(Press-News.org) Leonora Balaj, PhD, an investigator in the department of Neurosurgery at Massachusetts General Hospital and an assistant professor of Neurosurgery at Harvard Medical School, is co-senior author of a new paper in Nature Communications, Clinical Utility of a Blood Based Assay for the Detection of IDH1.R132H-Mutant Gliomas.
Bob Carter, MD, chair of Neurosurgery at Mass General, is co-senior author of the study. Syeda Maheen Batool, MD, an instructor in investigation in Neurosurgery at Mass General, is lead author.
Background:
Glioma represents the most common central nervous system cancer in adults. The current classification scheme uses molecular alterations, particularly IDH1.R132H, to stratify lesions into distinct prognostic groups.
Currently, neuroimaging followed by tissue biopsy testing (surgical biopsy and/or resection) is the gold standard for diagnosing IDHI mutant gliomas.
However, this process poses procedural risks and may not fully reflect the diverse and evolving tumor landscape. Also, preoperative knowledge of the IDH mutation status can influence operative procedural planning.
Here, we introduced a blood-based test, mt-IDHIdx, that allows for the minimally invasive detection of tumor-derived extracellular RNA using only 2ml of blood.
We performed validation testing across the study population (n=133), which included 80 patients with IDH1.R132H glioma, 44 patients with IDH1 wild-type gliomas and nine healthy controls.
What Were the Results?
Results from our plasma testing demonstrate an overall sensitivity of 75.0% (95% CI: 64.1%–84.0%), specificity 88.7% (95% CI: 77.0%–95.7%), positive predictive value 90.9%, and negative predictive value 70.1% compared to the tissue gold standard.
In addition to fundamental diagnostic applications, the study also highlights the utility of the platform for blood-based monitoring and surveillance.
Finally, the optimized workflow enables rapid and efficient completion of both tumor tissue and plasma testing in under four hours from the time of sampling.
What are the Next Steps?
Detection of the IDH1 mutation in blood means that these tumors can be diagnosed without a biopsy, and can be monitored overtime to track disease progression, response to treatment or recurrence using a simple blood sample.
Importantly, the FDA approved a drug (vorasidenib) for this mutation in glioma just a week ago—this means that the test, once approved, can be used to stratify these patients for this treatment and can monitor disease course.
Paper Cited:
Batool, S. M., Escobedo, A. K., Hsia, T., Ekanayake, E., Khanna, S. K., Gamblin, A. S., Zheng, H., Skog, J., Miller, J. J., Stemmer-Rachamimov, A. O., Cahill, D. P., Balaj, L., & Carter, B. S. (2024). Clinical utility of a blood based assay for the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomas. Nature communications, 15(1), 7074. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-51332-7
END
Research Spotlight: A blood-based assay for the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomas
In addition to fundamental diagnostic applications, the study also highlights the utility of the platform for blood-based monitoring and surveillance
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genomic dark matter solves butterfly evolutionary riddle
2024-08-30
[Note: High-resolution images related to this research available for download at this link. Caption and credit information provided.]
WASHINGTON (August 30, 2024) — A team of international researchers has uncovered a surprising genetic mechanism that influences the vibrant and complex patterns on butterfly wings. In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team, led by Luca Livraghi at the George Washington University and the University of Cambridge, discovered ...
Like people, vultures get set in their ways and have fewer friends as they age
2024-08-30
Key takeaways
Young griffon vultures move frequently between sleeping sites in different locations, interacting with many friends.
They get set in their ways as they age and roost in the same spots with the same individuals; older vultures follow the same paths.
Roosts act as information hubs; older vultures may have a more thorough knowledge of where to find food resources and less need to learn about them from other vultures.
If you’d rather be watching TV on your couch than dancing at the club, you might have something in common with aging ...
Not just a ‘bad guy,’ Tau also plays a ‘good guy’ role protecting our brains
2024-08-30
A study by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital, reveals that the protein Tau – a key player implicated in several neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease – also plays a positive role in the brain. Tau mitigates neuronal damage caused by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) or free radicals and promotes healthy aging. The study was published in Nature Neuroscience.
