(Press-News.org)
A research paper by scientists at Beijing Institute of Technology proposed a universal system for remote signal output control using infrared signals.
The new research paper, published on Jul. 05 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, proposed a system that integrates high-precision digital-to-analog converters capable of generating customized waveform electrical stimulation signals within defined ranges. This enhances the accuracy of locomotion control in cyborg insects while maintaining real-time control and dynamic parameter adjustment. The proposed system is verified by experiments.
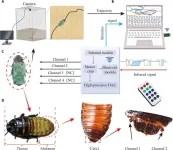
The integration of electronic stimulation devices with insects in the context of cyborg insect systems has great application potential, particularly in the fields of environmental monitoring, urban surveillance, and rescue missions. “Despite considerable advantages compared to the current robot technology, including flexibility, durability, and low energy consumption, this integration faces certain challenges related to the potential risk of charge accumulation caused by prolonged and repetitive electrical stimulations.” explained study author Jieliang Zhao, a professor at Beijing Institute of Technology. To address these challenges, this study proposes a universal system for remote signal output control using infrared signals. The experimental results show that the signals generated by the proposed system have a success rate of over 76.25% in controlling the turning locomotion of cyborg insects, which is higher than previously reported results. In addition, the charge-balanced characteristics of these signals can minimize muscle tissue damage, thus substantially enhancing control repeatability. This study provides a comprehensive solution for the remote control and monitoring of cyborg insects, whose flexibility and adaptability can meet various application and experimental requirements. “This study provides a comprehensive solution for the remote control and monitoring of cyborg insects, whose flexibility and adaptability can meet various application and experimental requirements.” said study authors.
Biphasic signals have been utilized in some studies for turning control experiments in cockroaches, achieving higher control success rates compared to monophasic signals. However, there remains a paucity of in-depth research on the control potential of biphasic electrical signals. “To address the limitations of existing solutions, this study adopts balanced charge technology and proposes the use of biphasic stimulation signals for insect locomotion control. This approach aims to mitigate the cumulative damage to the insect's sensory organs caused by electrical stimulation, thereby enhancing the stability and reliability of cyborg insect locomotion control.” said Zhong Liu. In practical demonstrations, the Madagascar hissing cockroach was utilized as a living insect platform. A wireless control system, acting as a “backpack”, was attached to the cockroach’s back to carry out turning control experiments. Directional movements were induced by stimulating the cockroach’s cerci through the outputs from the backpack, thus confirming the efficacy of the proposed system.
This study proposes a cyborg insect locomotion control system capable of generating high-precision analog signals. The proposed system is used to investigate a reliable turning locomotion control strategy for the Madagascar hissing cockroach. Totally, such electrophysiological analysis of brain network will provide a foundation for the advancement of driver assistance systems with distraction control strategies and development of brain-controlled systems, in both conventional human driving scenarios and autonomous driving contexts. The results presented in this study lay a robust foundation for further advancement of various technologies, particularly those related to cyborg insect locomotion control systems and wireless control mechanisms for cyborg insects. Future work could expand the functionality of the proposed insect wireless control system, modifying it into a high-quality platform for cyborg insect research. In addition, wireless control backpacks tailored for different host insects could be designed based on the proposed wireless control system.
Authors of the paper include Zhong Liu, Yongxia Gu, Li Yu, Xiang Yang, Zhiyun Ma, Jieliang Zhao, and Yufei Gu
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFB3400200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 52075038 and 52375282), the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (grant SKS-2022031), and the BIT Teli Young Fellow Recruitment Program (RCPT-20220005).
The paper, “Locomotion Control of Cyborg Insects by Charge-Balanced Biphasic Electrical Stimulation” was published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems on Jul 05, 2024, at DOI: 10.34133/cbsystems.0134.
END
A study on vaping behaviour among Australian high school students has found those who reported severe depressive symptoms were over twice as likely to have tried e-cigarettes, compared to those reporting no depressive symptoms.
Data showed overall higher e-cigarette use among those with poorer mental health, including severe depressive symptoms, moderate and high stress, and low wellbeing.
