some patients needing to stay overnight in hospital.
“Currently, most abortions after 12 weeks of pregnancy take place in hospitals and may require an overnight stay, which some women find stressful and isolating. Our trial results show that taking the first dose of misoprostol at home decreases the average time women spent in hospital, enabling them to leave the hospital within nine hours after admission and without an overnight stay. Offering the choice to take the first dose of misoprostol at home provides a safe and effective alternative to taking all misoprostol doses at hospital and enables women to self-manage some of the process, potentially leading to feelings of autonomy during a time where women can feel extremely vulnerable,” says author Dr Johanna Rydelius, Sahlgrenska Academy, University of Gothenburg, Sweden.
She adds, “Our study found 1% of the women who took misoprostol at home completed the abortion before attending hospital for the next dose. Previous studies suggest a 1% complete abortion rate within two hours after the misoprostol first dose, and women who took misoprostol at home were made aware of this risk when choosing to take part in the trial and provided with a number to call if they had any concerns. It’s extremely important that women who are given the choice to take the first dose of misoprostol at home are clearly informed about the very small risk of the abortion occurring before attending the hospital.”
The study took place at six hospitals in Sweden between January 2019 and December 2022. All participants were given mifepristone oral pills at an outpatient clinic and provided with a time to return. Women between 12 to 22 weeks pregnant planning to undergo a medical abortion and who chose to take part in the trial were randomised to either receive their first dose of misoprostol at home or at the hospital.
Women in the home treatment group administered the first dose of misoprostol vaginally at home and returned to hospital two hours later for the remaining treatment. Women in the hospital group self-administered the first dose of misoprostol upon arrival at the hospital. All participants then took repeated doses of misoprostol under the tongue every three hours until the abortion occurred.
Of the patients in the home treatment group, 71% (156/220) spent fewer than nine hours at hospital, compared to 46% (99/215) of those in the hospital treatment group. There was no difference in the average pain score, types and number of side effects, or rates of admittance to hospital earlier than planned between the two groups. Two patients in the home treatment group (1%) had the abortion on the way to the hospital, between one to two hours after taking the first dose of misoprostol.
The patients were asked to complete a follow up survey two to four weeks after the abortion. Five out of six participants in both trial arms (171/200 of those in the home treatment group and 152/188 of those in the hospital treatment group) said they were very satisfied with the care they received. When asked ‘if you were to choose, where would you prefer to take the first dose of misoprostol?’, 78% of women in the home group and 51% of women in the hospital group said they’d prefer to take the first dose of misoprostol at home.
The authors acknowledge some limitations of the study, including that the researchers were advised by the Data and Safety Monitoring Board to end the trial early due to a lower-than-expected enrolment and slow progress towards the trial's target of 784 participants. However, trial site feedback suggests the lower-than-expected enrolment rate was not due to reluctance to take misoprostol at home but rather due to patients feeling overwhelmed by the overall situation.
“Every patient who seeks abortion care must navigate a unique set of personal and medical circumstances. The choice of self-administering the first dose of misoprostol at home may provide some patients with a sense of autonomy and comfort during what can be a very overwhelming time in their lives. In addition, providing the option of the first dose of misoprostol at home would enable more abortion clinics with no overnight facilities to provide medical abortions for women who are over 12 weeks pregnant, something particularly important for locations where access to abortion care is limited,’ says author Prof Kristina Gemzell Danielsson, The Karolinska Institutet, Sweden.
Writing in a linked Comment, Heidi Moseson and Caitlin Gerdts, Ibis Reproductive Health, USA, who were not involved in the study, said: "Increasing access to abortion later in pregnancy is a crucial component of the struggle for reproductive autonomy; it requires innovation, and evidence, and a willingness to listen to the needs and experiences of people having abortions. Judging from the overwhelming preference for at-home administration of misoprostol in the PRIMA Trial, moving towards a less clinically supervised model of medical abortion care later in pregnancy is an important first step.”
NOTES TO EDITORS
This study was funded by Regional funds Västragötaland (LUA), Hjalmar Svensson’s Fund, The Gothenburg Society of Medicine, Region Stockholm and Karolinska Institutet (ALF) and the Swedish research council. For a full list of researchers and institutions see the paper.
Quotes from Authors cannot be found in the text of the Article, but have been supplied for the press release. The Comment quote is taken directly from the linked Comment.
The labels have been added to this press release as part of a project run by the Academy of Medical Sciences seeking to improve the communication of evidence. For more information, please see: http://www.sciencemediacentre.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/AMS-press-release-labelling-system-GUIDANCE.pdf if you have any questions or feedback, please contact The Lancet press office pressoffice@lancet.com
END
The Lancet: Managing early stages of abortion care at home after 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe and reduces time spent in hospital, study finds
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Billions worldwide consume inadequate levels of micronutrients critical to human health
2024-08-30
Embargoed for release: Thursday, August 29, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and E, according to new estimations.
Micronutrient inadequacies may be more severe than previously thought and may differ between males and females.
