Northwestern receives $55 million to advance health research
Largest active grant at Northwestern to fund clinical, translational research hub
2024-08-30
(Press-News.org) Funding will enable discoveries for diverse populations to go from lab to clinical care settings
Will translate scientific research to treatments, therapies that can improve patients’ quality of life
Institute will infuse implementation-science methods into research to make public health improvements more scalable
‘Clinical and translational research does not happen in a bubble’
CHICAGO --- The Northwestern University Clinical and Translational Sciences (NUCATS) Institute has received $55 million in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding to accelerate the development, evaluation and implementation of improved health care interventions.
The seven-year award is the largest current research grant at Northwestern and extends a legacy of NIH funding that began when the institute launched in 2008.
The NUCATS Institute helps translate novel discoveries from the laboratory to routine clinical care, leading to treatments and therapies that can extend and improve the quality of life for patients. This is a process that remains slow, complex and labor intensive. NUCATS provides scientists at its four health system partners (Northwestern; Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago and its Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute; Shirley Ryan AbilityLab; and Northwestern Medicine) with consultative resources and expertise to accelerate how quickly transformative scientific discoveries reach patients and communities.
“Clinical and translational research does not happen in a bubble. It requires dedicated investigators and members of the public to advance human health,” said Dr. Richard D’Aquila, associate vice president of research and senior associate dean for clinical and translational research at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “With generous support from the NIH and Northwestern, we will continue to work alongside our exceptional coalition of community and health system partners to help build a better framework for innovating and implementing discoveries in ever more inclusive ways.”
NUCATS is led by principal investigators D’Aquila; Sara Becker, the Alice Hamilton Professor of Psychiatry; and Dr. Clyde Yancy, chief of cardiology at Feinberg.
“The collection of extraordinary faculty and staff who will manage this iteration of NUCATS is a testament to the transformational mindsets held by the institute’s leadership,” said Dr. Eric G. Neilson, vice president for medical affairs and Lewis Landsberg Dean of Feinberg. “This funding allows us to further advance our mission to improve human health by investigating the mechanisms that drive the translation of discoveries toward real-world treatments.”
NUCATS and the multiple-principal investigator team will develop, evaluate and disseminate more effective health interventions to more patients more quickly following these three specific aims:
Include: Cultivate a culture of inclusive excellence as they expand their workforce, partnerships and research participants, including those historically underrepresented in biomedical science, to optimize the benefits of translation for all;
Innovate: Support innovation to accelerate and transform translation; and
Implement: Infuse implementation-science methods into clinical research.
The grant is awarded by the NIH's Clinical and Translational Science Awards (CTSA) Program, which supports a national network of medical institutions that speed the translation of research discoveries into improved care. The institute also is positioned to infuse implementation-science methods into work across the translational continuum to improve public health and meet the needs of all.
“Implementation science can help us accelerate and catalyze the uptake of evidence-based practice into routine clinical care,” said Becker, director of Northwestern’s Center for Dissemination and Implementation Science. “Northwestern is a national leader in this space. The NUCATS Institute will become a model CTSA hub that advances inclusive, innovative and implementable solutions to the evolving challenges that impede scalable public health progress.”
Yancy’s research in cardiology and health disparities addresses optimal treatment of heart failure. In a seminal contribution, he revealed the predominant cause of heart failure among Black people is hypertension rather than the ischemic heart disease, which is most often the commonly accepted cause in non-Black patients. His groundbreaking work informed how to optimize treatment strategies for Black patients, including the first-ever FDA-approved therapy specifically for Black patients.
“Diversity in the biomedical workforce is more than representativeness, it is rather about excellence, diverse ideas and unique strategies that will enrich our ability to provide care for the entire population,” said Yancy, vice dean for diversity and inclusion at Feinberg. “By addressing inequities with intentionality, we are positioned to understand and then overcome persistent systemic limitations that hurt those underrepresented and underserved populations and, in turn, impair best health for everyone. We commit to responsibly and courageously leading the path to inclusive excellence and belonging.”
Since launching in 2008, the NUCATS has supported more than 3,500 academic publications and annually facilitates more than $1 million in competitive pilot research projects that seed new NIH applications.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-08-30
The Lancet: Managing early stages of abortion care at home after 12 weeks of pregnancy is safe and reduces time spent in hospital, study finds
A randomised controlled trial of 435 women having a medical abortion after 12 weeks of pregnancy found 71% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at home spent fewer than 9 hours in hospital, compared to 46% of patients who took the first dose of misoprostol at hospital.
There was no difference in safety outcomes observed between the two groups, however, of the women who took the first ...