The findings show a critical need for effective mental health support at the same time as vaping prevention during early adolescence -- when these issues first emerge.
The researchers surveyed over ...
Korean researchers are pushing for a new AI-based policy intelligence research project that can assist the public decision-making and policy execution of domestic and foreign local governments.
Electronics and Communications Research Institute (ETRI) announced on July 1 that they have decided to establish a cooperative system with the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA)1) to conduct further research regarding the development of an AI policy intelligence system that can assist public policy decision-making.
1) International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA): An independent international research institute located ...
About The Study: Pulmonary vein isolation resulted in a statistically significant and clinically important decrease in atrial fibrillation burden at 6 months, with substantial improvements in symptoms and quality of life, compared with a sham procedure.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Rick A. Veasey, MD, (rick.veasey@nhs.net) and Rajdip Dulai, MBBS, (rajdip.dulai.21@ucl.ac.uk)
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.17921)
Editor’s ...
About The Study: At the lesion level, very intensive lipid-lowering therapy induced substantially greater percent atheroma volume regression than described in previous vessel-level analyses. Compared with statin therapy alone, alirocumab treatment was associated with greater enlargement of the lesion minimum lumen area and more frequent transition of presumably high-risk plaque phenotypes into more stable, less lipid-rich plaque phenotypes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lorenz ...
Alternative splicing is a genetic process where different segments of genes are removed, and the remaining pieces are joined together during transcription to messenger RNA (mRNA). This mechanism increases the diversity of proteins that can be generated from genes, by assembling sections of genetic code into different combinations. This is believed to enhance biological complexity by allowing genes to produce different versions of proteins, or protein isoforms, for many different uses.
New research from the University of Chicago suggests that alternative splicing may have an even greater influence on biology than just by creating new protein isoforms. The ...
Cities in the Global South are more exposed to extreme heat because they lack cooling green spaces, new research shows.
The study found that Global South cities have just 70% of the “cooling capacity” provided by urban greenery in the Global North.
With temperatures rising, combined with the “urban heat island” effects that make cities hotter than rural areas, heat-related illness and death in cities are becoming more common.
Urban green spaces can help reduce this risk, cooling down outdoor environments and providing vital refuges.
The research – led by an international team including Nanjing, Exeter, Aarhus and North Carolina State universities – ...
Securing the world's water supply is one of the greatest challenges of our time. Research at Stockholm University is now presenting an alternative method for quantifying the global risk of water scarcity. Results indicate higher risks to water supply than previously expected if accounting for the environmental conditions and governability where rain is produced.
The common idea of global water supply is rain falling on the earth's surface and then stored in aquifers, lakes, and rivers. This idea is usually used to assess water security and the risk of water scarcity. However, a new study published in Nature Water shows how the water risks are dependent on governance ...
Nowadays, there’s lots of buzz about spectacular new medical treatments such as personalised cancer therapy with modified immune cells or antibodies. Such treatments, however, are very complex and expensive and so find only limited application. Most medical therapies are still based on small chemical compounds that can be produced in large quantities and thus at low cost.
Billions of new molecules in just a few weeks
The bottleneck in the development of new molecular therapies is the limited number of new active ...
White women are paid up to eight times more for their eggs than Black women in the US, according to data uncovered by the author of a new book which exposes the lesser-known ramifications of egg donation.
Eggonomics by Diane M. Tober reveals statistics and stories which illuminate the rarely-told, complex realities of egg donation, and airs personal accounts of disturbing power imbalances within the industry. She takes a microscope to the industry across the globe, but in particular in the U.S. and Spain.
Donor disparities
Tober finds ...
DURHAM, N.C. – Wearable, long-term continuous heart monitors helped identify 52% more cases of atrial fibrillation compared to usual care, but that did not lead to a reduction in hospitalizations due to stroke, according to a study led by the Duke Clinical Research Institute.
The findings, reported Sept. 1 at the European Society of Cardiology meeting and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, provide inconclusive data about whether atrial fibrillation screening lowers stroke rates. The COVID pandemic led to an early halt of the study before fully enrolling, so it did not ...