The results provide a roadmap for taking action by showing which population groups are at risk of deficiency for specific nutrients.
Boston, MA—More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and ...
Lack of competition between petrol stations hits households most in poorest areas
2024-08-30
Households in low-income areas face significantly higher increases in petrol prices when rival fuel stations close compared to high-income areas, according to new research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
At the same time, low-income areas do not benefit from a higher drop in prices when new stations open.
The study is published today in the Journal of Industrial Economics. It shows that it matters who operates the petrol stations: large chains respond with higher price increases following the exit of one of their rivals.
Other factors, such as reliance on cars, commuting distance, age, or education also drive some of this ...
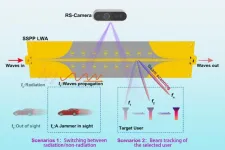
An externally perceivable smart leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240040, discusses an externally perceivable smart leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons.
Smart antennas have garnered significant attention for their ability to enable both communication and perception functions simultaneously, commonly with complicated control and high cost though. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) has led to new applications across disciplines, and a range of flexible and miniaturized perceptive devices. Therefore, smart antennas that can ...
MSU researchers find regional variations in concussion diagnoses
2024-08-30
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Researchers in Michigan State University’s Department of Kinesiology found significant geographic variations in concussion diagnoses in United States emergency departments — with the highest rates in the South and lower rates in the Midwest and Northeast.
The study, published by the Journal of Safety Research, analyzed a public database of emergency department visits from 2010 to 2018, focusing on sport-related concussions, or SRC, and nonsport-related concussions, or NSRC.
The study authors, from MSU’s College of Education and ...
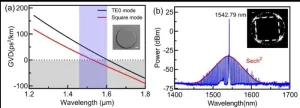
Soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240061, discusses soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes.
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a coherent light source consisting of a series of discrete, equally spaced and phase-locked frequency lines, which is crucial for practical applications in building optical clocks, searching Earth-like exoplanets, exploring quantum optics, optical frequency synthesis, high-resolution optical spectroscopy, lidar, high-speed telecom communication, microwave photonics, and many others.
In recent years, on-chip soliton microcomb, which finely balances ...
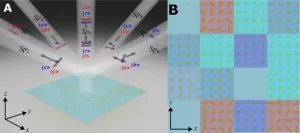
Spin-controlled generation of a complete polarization set with randomly-interleaved plasmonic metasurfaces
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240076 , discusses spin-controlled generation of a complete polarization set with randomly-interleaved plasmonic metasurfaces.
Optical metasurfaces are finely crafted two-dimensional artificial nanostructures composed of meticulously designed arrays of ultrathin artificial atoms. These surfaces possess capabilities beyond natural materials, enabling multifunctional control of electromagnetic waves. By designing the shape, ...
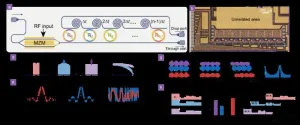
Multi-functional and highly reconfigurable monolithic signal processing system
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240012, discusses a multi-functional and highly reconfigurable monolithic signal processing system.
Photonic signal processing offers a versatile and promising toolkit for contemporary scenarios ranging from digital optical communication to analog microwave operation. Compared to its electronic counterpart, it eliminates inherent bandwidth limitations and meanwhile exhibits the potential to provide unparalleled scalability and flexibility, particularly through ...
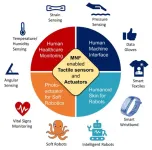
Advances in optical micronanofiber enabled tactile sensors and soft actuators
2024-08-30
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240005, discusses advances in optical micronanofiber enabled tactile sensors and soft actuators.
As a perfect combination of fiber optics and micro/nanotechnology, optical micro/nanofiber (MNF) is a new type of micro/nano-waveguide structure developed in recent years. Compared with standard fiber, MNF has smaller diameter and larger core cladding refractive index contrast, so it offers unique optical properties, including low transmission loss, strong light-field constraint, large evanescent ...
RISE project awarded NIH grant
2024-08-29
Xiaopeng Zhao, a professor in the Department of Mechanical, Aerospace, and Biomedical Engineering and founding director of the Applied AI Program in the College of Emerging and Collaborative Studies at UT, is part of a collaborative team that has been awarded a $401,090 grant from the National Institutes of Health.
The team received the multi-year funded grant for the project “Robot-based Information and Support to Enhance Alzheimer’s Caregiver Health (RISE).” The research is supported ...
Physical health has its yardsticks. Mental health is still searching for the right ruler
2024-08-29
While doctors can track cancer progression at the cellular level or use a blood test to obtain precise blood cholesterol levels, talk therapy’s impact on mental health is still largely reliant on gut feelings more than hard data.
A national initiative led by the National Institute of Mental Health is now underway to find figurative “rulers” that can accurately measure and compare the quality of the various mental health treatments available. To lead off this effort, UCLA Health researchers were awarded a four-year, $2.1 million federal grant to study and test whether such a quality measure can be created and applied across all social groups in the United States.
“We ...