(Press-News.org) The only Injury Control Research Center in Texas has been established by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention at UTHealth Houston in partnership with Baylor College of Medicine.
“I’m beyond thrilled to bring an Injury Control Research Center to Texas,” said Jeff Temple, PhD, director of the new center and associate dean for clinical research at UTHealth Houston School of Behavioral Health Sciences. “This collaboration between the community, policymakers, UTHealth Houston, and Baylor College of Medicine will undoubtedly save lives.”
An Injury Control Research Center, or ICRC, hones in on the study of injury and violence prevention, which is then used to create solutions that can be implemented in the real world. The first year grant amount is $850,000 with an anticipated total of $4.25 million over five years.
“The center will be transformative,” said Christopher Spencer Greeley, MD, professor of pediatrics at Baylor and chief in the section of public health pediatrics at Texas Children’s Hospital. “It leverages long-term collaborations between two leading research and service organizations to substantively address profound challenges impacting children and families.”
The new Injury Control Research Center, which is named the Violence and Injury Prevention Research (VIPR) Center, is the first of its kind in the Southwest United States. Its location is ideal to test the potential statewide and national impacts of the center’s work.
“We’ll work collaboratively with the community to evaluate novel interventions and improve existing programs,” said Temple, who is also professor and Betty and Rose Pfefferbaum Chair in Child Mass Trauma and Resilience at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston. “We’ll also train community members and other professionals on best practices related to violence and injury prevention. Finally, we’ll work directly with policymakers to make sure our work is beneficial and enduring to the public.”
The center’s focus will be on preventing adverse childhood and community experiences, violence across the lifespan, suicide, and firearm violence.
“Over time, we will bolster our efforts to prevent and reduce the burden of unintentional injuries like car crashes and drownings,” Temple said.
“We are excited to join the strong network of ICRCs around the nation,” said Mary Aitken, MD, MPH, professor and Dan L Duncan Distinguished University Chair of the Department of Pediatrics at McGovern Medical School. “The work of these centers is critical to help prevent injury-related suffering and death, and our new center will bring a much-needed focus on the issue for Texas.”
Melissa Peskin, PhD, professor and vice chair of health promotion and behavioral sciences at UTHealth Houston School of Public Health, as well as the school’s assistant dean of Students, is a co-director of the center. Outside of UTHealth Houston, Greeley, who is also vice-chair of community health at Baylor, will also co-direct the Violence and Injury Prevention Research Center.
Media Inquiries: 713-500-3030
END
UTHealth Houston and Baylor College of Medicine collaborate on first CDC Injury Control Research Center in Southwest, established to study injury and violence prevention
2024-08-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New findings on TB could change how we treat inflammatory disorders
2024-08-30
Tuberculosis is a confounding scourge. It’s the leading cause of death from infectious disease in the world, and yet it’s estimated that those deaths represent perhaps 5% of infections with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Antibiotics can take credit for saving the lives of some of those with Mtb, but a chasm nevertheless persists between the prevalence of infection and the targeted severity of its impact. A growing body of evidence suggests genetic vulnerabilities to TB account for that gap.
Now researchers from ...
Research Spotlight: A blood-based assay for the detection of IDH1.R132H-mutant gliomas
2024-08-30
Leonora Balaj, PhD, an investigator in the department of Neurosurgery at Massachusetts General Hospital and an assistant professor of Neurosurgery at Harvard Medical School, is co-senior author of a new paper in Nature Communications, Clinical Utility of a Blood Based Assay for the Detection of IDH1.R132H-Mutant Gliomas.
Bob Carter, MD, chair of Neurosurgery at Mass General, is co-senior author of the study. Syeda Maheen Batool, MD, an instructor in investigation in Neurosurgery at Mass General, is lead author.
Background:
Glioma represents the most common central nervous system cancer in adults. The current ...
Genomic dark matter solves butterfly evolutionary riddle
2024-08-30
[Note: High-resolution images related to this research available for download at this link. Caption and credit information provided.]
WASHINGTON (August 30, 2024) — A team of international researchers has uncovered a surprising genetic mechanism that influences the vibrant and complex patterns on butterfly wings. In a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team, led by Luca Livraghi at the George Washington University and the University of Cambridge, discovered ...
Like people, vultures get set in their ways and have fewer friends as they age
2024-08-30
Key takeaways
Young griffon vultures move frequently between sleeping sites in different locations, interacting with many friends.
They get set in their ways as they age and roost in the same spots with the same individuals; older vultures follow the same paths.
Roosts act as information hubs; older vultures may have a more thorough knowledge of where to find food resources and less need to learn about them from other vultures.
If you’d rather be watching TV on your couch than dancing at the club, you might have something in common with aging ...
Not just a ‘bad guy,’ Tau also plays a ‘good guy’ role protecting our brains
2024-08-30
A study by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital, reveals that the protein Tau – a key player implicated in several neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease – also plays a positive role in the brain. Tau mitigates neuronal damage caused by excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) or free radicals and promotes healthy aging. The study was published in Nature Neuroscience.
“ROS ...
Doughnut-shaped region found inside Earth’s core deepens understanding of planet’s magnetic field
2024-08-30
A doughnut-shaped region thousands of kilometres beneath our feet within Earth’s liquid core has been discovered by scientists from The Australian National University (ANU), providing new clues about the dynamics of our planet’s magnetic field.
The structure within Earth’s liquid core is found only at low latitudes and sits parallel to the equator. According to ANU seismologists, it has remained undetected until now.
The Earth has two core layers: the inner core, a solid layer, and the outer core, a liquid layer. Surrounding the Earth’s core is the mantle. The ...
Study combines data, molecular simulations to accelerate drug discovery
2024-08-30
Researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital have found a new method to increase both speed and success rates in drug discovery.
The study, published Aug. 30 in the journal Science Advances, offers renewed promise when it comes to discovering new drugs.
“The hope is we can speed up the timeline of drug discovery from years to months,” said Alex Thorman, PhD, co-first author and a postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Environmental and Public ...
NCT/UCC Dresden: Millions in funding from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative for state-of-the-art imaging to accurately detect minute tumors
2024-08-30
The imaging techniques currently used in biological research cannot penetrate into deeper tissue layers. In cancer treatment, this means that remnants of tumors or individual cancer cells at tumor margins and in lymph nodes are not visible. Doctors performing surgery are therefore repeatedly faced with the difficult question of whether all of the affected tissue has actually been removed. For the patient's quality of life, however, the complete removal of the tumor is just as essential as the preservation of healthy tissue ...
CNIC scientists discover a new cardiovascular risk factor and identify a drug able to reduce its effects
2024-08-30
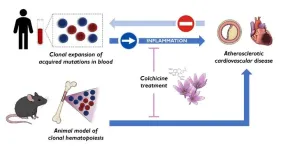
To the known risk factors for cardiovascular disease—high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, overweight and obesity, smoking, and physical inactivity—a new one has to be added: clonal hematopoiesis. This condition is triggered by acquired mutations in blood stem cells and was already known to be associated with an elevated cardiovascular risk. However, until now it was uncertain if clonal hematopoiesis was a cause or consequence of cardiovascular disease. Now, a new study published in Nature Medicine and carried out by researchers at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) resolves this critical debate ...
When the heat makes you disoriented
2024-08-30
Climate change is affecting ecosystems in many different ways. One of its consequences are increasingly longer and more intense periods of heat, which affect essential natural processes – such as pollination. A team of researchers from Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU) has now investigated in more detail how heat affects one particular player in these processes: The bumblebee.
"Bumblebees are important pollinators in natural and agricultural systems. They therefore ...