2024-08-30
Embargoed for release: Thursday, August 29, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and E, according to new estimations.
Micronutrient inadequacies may be more severe than previously thought and may differ between males and females.
The results provide a roadmap for taking action by showing which population groups are at risk of deficiency for specific nutrients.
Boston, MA—More than half of the global population consumes inadequate levels of several micronutrients essential to health, including calcium, iron, and vitamins C and ...
2024-08-30
Households in low-income areas face significantly higher increases in petrol prices when rival fuel stations close compared to high-income areas, according to new research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
At the same time, low-income areas do not benefit from a higher drop in prices when new stations open.
The study is published today in the Journal of Industrial Economics. It shows that it matters who operates the petrol stations: large chains respond with higher price increases following the exit of one of their rivals.
Other factors, such as reliance on cars, commuting distance, age, or education also drive some of this ...
2024-08-30
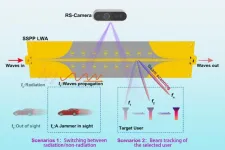
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240040, discusses an externally perceivable smart leaky-wave antenna based on spoof surface plasmon polaritons.
Smart antennas have garnered significant attention for their ability to enable both communication and perception functions simultaneously, commonly with complicated control and high cost though. The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) has led to new applications across disciplines, and a range of flexible and miniaturized perceptive devices. Therefore, smart antennas that can ...
2024-08-30
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Researchers in Michigan State University’s Department of Kinesiology found significant geographic variations in concussion diagnoses in United States emergency departments — with the highest rates in the South and lower rates in the Midwest and Northeast.
The study, published by the Journal of Safety Research, analyzed a public database of emergency department visits from 2010 to 2018, focusing on sport-related concussions, or SRC, and nonsport-related concussions, or NSRC.
The study authors, from MSU’s College of Education and ...
2024-08-30
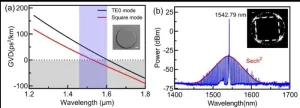
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240061, discusses soliton microcomb generation by cavity polygon modes.
Optical frequency comb (OFC) is a coherent light source consisting of a series of discrete, equally spaced and phase-locked frequency lines, which is crucial for practical applications in building optical clocks, searching Earth-like exoplanets, exploring quantum optics, optical frequency synthesis, high-resolution optical spectroscopy, lidar, high-speed telecom communication, microwave photonics, and many others.
In recent years, on-chip soliton microcomb, which finely balances ...
2024-08-30
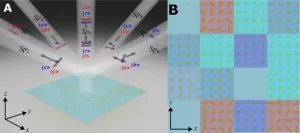
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.240076 , discusses spin-controlled generation of a complete polarization set with randomly-interleaved plasmonic metasurfaces.
Optical metasurfaces are finely crafted two-dimensional artificial nanostructures composed of meticulously designed arrays of ultrathin artificial atoms. These surfaces possess capabilities beyond natural materials, enabling multifunctional control of electromagnetic waves. By designing the shape, ...
2024-08-30
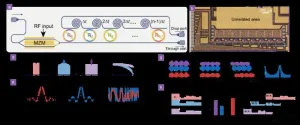
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240012, discusses a multi-functional and highly reconfigurable monolithic signal processing system.
Photonic signal processing offers a versatile and promising toolkit for contemporary scenarios ranging from digital optical communication to analog microwave operation. Compared to its electronic counterpart, it eliminates inherent bandwidth limitations and meanwhile exhibits the potential to provide unparalleled scalability and flexibility, particularly through ...
2024-08-30
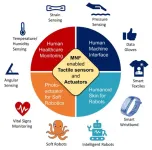
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Sciences; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.240005, discusses advances in optical micronanofiber enabled tactile sensors and soft actuators.
As a perfect combination of fiber optics and micro/nanotechnology, optical micro/nanofiber (MNF) is a new type of micro/nano-waveguide structure developed in recent years. Compared with standard fiber, MNF has smaller diameter and larger core cladding refractive index contrast, so it offers unique optical properties, including low transmission loss, strong light-field constraint, large evanescent ...
2024-08-29
Xiaopeng Zhao, a professor in the Department of Mechanical, Aerospace, and Biomedical Engineering and founding director of the Applied AI Program in the College of Emerging and Collaborative Studies at UT, is part of a collaborative team that has been awarded a $401,090 grant from the National Institutes of Health.
The team received the multi-year funded grant for the project “Robot-based Information and Support to Enhance Alzheimer’s Caregiver Health (RISE).” The research is supported ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Northwestern receives $55 million to advance health research
Largest active grant at Northwestern to fund clinical, translational research hub