HeterMM: Applying in-DRAM index to heterogeneous memory-based key-value stores
2024-08-30
(Press-News.org)
Emerging byte-addressable storage technologies, such as NVM, provide a more cost-effective and larger-capacity alternative to DRAM, presenting new opportunities to address the high cost, limited capacity, and volatility of in-memory key-value (KV) stores. Numerous efforts have been dedicated to redesigning conventional structures on NVM. However, they were challenged by the substantial engineering cost and increased complexity to be integrated into existing systems. Thus, a general framework to apply existing indexes to KV stores on NVM becomes more attractive.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Xuan Zhou published their new research on 15 August 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and Springer Nature.
The team proposed a general framework named HeterMM, for heterogeneous memory architecture consisting of DRAM and NVM. It is designed to fully leverage the superior performance of DRAM, and make the performance of the system as close to the in-DRAM one as possible.
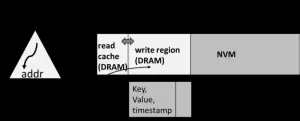
In the research, they emphases the importance of fully leveraging the superior performance of DRAM by holding the index and hot data in DRAM. Typically, NVM suffers from the inferior performance than DRAM. Besides, its specific accessing characteristics also necessitate special designs to maximize its performance. The typical characteristics of NVM include its read-write asymmetry in terms of latency and bandwidth and the poor random access performance compared to sequential accesses. In response, the research team provides a framework, composing of a plugged-in in-DRAM index, a data storage mechanism on heterogeneous memory, and an operation log for failure recovery.
In particular, the index, which is the most frequently accessed and typically in a small unit and random order, is not friendly to NVM. Besides, their data structures, which are usually optimized for DRAM, may not perform as effectively on NVM. Moreover, the hotness-aware data storage on heterogeneous memory, aiming at holding the hot data in DRAM, which allows most requests being served by the DRAM, hiding the inferior performance of NVM as much as possible. Specifically, newly written data in HeterMM resides in DRAM, and old data is flushed to NVM in batches. Each data is allocated a logical address upon its arrival, which remains the same unless the data is updated out-of-place.
The persistence of NVM can ensure the durability of data residing in it, while an operation log is applied to ensure the durability of data residing in DRAM. Firstly, data in DRAM is updated in place, which could be regarded as early compaction and reduces data volume flushed to NVM. Secondly, data in NVM can be regarded as a checkpoint which can be used to cut off the operation log. Moreover, to optimize access to read-only data in NVM, the DRAM region is divided into a read cache and a write region, with the former holding frequently accessed data residing in NVM while the latter holding newly arrived data. They share the same space in DRAM and can be resized dynamically according to the workload.
Extensive experiments which combine HeterMM with different kinds of indexes, including CLHT, LFHT, and B+ tree, verifies the efficiency of HeterMM. Specifically, HeterMM could outperform both the state-of-the-art index persist framework and state-of-the-art hybrid DRAM and NVM-based hash tables and B+ trees. This benefits from the fact that HeterMM holds the hot data in NVM which could allows the read requests being served by the DRAM without accessing NVM.
DOI: 10.1007/s11704-024-3713-0
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-30
Being at home is as safe as at the hospital when a medical abortion after twelve weeks of pregnancy is initiated. These are the findings of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg. When starting at home, day patient care is usually sufficient, and women are satisfied with the treatment.
In the case of medical abortion up to and including the tenth week of pregnancy, the procedure used is a so-called home abortion. At ten to twelve weeks, day patient care is most commonly used, while s medical abortion after twelve ...
2024-08-30
Funding will enable discoveries for diverse populations to go from lab to clinical care settings
Will translate scientific research to treatments, therapies that can improve patients’ quality of life
Institute will infuse implementation-science methods into research to make public health improvements more scalable
‘Clinical and translational research does not happen in a bubble’
CHICAGO --- The Northwestern University Clinical and Translational Sciences (NUCATS) Institute has received $55 million in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding to accelerate the development, evaluation and implementation of improved health care interventions.
