(Press-News.org) Scientists from China have investigated how short peptide chains aggregate together in order to deepen our understanding of the process, which is crucial for drug stability and material development. Their study, published in JACS Au, provides valuable insights into how short proteins called peptides interact, fold, and function. These findings have significant implications for medicine, material science, and biotechnology.
Peptides are short chains of amino acids that play essential roles in the body by building structures, speeding up chemical reactions, and supporting our immune system. The specific function of a protein is determined by how its amino acids interact with each other and aggregate into a three-dimensional structure.
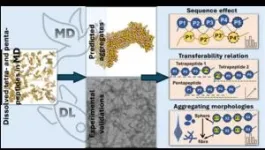
The research team used molecular dynamics simulations together with advanced AI techniques, including deep learning models like Transformer Regression Networks, to predict how various peptides of four or five amino acids (tetrapeptides and pentapeptides, respectively) would aggregate based on their amino acid sequence.
By analysing 160,000 tetrapeptides and 3.2 million pentapeptides, they discovered that certain amino acids, particularly aromatic ones like tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine, significantly enhance aggregation, especially when located towards one end (the C-terminus) of the peptide chain. This is probably because aromatic amino acids have ring-shaped structures that attract each other through their electron clouds, normally termed as "π-π" interactions, which helps them clump together. By contrast, hydrophilic amino acids, such as aspartic acid and glutamic acid, inhibit aggregation due to the strong interaction with water molecules that prevents the peptides from sticking together.
The study also showed that changing the amino acid sequence affects aggregation. For example, adding aromatic amino acids to the end of the peptide chain increases aggregation, while placing negatively charged amino acids at the beginning reduces it. The team also found that peptides clump together into different shapes based on the types and positions of their amino acids.
"Amino acids with a charge generally cause peptides to form long, thread-like structures, while those that avoid water tend to create round, ball-like clusters," explains Dr Wenbin Li, an assistant professor at Westlake University and corresponding author of the study. "We also discovered that by understanding how tetrapeptides stick to each other, we can predict how pentapeptides will behave, making it easier to predict how longer peptides will clump together."
The findings provide important guidelines for predicting and managing how peptides aggregate. "This knowledge could help in creating new materials, designing more stable drugs and drug delivery systems, and understanding diseases linked to peptide aggregation, such as Alzheimer's disease, where clumped amyloid-beta peptides form damaging plaques in the brain," says Dr Jiaqi Wang, an assistant professor at Xi'an Jiaotong-Liverpool University (XJTLU) and first author of the study.
"It can also improve biotechnology, such as semiconductors, biosensors and diagnostics, ensuring these tools work accurately and consistently.
"By offering new insights into peptide aggregation, this research is set to advance biochemistry, materials science, and computational biology. It also demonstrates the integration of AI into scientific discovery. These advances could lead to breakthroughs in medical treatments, eco-friendly products, and innovative technologies.
END
Exploring peptide clumping for improved drug and material solutions
Understanding the clumping behaviour of short proteins offers valuable insights to improve drug development and disease biology
2024-09-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Young adults let down by ‘postcode lottery’ for ADHD treatment - national survey
2024-09-03
A national survey conducted as part of University of Exeter research has found huge variation in treatment for ADHD, highlighting the struggle many young adults face once they turn 18.
Researchers have warned that the current system is failing many young adults as they transition from children’s to adult’s services - suddenly finding themselves unable to access treatment because services do not link up effectively.
More than 750 people from across the country – including commissioners, healthcare professionals working ...
False-positive mammography result may discourage women from subsequent screening
2024-09-02
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 2 September 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
False-positive mammograms discourage some women from future screenings
2024-09-02
Early detection of breast cancer through mammography screening continues to save lives. However, abnormal findings on mammograms can lead to women being recalled for additional imaging and biopsies, many of which turn out to be “false positives,” meaning they do not result in a cancer diagnosis. False positives can also have financial implications for patients and cause significant emotional anxiety.