“ROS ...
Doughnut-shaped region found inside Earth’s core deepens understanding of planet’s magnetic field
2024-08-30
A doughnut-shaped region thousands of kilometres beneath our feet within Earth’s liquid core has been discovered by scientists from The Australian National University (ANU), providing new clues about the dynamics of our planet’s magnetic field.
The structure within Earth’s liquid core is found only at low latitudes and sits parallel to the equator. According to ANU seismologists, it has remained undetected until now.
The Earth has two core layers: the inner core, a solid layer, and the outer core, a liquid layer. Surrounding the Earth’s core is the mantle. The ...
Study combines data, molecular simulations to accelerate drug discovery
2024-08-30
Researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital have found a new method to increase both speed and success rates in drug discovery.
The study, published Aug. 30 in the journal Science Advances, offers renewed promise when it comes to discovering new drugs.
“The hope is we can speed up the timeline of drug discovery from years to months,” said Alex Thorman, PhD, co-first author and a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Environmental and Public ...
NCT/UCC Dresden: Millions in funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative for state-of-the-art imaging to accurately detect minute tumors
2024-08-30
The imaging techniques currently used in biological research cannot penetrate into deeper tissue layers. In cancer treatment, this means that remnants of tumors or individual cancer cells at tumor margins and in lymph nodes are not visible. Doctors performing surgery are therefore repeatedly faced with the difficult question of whether all of the affected tissue has actually been removed. For the patient's quality of life, however, the complete removal of the tumor is just as essential as the preservation of healthy tissue ...
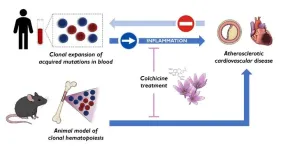
CNIC scientists discover a new cardiovascular risk factor and identify a drug able to reduce its effects
2024-08-30
To the known risk factors for cardiovascular disease—high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, overweight and obesity, smoking, and physical inactivity—a new one has to be added: clonal hematopoiesis. This condition is triggered by acquired mutations in blood stem cells and was already known to be associated with an elevated cardiovascular risk. However, until now it was uncertain if clonal hematopoiesis was a cause or consequence of cardiovascular disease. Now, a new study published in Nature Medicine and carried out by researchers at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) resolves this critical debate ...
When the heat makes you disoriented
2024-08-30
Climate change is affecting ecosystems in many different ways. One of its consequences are increasingly longer and more intense periods of heat, which affect essential natural processes – such as pollination. A team of researchers from Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) has now investigated in more detail how heat affects one particular player in these processes: The bumblebee.
"Bumblebees are important pollinators in natural and agricultural systems. They therefore ...
Showcasing latest AI updates, Insilico Medicine attends 2024 EFMC International Symposium on Medicinal Chemistry
2024-08-30
Attracting around 1,000 participants from industry and academia, the XXVIII EFMC International Symposium on Medicinal Chemistry (EFMC-ISMC) is supposed to take place in Rome, Italy from September 1-5, 2024. After the generative AI updates recently announced on the IMGAIA webinar, Insilico Medicine will be sharing more innovative details while exploring collaboration chances at Booth #50.
EFMC-ISMC is a key symposium in the field of medicinal chemistry and drug discovery, and the symposium this year features ...
Novel chemical tool aims to streamline drug-making process
2024-08-30
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The invention of a tool capable of unlocking previously impossible organic chemical reactions has opened new pathways in the pharmaceutical industry to create effective drugs more quickly.
Traditionally, most drugs are assembled using molecular fragments called alkyl building blocks, organic compounds that have a wide variety of applications. However, because of how difficult it can be to combine different types of these compounds into something new, this method of creation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
[Press-News.org] Research Spotlight: A blood-based assay for the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomasIn addition to fundamental diagnostic applications, the study also highlights the utility of the platform for blood-based monitoring and surveillance