The seven-year ...
2024-08-30
The Lancet: Managing early stages of abortion care at home after 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe and reduces time spent in hospital, study finds
A randomised controlled trial of 435 women having a medical abortion after 12 weeks of pregnancy found 71% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at home spent fewer than 9 hours in hospital, compared to 46% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at hospital.
There was no difference in safety outcomes observed between the two groups, however, of the women who took the first ...
2024-08-30
Embargoed for release: Thursday, August 29, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and E, according to new estimations.
Micronutrient inadequacies may be more severe than previously thought and may differ between males and females.
The results provide a roadmap for taking action by showing which population groups are at risk of deficiency for specific nutrients.
Boston, MA—More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and ...
2024-08-30
Households in low-income areas face significantly higher increases in petrol prices when rival fuel stations close compared to high-income areas, according to new research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
At the same time, low-income areas do not benefit from a higher drop in prices when new stations open.
The study is published today in the Journal of Industrial Economics. It shows that it matters who operates the petrol stations: large chains respond with higher price increases following the exit of one of their rivals.
Other factors, such as reliance on cars, commuting distance, age, or education also drive some of this ...
2024-08-30
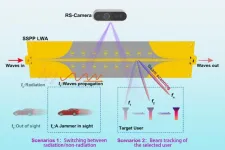
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240040, discusses an externally perceivable smart leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons.
Smart antennas have garnered significant attention for their ability to enable both communication and perception functions simultaneously, commonly with complicated control and high cost though. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) has led to new applications across disciplines, and a range of flexible and miniaturized perceptive devices. Therefore, smart antennas that can ...
2024-08-30
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Researchers in Michigan State University’s Department of Kinesiology found significant geographic variations in concussion diagnoses in United States emergency departments — with the highest rates in the South and lower rates in the Midwest and Northeast.
The study, published by the Journal of Safety Research, analyzed a public database of emergency department visits from 2010 to 2018, focusing on sport-related concussions, or SRC, and nonsport-related concussions, or NSRC.
The study authors, from MSU’s College of Education and ...
2024-08-30
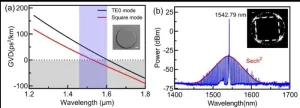
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240061, discusses soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes.
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a coherent light source consisting of a series of discrete, equally spaced and phase-locked frequency lines, which is crucial for practical applications in building optical clocks, searching Earth-like exoplanets, exploring quantum optics, optical frequency synthesis, high-resolution optical spectroscopy, lidar, high-speed telecom communication, microwave photonics, and many others.
In recent years, on-chip soliton microcomb, which finely balances ...
2024-08-30
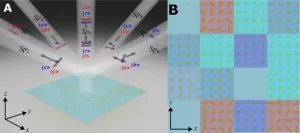
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240076 , discusses spin-controlled generation of a complete polarization set with randomly-interleaved plasmonic metasurfaces.
Optical metasurfaces are finely crafted two-dimensional artificial nanostructures composed of meticulously designed arrays of ultrathin artificial atoms. These surfaces possess capabilities beyond natural materials, enabling multifunctional control of electromagnetic waves. By designing the shape, ...
2024-08-30
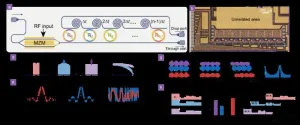
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240012, discusses a multi-functional and highly reconfigurable monolithic signal processing system.
Photonic signal processing offers a versatile and promising toolkit for contemporary scenarios ranging from digital optical communication to analog microwave operation. Compared to its electronic counterpart, it eliminates inherent bandwidth limitations and meanwhile exhibits the potential to provide unparalleled scalability and flexibility, particularly through ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] HeterMM: Applying in-DRAM index to heterogeneous memory-based key-value stores