A major, new study led by the UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center has found that women who received a false-positive result that required additional imaging or biopsy were less likely to return ...
The nervous system’s matchmaker
2024-09-02
When you ask a rideshare app to find you a car, the company’s computers get to work. They know you want to reach your destination quickly. They know you’re not the only user who needs a ride. And they know drivers want to minimize idle time by picking up someone nearby. The computer’s job, says Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Associate Professor Saket Navlakha, is to pair drivers with riders in a way that maximizes everyone’s happiness.
Computer scientists like Navlakha call this bipartite matching. It’s the same task handled by systems pairing organ donors with transplant candidates, medical students with residency ...
Open Wide: Human Mouth Bacteria Reproduce through Rare Form of Cell Division
2024-09-02
By Emily Greenhalgh
One of the most diverse ecosystems on the planet is closer than you think — right inside your mouth. Your mouth is a thriving ecosystem of more than 500 different species of bacteria living in distinct, structured communities called biofilms. Nearly all of these bacteria grow by splitting [or dividing] into two, with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
New research from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) and ADA Forsyth uncovered an extraordinary mechanism of cell division in Corynebacterium matruchotii, one of the most common bacteria living in dental plaque. ...
KIMM develops wheel that alters stiffness in real time based on situation
2024-09-02
A new technology for wheels and mobile systems, necessary for overcoming various obstacles in daily life such as stairs or rocks by adjusting the stiffness of the wheel in real time, has been developed for the first time in the world. This noble technology is anticipated to find wide applications in various moving vehicles equipped with wheels, where overcoming terrain obstacles is essential.
The Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seog-Hyeon Ryu, hereinafter referred to as KIMM), an institute under the jurisdiction of the ...
Blood stem cell breakthrough could transform bone marrow transplants
2024-09-02
Melbourne researchers have made a world first breakthrough into creating blood stem cells that closely resemble those in the human body. And the discovery could soon lead to personalised treatments for children with leukaemia and bone marrow failure disorders.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in Nature Biotechnology, has overcome a major hurdle for producing human blood stem cells, which can create red cells, white blood cells and platelets, that closely match those in the human embryo.
MCRI Associate Professor Elizabeth Ng said the team had made a significant discovery in human blood stem ...
Rare genetic variants linked to bicuspid aortic valve disease in young adults identified by UTHealth Houston researchers
2024-09-02
Genetic variants linked to a rare form of bicuspid aortic valve disease that affects young adults and can lead to dangerous and potentially life-threatening aortic complications have been identified by researchers at UTHealth Houston.
The study was published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
“We previously found that young individuals who present due to early onset thoracic aortic dissections are more likely to have bicuspid aortic valves and more likely to have rare variants in bicuspid aortic valve-associated genes,” said Siddharth Prakash, MD, PhD, co-principal investigator of the study and associate professor of medical ...
Locomotion control of cyborg insects by charge-balanced biphasic electrical stimulation
2024-09-02
A research paper by scientists at Beijing Institute of Technology proposed a universal system for remote signal output control using infrared signals.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 05 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, proposed a system that integrates high-precision digital-to-analog converters capable of generating customized waveform electrical stimulation signals within defined ranges. This enhances the accuracy of locomotion control in cyborg insects while maintaining real-time control and dynamic parameter adjustment. The proposed system is verified by experiments.
The integration of electronic stimulation devices with insects in ...
Depressed adolescents twice as likely to vape
2024-09-02
A study on vaping behaviour among Australian high school students has found those who reported severe depressive symptoms were over twice as likely to have tried e-cigarettes, compared to those reporting no depressive symptoms.
Data showed overall higher e-cigarette use among those with poorer mental health, including severe depressive symptoms, moderate and high stress, and low wellbeing.
The findings show a critical need for effective mental health support at the same time as vaping prevention during early adolescence -- when these issues first emerge.
The researchers surveyed over ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Exploring peptide clumping for improved drug and material solutionsUnderstanding the clumping behaviour of short proteins offers valuable insights to improve drug development and disease biology